Rajesh N Rao
Vec2GC -- A Graph Based Clustering Method for Text Representations
Apr 15, 2021



Abstract:NLP pipelines with limited or no labeled data, rely on unsupervised methods for document processing. Unsupervised approaches typically depend on clustering of terms or documents. In this paper, we introduce a novel clustering algorithm, Vec2GC (Vector to Graph Communities), an end-to-end pipeline to cluster terms or documents for any given text corpus. Our method uses community detection on a weighted graph of the terms or documents, created using text representation learning. Vec2GC clustering algorithm is a density based approach, that supports hierarchical clustering as well.
SEMIE: SEMantically Infused Embeddings with Enhanced Interpretability for Domain-specific Small Corpus
Mar 21, 2021



Abstract:Word embeddings are a basic building block of modern NLP pipelines. Efforts have been made to learn rich, efficient, and interpretable embeddings for large generic datasets available in the public domain. However, these embeddings have limited applicability for small corpora from specific domains such as automotive, manufacturing, maintenance and support, etc. In this work, we present a comprehensive notion of interpretability for word embeddings and propose a novel method to generate highly interpretable and efficient embeddings for a domain-specific small corpus. We report the evaluation results of our resulting word embeddings and demonstrate their novel features for enhanced interpretability.
Towards Semantic Noise Cleansing of Categorical Data based on Semantic Infusion
Feb 06, 2020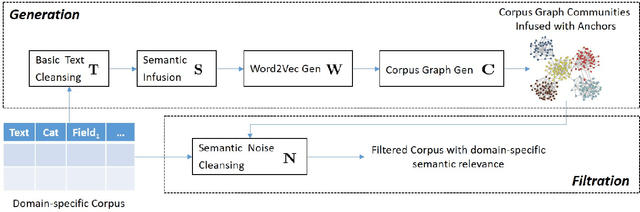
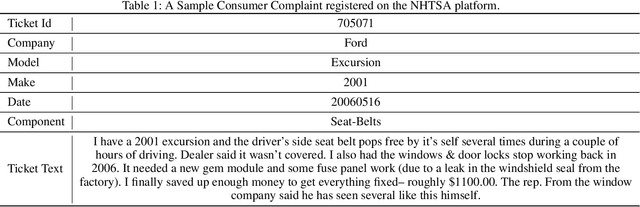
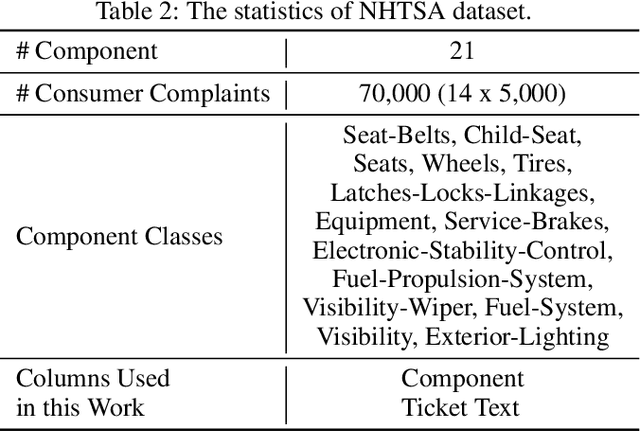
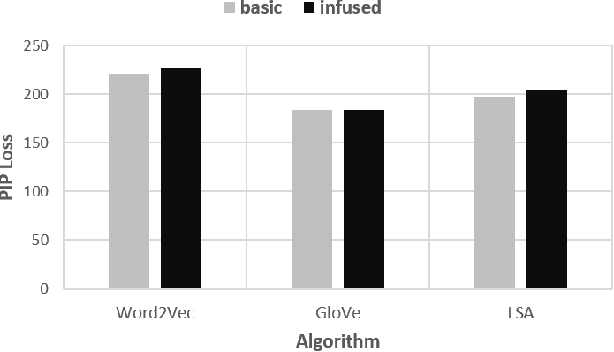
Abstract:Semantic Noise affects text analytics activities for the domain-specific industries significantly. It impedes the text understanding which holds prime importance in the critical decision making tasks. In this work, we formalize semantic noise as a sequence of terms that do not contribute to the narrative of the text. We look beyond the notion of standard statistically-based stop words and consider the semantics of terms to exclude the semantic noise. We present a novel Semantic Infusion technique to associate meta-data with the categorical corpus text and demonstrate its near-lossless nature. Based on this technique, we propose an unsupervised text-preprocessing framework to filter the semantic noise using the context of the terms. Later we present the evaluation results of the proposed framework using a web forum dataset from the automobile-domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge