Rahul Ahuja
OptFlow: Fast Optimization-based Scene Flow Estimation without Supervision
Jan 04, 2024



Abstract:Scene flow estimation is a crucial component in the development of autonomous driving and 3D robotics, providing valuable information for environment perception and navigation. Despite the advantages of learning-based scene flow estimation techniques, their domain specificity and limited generalizability across varied scenarios pose challenges. In contrast, non-learning optimization-based methods, incorporating robust priors or regularization, offer competitive scene flow estimation performance, require no training, and show extensive applicability across datasets, but suffer from lengthy inference times. In this paper, we present OptFlow, a fast optimization-based scene flow estimation method. Without relying on learning or any labeled datasets, OptFlow achieves state-of-the-art performance for scene flow estimation on popular autonomous driving benchmarks. It integrates a local correlation weight matrix for correspondence matching, an adaptive correspondence threshold limit for nearest-neighbor search, and graph prior rigidity constraints, resulting in expedited convergence and improved point correspondence identification. Moreover, we demonstrate how integrating a point cloud registration function within our objective function bolsters accuracy and differentiates between static and dynamic points without relying on external odometry data. Consequently, OptFlow outperforms the baseline graph-prior method by approximately 20% and the Neural Scene Flow Prior method by 5%-7% in accuracy, all while offering the fastest inference time among all non-learning scene flow estimation methods.
No Offense Taken: Eliciting Offensiveness from Language Models
Oct 02, 2023



Abstract:This work was completed in May 2022. For safe and reliable deployment of language models in the real world, testing needs to be robust. This robustness can be characterized by the difficulty and diversity of the test cases we evaluate these models on. Limitations in human-in-the-loop test case generation has prompted an advent of automated test case generation approaches. In particular, we focus on Red Teaming Language Models with Language Models by Perez et al.(2022). Our contributions include developing a pipeline for automated test case generation via red teaming that leverages publicly available smaller language models (LMs), experimenting with different target LMs and red classifiers, and generating a corpus of test cases that can help in eliciting offensive responses from widely deployed LMs and identifying their failure modes.
Adversarial Pairwise Reverse Attention for Camera Performance Imbalance in Person Re-identification: New Dataset and Metrics
Jul 04, 2022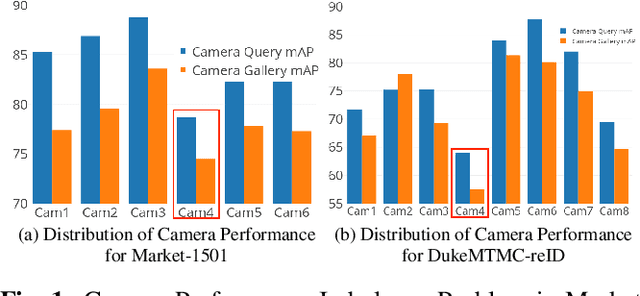
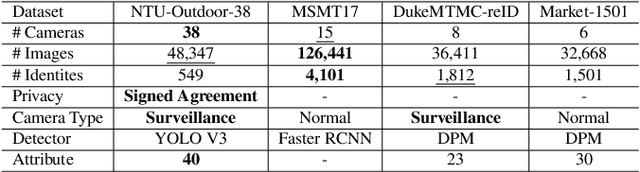

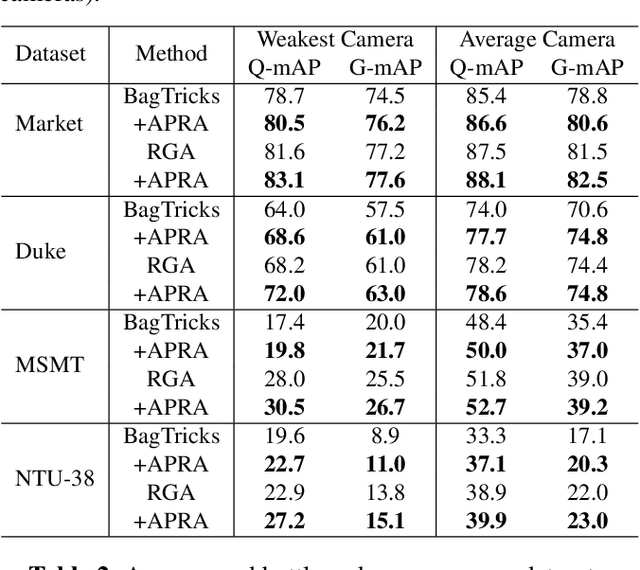
Abstract:Existing evaluation metrics for Person Re-Identification (Person ReID) models focus on system-wide performance. However, our studies reveal weaknesses due to the uneven data distributions among cameras and different camera properties that expose the ReID system to exploitation. In this work, we raise the long-ignored ReID problem of camera performance imbalance and collect a real-world privacy-aware dataset from 38 cameras to assist the study of the imbalance issue. We propose new metrics to quantify camera performance imbalance and further propose the Adversarial Pairwise Reverse Attention (APRA) Module to guide the model learning the camera invariant feature with a novel pairwise attention inversion mechanism.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge