Qian You
Efficient Document Image Classification Using Region-Based Graph Neural Network
Jun 25, 2021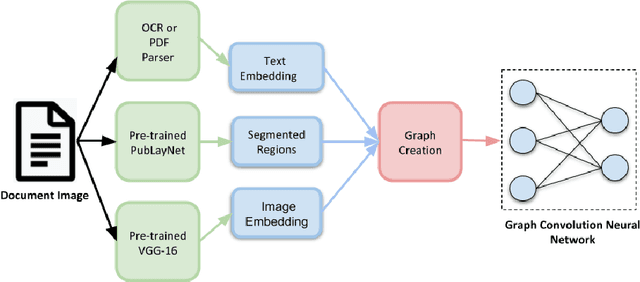
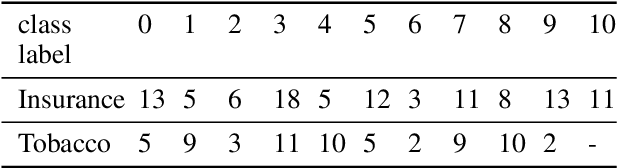

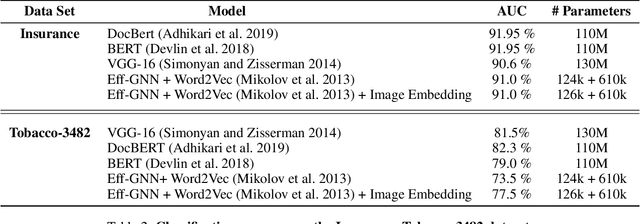
Abstract:Document image classification remains a popular research area because it can be commercialized in many enterprise applications across different industries. Recent advancements in large pre-trained computer vision and language models and graph neural networks has lent document image classification many tools. However using large pre-trained models usually requires substantial computing resources which could defeat the cost-saving advantages of automatic document image classification. In the paper we propose an efficient document image classification framework that uses graph convolution neural networks and incorporates textual, visual and layout information of the document. We have rigorously benchmarked our proposed algorithm against several state-of-art vision and language models on both publicly available dataset and a real-life insurance document classification dataset. Empirical results on both publicly available and real-world data show that our methods achieve near SOTA performance yet require much less computing resources and time for model training and inference. This results in solutions than offer better cost advantages, especially in scalable deployment for enterprise applications. The results showed that our algorithm can achieve classification performance quite close to SOTA. We also provide comprehensive comparisons of computing resources, model sizes, train and inference time between our proposed methods and baselines. In addition we delineate the cost per image using our method and other baselines.
A Simple yet Brisk and Efficient Active Learning Platform for Text Classification
Jan 31, 2021
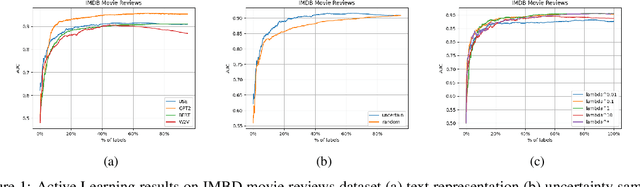
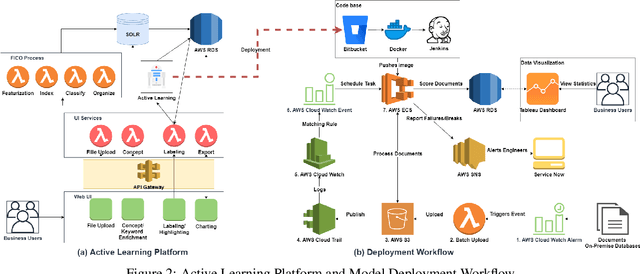

Abstract:In this work, we propose the use of a fully managed machine learning service, which utilizes active learning to directly build models from unstructured data. With this tool, business users can quickly and easily build machine learning models and then directly deploy them into a production ready hosted environment without much involvement from data scientists. Our approach leverages state-of-the-art text representation like OpenAI's GPT2 and a fast implementation of the active learning workflow that relies on a simple construction of incremental learning using linear models, thus providing a brisk and efficient labeling experience for the users. Experiments on both publicly available and real-life insurance datasets empirically show why our choices of simple and fast classification algorithms are ideal for the task at hand.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge