Qiufang Ma
Hybrid Transformer and CNN Attention Network for Stereo Image Super-resolution
May 09, 2023Abstract:Multi-stage strategies are frequently employed in image restoration tasks. While transformer-based methods have exhibited high efficiency in single-image super-resolution tasks, they have not yet shown significant advantages over CNN-based methods in stereo super-resolution tasks. This can be attributed to two key factors: first, current single-image super-resolution transformers are unable to leverage the complementary stereo information during the process; second, the performance of transformers is typically reliant on sufficient data, which is absent in common stereo-image super-resolution algorithms. To address these issues, we propose a Hybrid Transformer and CNN Attention Network (HTCAN), which utilizes a transformer-based network for single-image enhancement and a CNN-based network for stereo information fusion. Furthermore, we employ a multi-patch training strategy and larger window sizes to activate more input pixels for super-resolution. We also revisit other advanced techniques, such as data augmentation, data ensemble, and model ensemble to reduce overfitting and data bias. Finally, our approach achieved a score of 23.90dB and emerged as the winner in Track 1 of the NTIRE 2023 Stereo Image Super-Resolution Challenge.
OPDN: Omnidirectional Position-aware Deformable Network for Omnidirectional Image Super-Resolution
Apr 26, 2023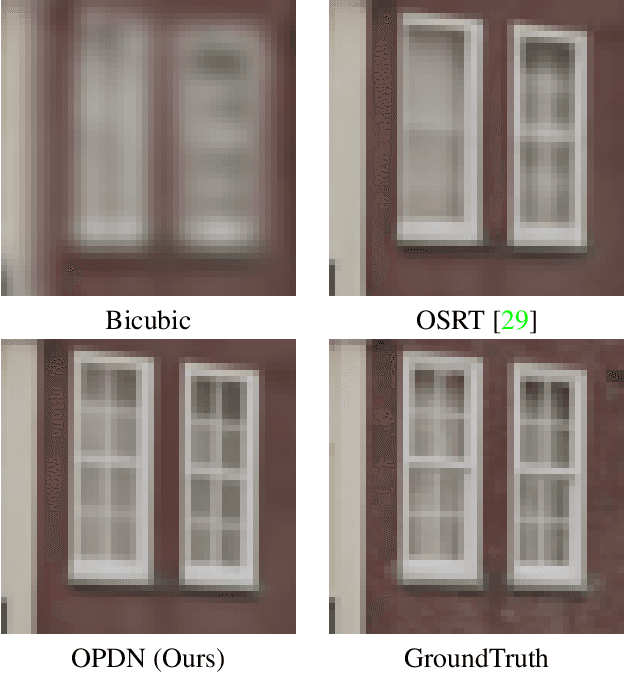
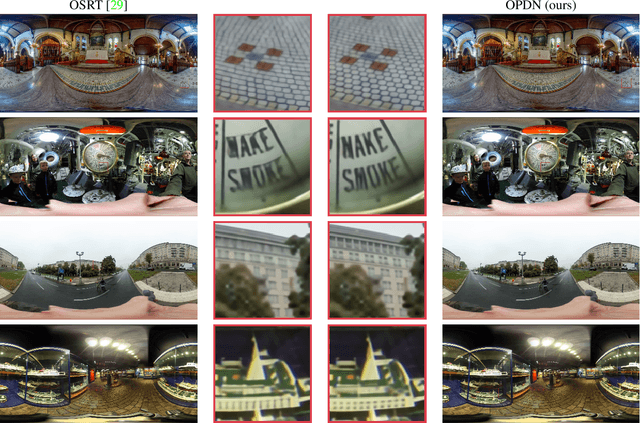
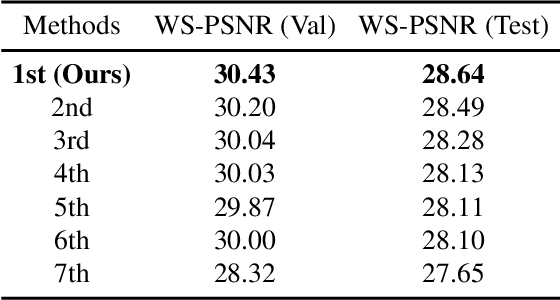

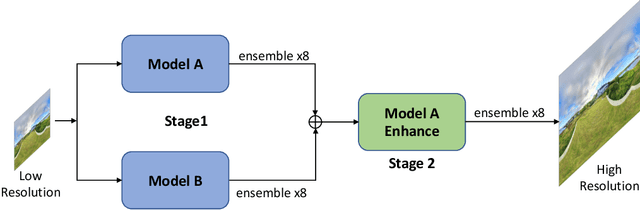
Abstract:360{\deg} omnidirectional images have gained research attention due to their immersive and interactive experience, particularly in AR/VR applications. However, they suffer from lower angular resolution due to being captured by fisheye lenses with the same sensor size for capturing planar images. To solve the above issues, we propose a two-stage framework for 360{\deg} omnidirectional image superresolution. The first stage employs two branches: model A, which incorporates omnidirectional position-aware deformable blocks (OPDB) and Fourier upsampling, and model B, which adds a spatial frequency fusion module (SFF) to model A. Model A aims to enhance the feature extraction ability of 360{\deg} image positional information, while Model B further focuses on the high-frequency information of 360{\deg} images. The second stage performs same-resolution enhancement based on the structure of model A with a pixel unshuffle operation. In addition, we collected data from YouTube to improve the fitting ability of the transformer, and created pseudo low-resolution images using a degradation network. Our proposed method achieves superior performance and wins the NTIRE 2023 challenge of 360{\deg} omnidirectional image super-resolution.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge