Qichen Li
Meta-Embeddings Based On Self-Attention
Mar 03, 2020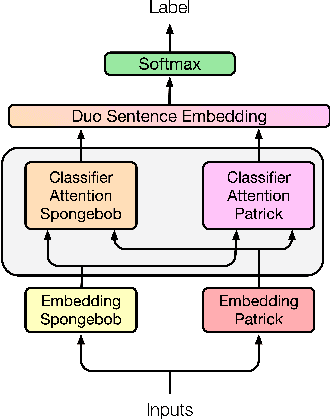
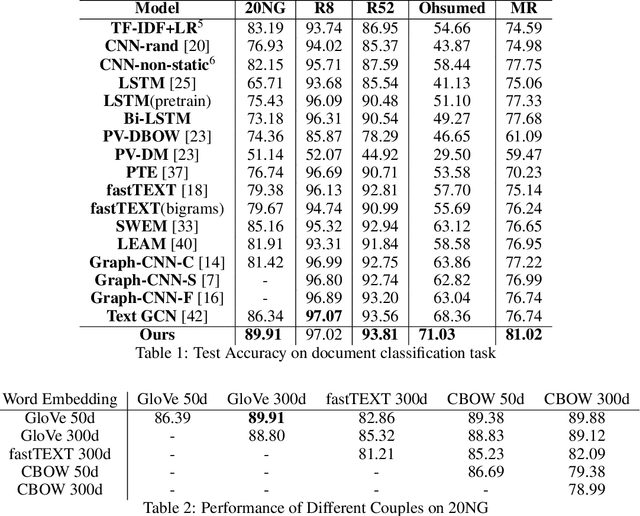
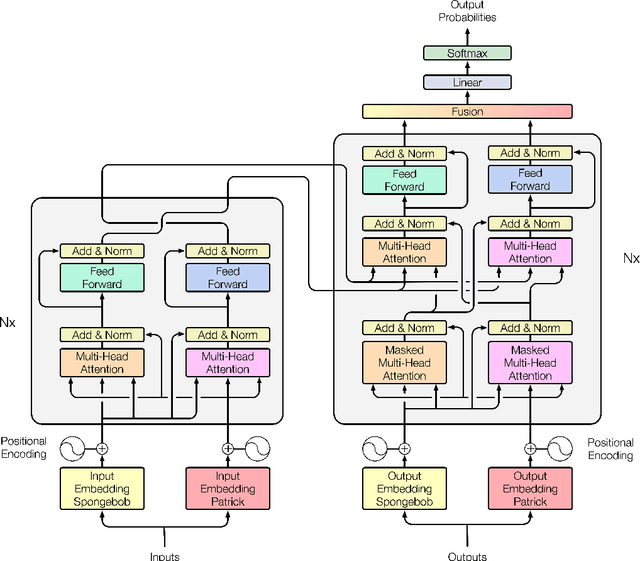
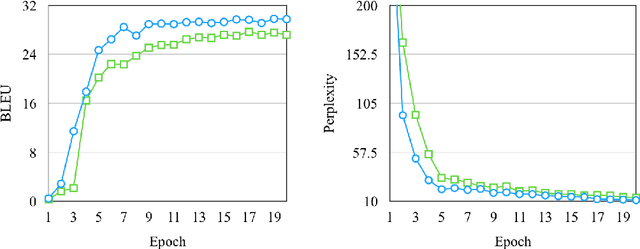
Abstract:Creating meta-embeddings for better performance in language modelling has received attention lately, and methods based on concatenation or merely calculating the arithmetic mean of more than one separately trained embeddings to perform meta-embeddings have shown to be beneficial. In this paper, we devise a new meta-embedding model based on the self-attention mechanism, namely the Duo. With less than 0.4M parameters, the Duo mechanism achieves state-of-the-art accuracy in text classification tasks such as 20NG. Additionally, we propose a new meta-embedding sequece-to-sequence model for machine translation, which to the best of our knowledge, is the first machine translation model based on more than one word-embedding. Furthermore, it has turned out that our model outperform the Transformer not only in terms of achieving a better result, but also a faster convergence on recognized benchmarks, such as the WMT 2014 English-to-French translation task.
SUM: Suboptimal Unitary Multi-task Learning Framework for Spatiotemporal Data Prediction
Oct 11, 2019



Abstract:The typical multi-task learning methods for spatio-temporal data prediction involve low-rank tensor computation. However, such a method have relatively weak performance when the task number is small, and we cannot integrate it into non-linear models. In this paper, we propose a two-step suboptimal unitary method (SUM) to combine a meta-learning strategy into multi-task models. In the first step, it searches for a global pattern by optimising the general parameters with gradient descents under constraints, which is a geological regularizer to enable model learning with less training data. In the second step, we derive an optimised model on each specific task from the global pattern with only a few local training data. Compared with traditional multi-task learning methods, SUM shows advantages of generalisation ability on distant tasks. It can be applied on any multi-task models with the gradient descent as its optimiser regardless if the prediction function is linear or not. Moreover, we can harness the model to enable traditional prediction model to make coKriging. The experiments on public datasets have suggested that our framework, when combined with current multi-task models, has a conspicuously better prediction result when the task number is small compared to low-rank tensor learning, and our model has a quite satisfying outcome when adjusting the current prediction models for coKriging.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge