Rafael C. Carrasco
Learning synchronous context-free grammars with multiple specialised non-terminals for hierarchical phrase-based translation
Apr 03, 2020



Abstract:Translation models based on hierarchical phrase-based statistical machine translation (HSMT) have shown better performances than the non-hierarchical phrase-based counterparts for some language pairs. The standard approach to HSMT learns and apply a synchronous context-free grammar with a single non-terminal. The hypothesis behind the grammar refinement algorithm presented in this work is that this single non-terminal is overloaded, and insufficiently discriminative, and therefore, an adequate split of it into more specialised symbols could lead to improved models. This paper presents a method to learn synchronous context-free grammars with a huge number of initial non-terminals, which are then grouped via a clustering algorithm. Our experiments show that the resulting smaller set of non-terminals correctly capture the contextual information that makes it possible to statistically significantly improve the BLEU score of the standard HSMT approach.
Generalized Biwords for Bitext Compression and Translation Spotting
Jan 18, 2014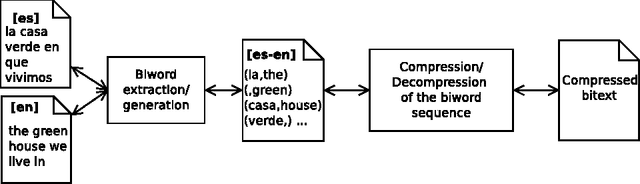
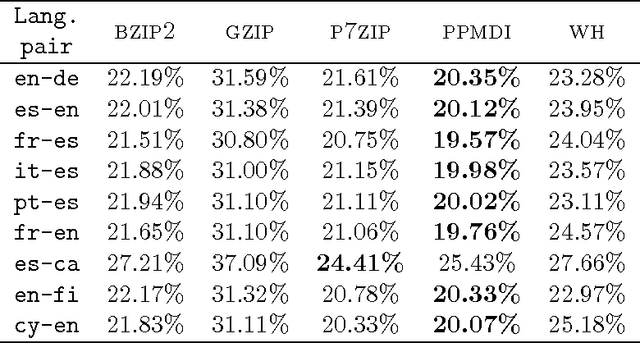

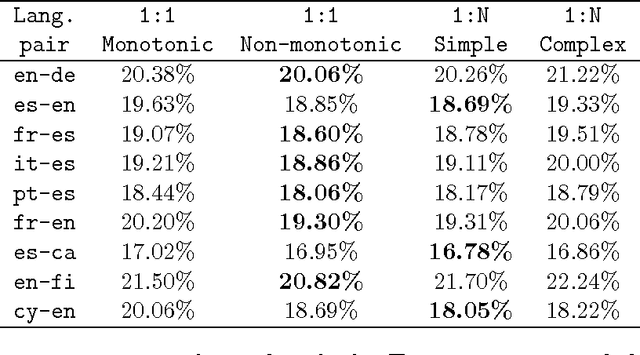
Abstract:Large bilingual parallel texts (also known as bitexts) are usually stored in a compressed form, and previous work has shown that they can be more efficiently compressed if the fact that the two texts are mutual translations is exploited. For example, a bitext can be seen as a sequence of biwords ---pairs of parallel words with a high probability of co-occurrence--- that can be used as an intermediate representation in the compression process. However, the simple biword approach described in the literature can only exploit one-to-one word alignments and cannot tackle the reordering of words. We therefore introduce a generalization of biwords which can describe multi-word expressions and reorderings. We also describe some methods for the binary compression of generalized biword sequences, and compare their performance when different schemes are applied to the extraction of the biword sequence. In addition, we show that this generalization of biwords allows for the implementation of an efficient algorithm to look on the compressed bitext for words or text segments in one of the texts and retrieve their counterpart translations in the other text ---an application usually referred to as translation spotting--- with only some minor modifications in the compression algorithm.
An open diachronic corpus of historical Spanish: annotation criteria and automatic modernisation of spelling
Jun 28, 2013



Abstract:The IMPACT-es diachronic corpus of historical Spanish compiles over one hundred books --containing approximately 8 million words-- in addition to a complementary lexicon which links more than 10 thousand lemmas with attestations of the different variants found in the documents. This textual corpus and the accompanying lexicon have been released under an open license (Creative Commons by-nc-sa) in order to permit their intensive exploitation in linguistic research. Approximately 7% of the words in the corpus (a selection aimed at enhancing the coverage of the most frequent word forms) have been annotated with their lemma, part of speech, and modern equivalent. This paper describes the annotation criteria followed and the standards, based on the Text Encoding Initiative recommendations, used to the represent the texts in digital form. As an illustration of the possible synergies between diachronic textual resources and linguistic research, we describe the application of statistical machine translation techniques to infer probabilistic context-sensitive rules for the automatic modernisation of spelling. The automatic modernisation with this type of statistical methods leads to very low character error rates when the output is compared with the supervised modern version of the text.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge