Rafael Ayllón-Gavilán
TOC-UCO: a comprehensive repository of tabular ordinal classification datasets
Jul 24, 2025Abstract:An ordinal classification (OC) problem corresponds to a special type of classification characterised by the presence of a natural order relationship among the classes. This type of problem can be found in a number of real-world applications, motivating the design and development of many ordinal methodologies over the last years. However, it is important to highlight that the development of the OC field suffers from one main disadvantage: the lack of a comprehensive set of datasets on which novel approaches to the literature have to be benchmarked. In order to approach this objective, this manuscript from the University of C\'ordoba (UCO), which have previous experience on the OC field, provides the literature with a publicly available repository of tabular data for a robust validation of novel OC approaches, namely TOC-UCO (Tabular Ordinal Classification repository of the UCO). Specifically, this repository includes a set of $46$ tabular ordinal datasets, preprocessed under a common framework and ensured to have a reasonable number of patterns and an appropriate class distribution. We also provide the sources and preprocessing steps of each dataset, along with details on how to benchmark a novel approach using the TOC-UCO repository. For this, indices for $30$ different randomised train-test partitions are provided to facilitate the reproducibility of the experiments.
Splitting criteria for ordinal decision trees: an experimental study
Dec 18, 2024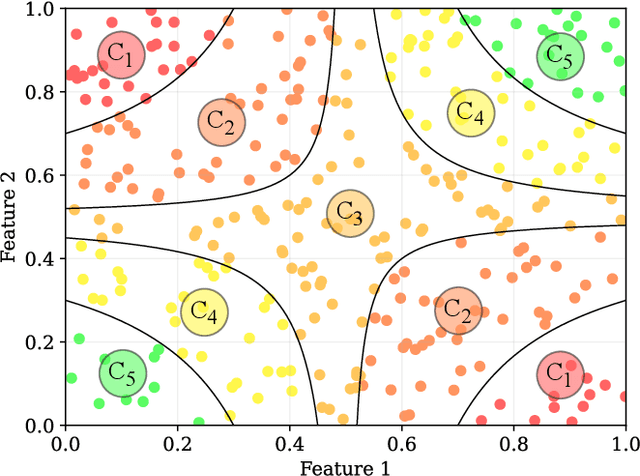
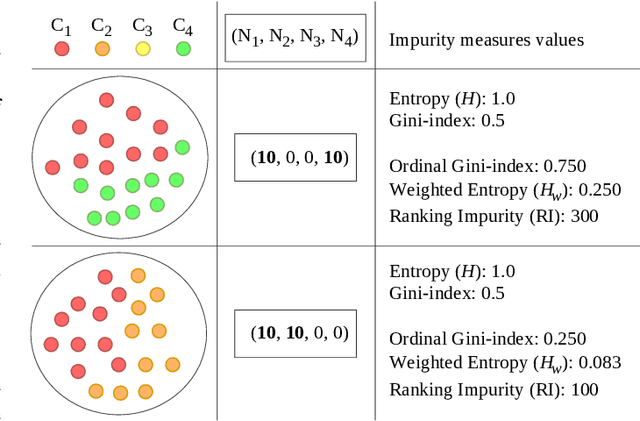
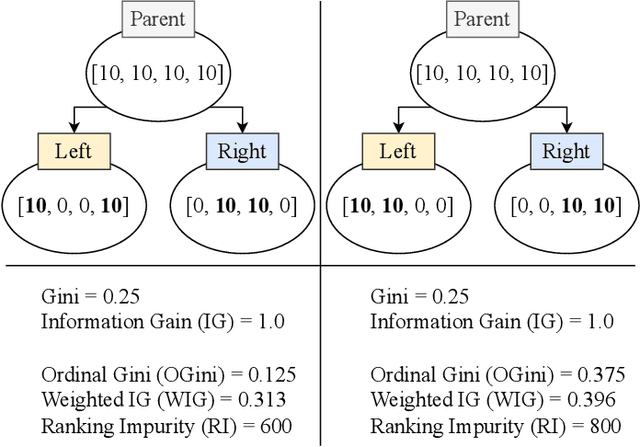
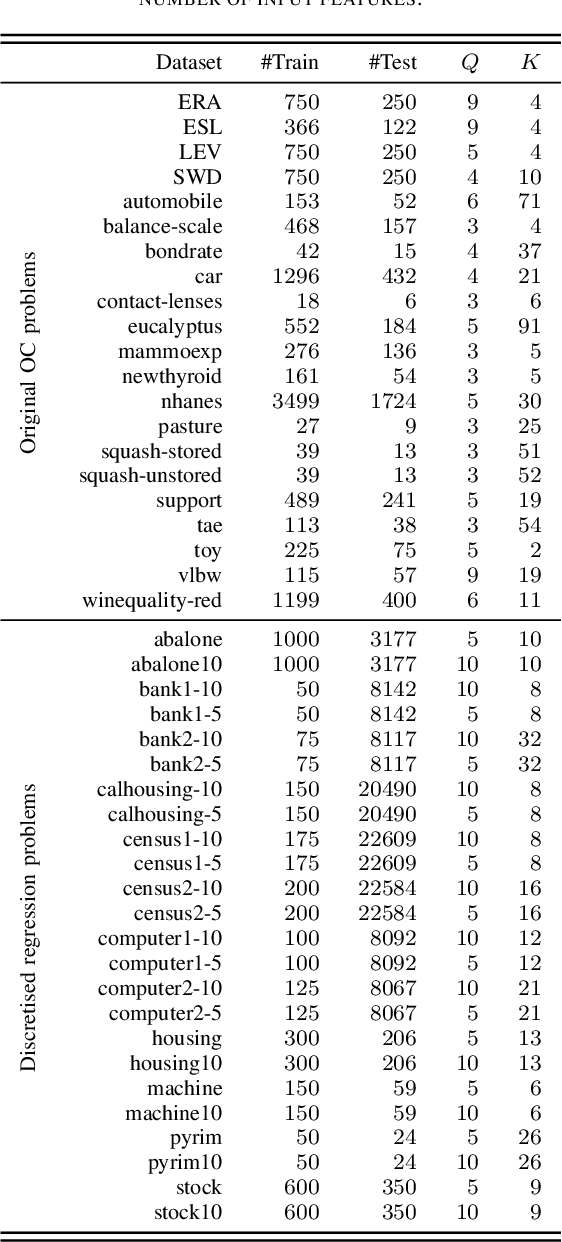
Abstract:Ordinal Classification (OC) is a machine learning field that addresses classification tasks where the labels exhibit a natural order. Unlike nominal classification, which treats all classes as equally distinct, OC takes the ordinal relationship into account, producing more accurate and relevant results. This is particularly critical in applications where the magnitude of classification errors has implications. Despite this, OC problems are often tackled using nominal methods, leading to suboptimal solutions. Although decision trees are one of the most popular classification approaches, ordinal tree-based approaches have received less attention when compared to other classifiers. This work conducts an experimental study of tree-based methodologies specifically designed to capture ordinal relationships. A comprehensive survey of ordinal splitting criteria is provided, standardising the notations used in the literature for clarity. Three ordinal splitting criteria, Ordinal Gini (OGini), Weighted Information Gain (WIG), and Ranking Impurity (RI), are compared to the nominal counterparts of the first two (Gini and information gain), by incorporating them into a decision tree classifier. An extensive repository considering 45 publicly available OC datasets is presented, supporting the first experimental comparison of ordinal and nominal splitting criteria using well-known OC evaluation metrics. Statistical analysis of the results highlights OGini as the most effective ordinal splitting criterion to date. Source code, datasets, and results are made available to the research community.
dlordinal: a Python package for deep ordinal classification
Jul 24, 2024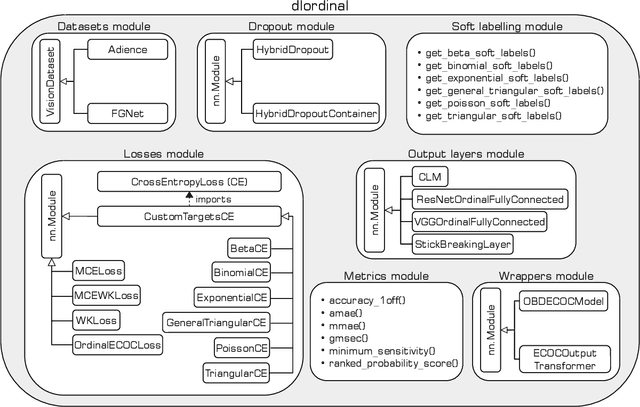
Abstract:dlordinal is a new Python library that unifies many recent deep ordinal classification methodologies available in the literature. Developed using PyTorch as underlying framework, it implements the top performing state-of-the-art deep learning techniques for ordinal classification problems. Ordinal approaches are designed to leverage the ordering information present in the target variable. Specifically, it includes loss functions, various output layers, dropout techniques, soft labelling methodologies, and other classification strategies, all of which are appropriately designed to incorporate the ordinal information. Furthermore, as the performance metrics to assess novel proposals in ordinal classification depend on the distance between target and predicted classes in the ordinal scale, suitable ordinal evaluation metrics are also included. dlordinal is distributed under the BSD-3-Clause license and is available at https://github.com/ayrna/dlordinal.
Convolutional and Deep Learning based techniques for Time Series Ordinal Classification
Jun 16, 2023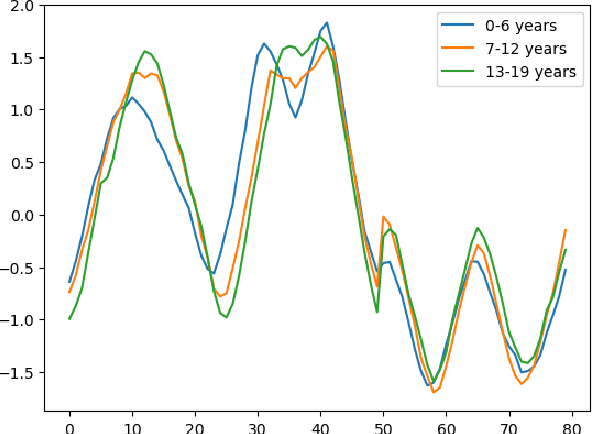

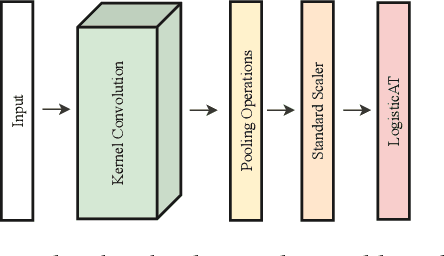
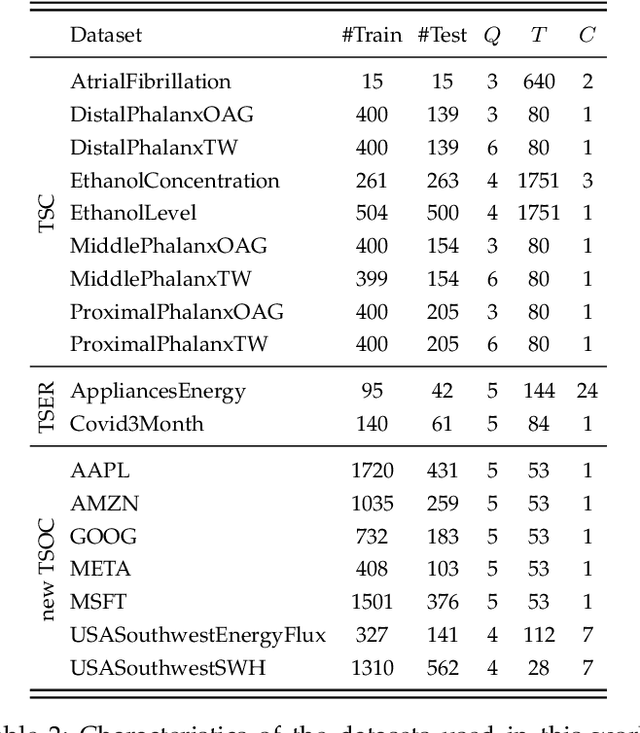
Abstract:Time Series Classification (TSC) covers the supervised learning problem where input data is provided in the form of series of values observed through repeated measurements over time, and whose objective is to predict the category to which they belong. When the class values are ordinal, classifiers that take this into account can perform better than nominal classifiers. Time Series Ordinal Classification (TSOC) is the field covering this gap, yet unexplored in the literature. There are a wide range of time series problems showing an ordered label structure, and TSC techniques that ignore the order relationship discard useful information. Hence, this paper presents a first benchmarking of TSOC methodologies, exploiting the ordering of the target labels to boost the performance of current TSC state-of-the-art. Both convolutional- and deep learning-based methodologies (among the best performing alternatives for nominal TSC) are adapted for TSOC. For the experiments, a selection of 18 ordinal problems from two well-known archives has been made. In this way, this paper contributes to the establishment of the state-of-the-art in TSOC. The results obtained by ordinal versions are found to be significantly better than current nominal TSC techniques in terms of ordinal performance metrics, outlining the importance of considering the ordering of the labels when dealing with this kind of problems.
A Dictionary-based approach to Time Series Ordinal Classification
May 16, 2023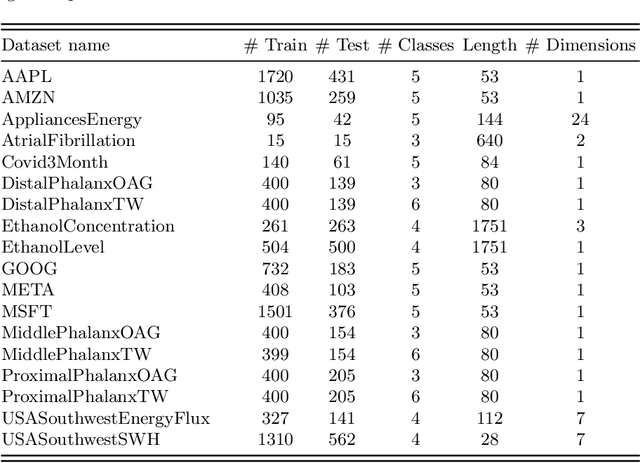
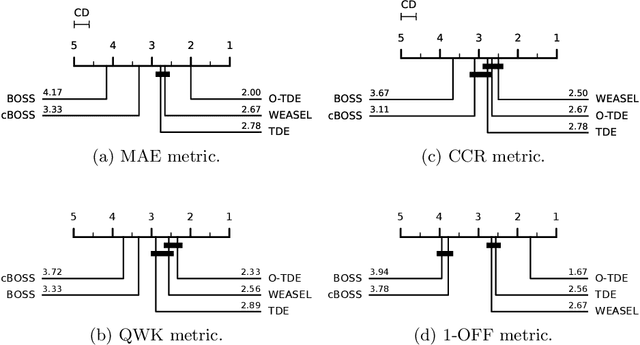

Abstract:Time Series Classification (TSC) is an extensively researched field from which a broad range of real-world problems can be addressed obtaining excellent results. One sort of the approaches performing well are the so-called dictionary-based techniques. The Temporal Dictionary Ensemble (TDE) is the current state-of-the-art dictionary-based TSC approach. In many TSC problems we find a natural ordering in the labels associated with the time series. This characteristic is referred to as ordinality, and can be exploited to improve the methods performance. The area dealing with ordinal time series is the Time Series Ordinal Classification (TSOC) field, which is yet unexplored. In this work, we present an ordinal adaptation of the TDE algorithm, known as ordinal TDE (O-TDE). For this, a comprehensive comparison using a set of 18 TSOC problems is performed. Experiments conducted show the improvement achieved by the ordinal dictionary-based approach in comparison to four other existing nominal dictionary-based techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge