Qisong Wang
EEG-DG: A Multi-Source Domain Generalization Framework for Motor Imagery EEG Classification
Nov 09, 2023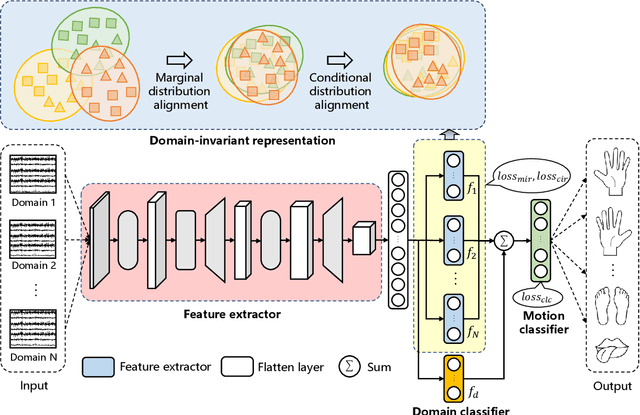
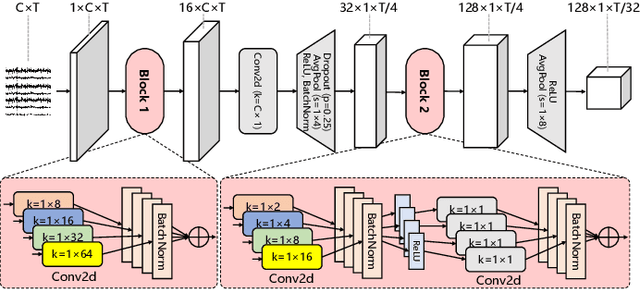
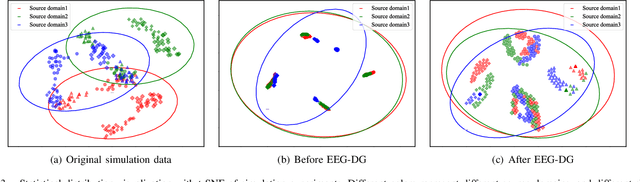
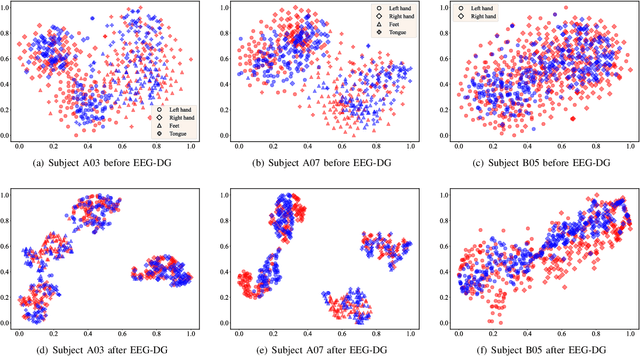
Abstract:Motor imagery EEG classification plays a crucial role in non-invasive Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) research. However, the classification is affected by the non-stationarity and individual variations of EEG signals. Simply pooling EEG data with different statistical distributions to train a classification model can severely degrade the generalization performance. To address this issue, the existing methods primarily focus on domain adaptation, which requires access to the target data during training. This is unrealistic in many EEG application scenarios. In this paper, we propose a novel multi-source domain generalization framework called EEG-DG, which leverages multiple source domains with different statistical distributions to build generalizable models on unseen target EEG data. We optimize both the marginal and conditional distributions to ensure the stability of the joint distribution across source domains and extend it to a multi-source domain generalization framework to achieve domain-invariant feature representation, thereby alleviating calibration efforts. Systematic experiments on a simulative dataset and BCI competition datasets IV-2a and IV-2b demonstrate the superiority of our proposed EEG-DG over state-of-the-art methods. Specifically, EEG-DG achieves an average classification accuracy/kappa value of 81.79%/0.7572 and 87.12%/0.7424 on datasets IV-2a and IV-2b, respectively, which even outperforms some domain adaptation methods. Our code is available at https://github.com/XC-ZhongHIT/EEG-DG for free download and evaluation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge