Qiaojie Zheng
Improving reliability of uncertainty-aware gaze estimation with probability calibration
Jan 24, 2025



Abstract:Current deep learning powered appearance based uncertainty-aware gaze estimation models produce inconsistent and unreliable uncertainty estimation that limits their adoptions in downstream applications. In this study, we propose a workflow to improve the accuracy of uncertainty estimation using probability calibration with a few post hoc samples. The probability calibration process employs a simple secondary regression model to compensate for inaccuracies in estimated uncertainties from the deep learning model. Training of the secondary model is detached from the main deep learning model and thus no expensive weight tuning is required. The added calibration process is lightweight and relatively independent from the deep learning process, making it fast to run and easy to implement. We evaluated the effectiveness of the calibration process under four potential application scenarios with two datasets that have distinctive image characteristics due to the data collection setups. The calibration process is most effective when the calibration and testing data share similar characteristics. Even under suboptimal circumstances that calibration and testing data differ, the calibration process can still make corrections to reduce prediction errors in uncertainty estimates made by uncalibrated models.
Curriculum-based Sensing Reduction in Simulation to Real-World Transfer for In-hand Manipulation
Sep 13, 2023



Abstract:Simulation to Real-World Transfer allows affordable and fast training of learning-based robots for manipulation tasks using Deep Reinforcement Learning methods. Currently, Sim2Real uses Asymmetric Actor-Critic approaches to reduce the rich idealized features in simulation to the accessible ones in the real world. However, the feature reduction from the simulation to the real world is conducted through an empirically defined one-step curtail. Small feature reduction does not sufficiently remove the actor's features, which may still cause difficulty setting up the physical system, while large feature reduction may cause difficulty and inefficiency in training. To address this issue, we proposed Curriculum-based Sensing Reduction to enable the actor to start with the same rich feature space as the critic and then get rid of the hard-to-extract features step-by-step for higher training performance and better adaptation for real-world feature space. The reduced features are replaced with random signals from a Deep Random Generator to remove the dependency between the output and the removed features and avoid creating new dependencies. The methods are evaluated on the Allegro robot hand in a real-world in-hand manipulation task. The results show that our methods have faster training and higher task performance than baselines and can solve real-world tasks when selected tactile features are reduced.
Confidence-aware 3D Gaze Estimation and Evaluation Metric
Mar 17, 2023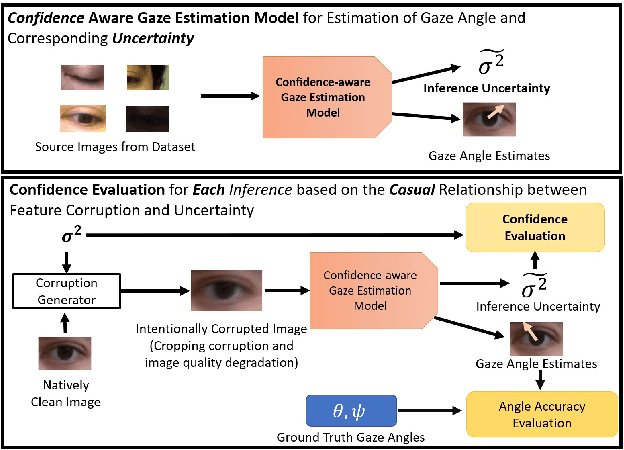
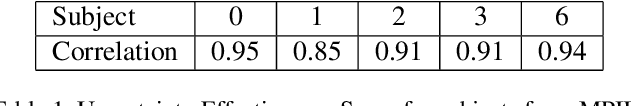
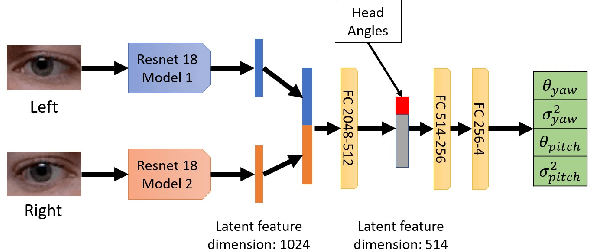
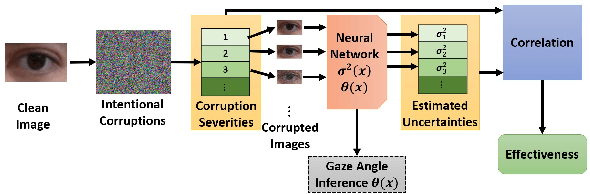
Abstract:Deep learning appearance-based 3D gaze estimation is gaining popularity due to its minimal hardware requirements and being free of constraint. Unreliable and overconfident inferences, however, still limit the adoption of this gaze estimation method. To address the unreliable and overconfident issues, we introduce a confidence-aware model that predicts uncertainties together with gaze angle estimations. We also introduce a novel effectiveness evaluation method based on the causality between eye feature degradation and the rise in inference uncertainty to assess the uncertainty estimation. Our confidence-aware model demonstrates reliable uncertainty estimations while providing angular estimation accuracies on par with the state-of-the-art. Compared with the existing statistical uncertainty-angular-error evaluation metric, the proposed effectiveness evaluation approach can more effectively judge inferred uncertainties' performance at each prediction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge