Qi Shao
CCMamba: Selective State-Space Models for Higher-Order Graph Learning on Combinatorial Complexes
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Topological deep learning has emerged for modeling higher-order relational structures beyond pairwise interactions that standard graph neural networks fail to capture. Although combinatorial complexes offer a unified topological framework, most existing topological deep learning methods rely on local message passing via attention mechanisms, which incur quadratic complexity and remain low-dimensional, limiting scalability and rank-aware information aggregation in higher-order complexes.We propose Combinatorial Complex Mamba (CCMamba), the first unified mamba-based neural framework for learning on combinatorial complexes. CCMamba reformulates message passing as a selective state-space modeling problem by organizing multi-rank incidence relations into structured sequences processed by rank-aware state-space models. This enables adaptive, directional, and long range information propagation in linear time without self attention. We further establish the theoretical analysis that the expressive power upper-bound of CCMamba message passing is the 1-Weisfeiler-Lehman test. Experiments on graph, hypergraph, and simplicial benchmarks demonstrate that CCMamba consistently outperforms existing methods while exhibiting improved scalability and robustness to depth.
MetaHGNIE: Meta-Path Induced Hypergraph Contrastive Learning in Heterogeneous Knowledge Graphs
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:Node importance estimation (NIE) in heterogeneous knowledge graphs is a critical yet challenging task, essential for applications such as recommendation, knowledge reasoning, and question answering. Existing methods often rely on pairwise connections, neglecting high-order dependencies among multiple entities and relations, and they treat structural and semantic signals independently, hindering effective cross-modal integration. To address these challenges, we propose MetaHGNIE, a meta-path induced hypergraph contrastive learning framework for disentangling and aligning structural and semantic information. MetaHGNIE constructs a higher-order knowledge graph via meta-path sequences, where typed hyperedges capture multi-entity relational contexts. Structural dependencies are aggregated with local attention, while semantic representations are encoded through a hypergraph transformer equipped with sparse chunking to reduce redundancy. Finally, a multimodal fusion module integrates structural and semantic embeddings under contrastive learning with auxiliary supervision, ensuring robust cross-modal alignment. Extensive experiments on benchmark NIE datasets demonstrate that MetaHGNIE consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines. These results highlight the effectiveness of explicitly modeling higher-order interactions and cross-modal alignment in heterogeneous knowledge graphs. Our code is available at https://github.com/SEU-WENJIA/DualHNIE
See Once, Then Act: Vision-Language-Action Model with Task Learning from One-Shot Video Demonstrations
Dec 08, 2025Abstract:Developing robust and general-purpose manipulation policies represents a fundamental objective in robotics research. While Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have demonstrated promising capabilities for end-to-end robot control, existing approaches still exhibit limited generalization to tasks beyond their training distributions. In contrast, humans possess remarkable proficiency in acquiring novel skills by simply observing others performing them once. Inspired by this capability, we propose ViVLA, a generalist robotic manipulation policy that achieves efficient task learning from a single expert demonstration video at test time. Our approach jointly processes an expert demonstration video alongside the robot's visual observations to predict both the demonstrated action sequences and subsequent robot actions, effectively distilling fine-grained manipulation knowledge from expert behavior and transferring it seamlessly to the agent. To enhance the performance of ViVLA, we develop a scalable expert-agent pair data generation pipeline capable of synthesizing paired trajectories from easily accessible human videos, further augmented by curated pairs from publicly available datasets. This pipeline produces a total of 892,911 expert-agent samples for training ViVLA. Experimental results demonstrate that our ViVLA is able to acquire novel manipulation skills from only a single expert demonstration video at test time. Our approach achieves over 30% improvement on unseen LIBERO tasks and maintains above 35% gains with cross-embodiment videos. Real-world experiments demonstrate effective learning from human videos, yielding more than 38% improvement on unseen tasks.
EquiMus: Energy-Equivalent Dynamic Modeling and Simulation of Musculoskeletal Robots Driven by Linear Elastic Actuators
Nov 11, 2025Abstract:Dynamic modeling and control are critical for unleashing soft robots' potential, yet remain challenging due to their complex constitutive behaviors and real-world operating conditions. Bio-inspired musculoskeletal robots, which integrate rigid skeletons with soft actuators, combine high load-bearing capacity with inherent flexibility. Although actuation dynamics have been studied through experimental methods and surrogate models, accurate and effective modeling and simulation remain a significant challenge, especially for large-scale hybrid rigid--soft robots with continuously distributed mass, kinematic loops, and diverse motion modes. To address these challenges, we propose EquiMus, an energy-equivalent dynamic modeling framework and MuJoCo-based simulation for musculoskeletal rigid--soft hybrid robots with linear elastic actuators. The equivalence and effectiveness of the proposed approach are validated and examined through both simulations and real-world experiments on a bionic robotic leg. EquiMus further demonstrates its utility for downstream tasks, including controller design and learning-based control strategies.
Decoupling Spatio-Temporal Prediction: When Lightweight Large Models Meet Adaptive Hypergraphs
May 26, 2025Abstract:Spatio-temporal prediction is a pivotal task with broad applications in traffic management, climate monitoring, energy scheduling, etc. However, existing methodologies often struggle to balance model expressiveness and computational efficiency, especially when scaling to large real-world datasets. To tackle these challenges, we propose STH-SepNet (Spatio-Temporal Hypergraph Separation Networks), a novel framework that decouples temporal and spatial modeling to enhance both efficiency and precision. Therein, the temporal dimension is modeled using lightweight large language models, which effectively capture low-rank temporal dynamics. Concurrently, the spatial dimension is addressed through an adaptive hypergraph neural network, which dynamically constructs hyperedges to model intricate, higher-order interactions. A carefully designed gating mechanism is integrated to seamlessly fuse temporal and spatial representations. By leveraging the fundamental principles of low-rank temporal dynamics and spatial interactions, STH-SepNet offers a pragmatic and scalable solution for spatio-temporal prediction in real-world applications. Extensive experiments on large-scale real-world datasets across multiple benchmarks demonstrate the effectiveness of STH-SepNet in boosting predictive performance while maintaining computational efficiency. This work may provide a promising lightweight framework for spatio-temporal prediction, aiming to reduce computational demands and while enhancing predictive performance. Our code is avaliable at https://github.com/SEU-WENJIA/ST-SepNet-Lightweight-LLMs-Meet-Adaptive-Hypergraphs.
LanTu: Dynamics-Enhanced Deep Learning for Eddy-Resolving Ocean Forecasting
May 15, 2025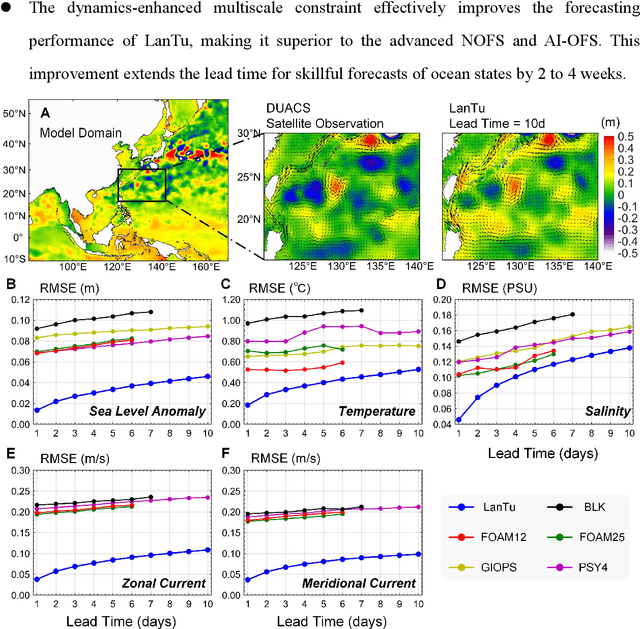
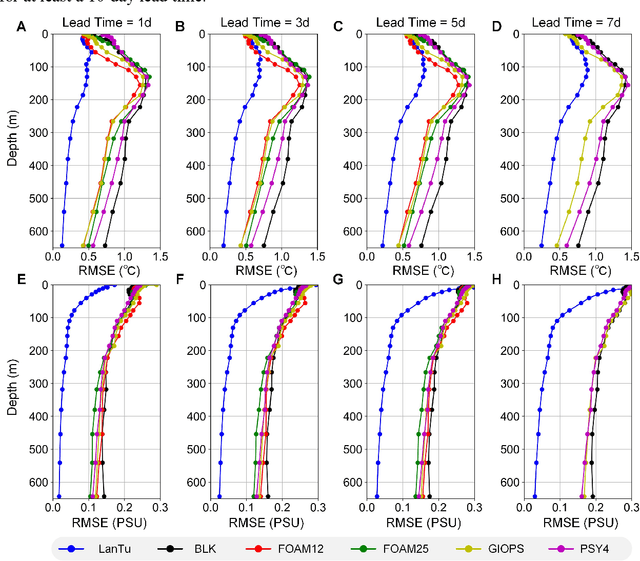
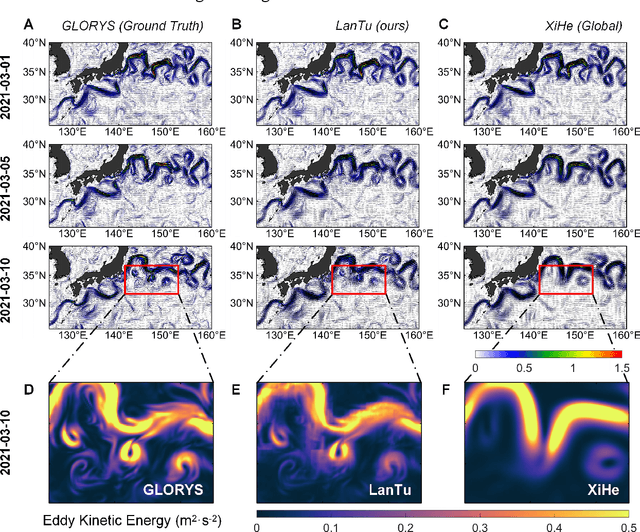
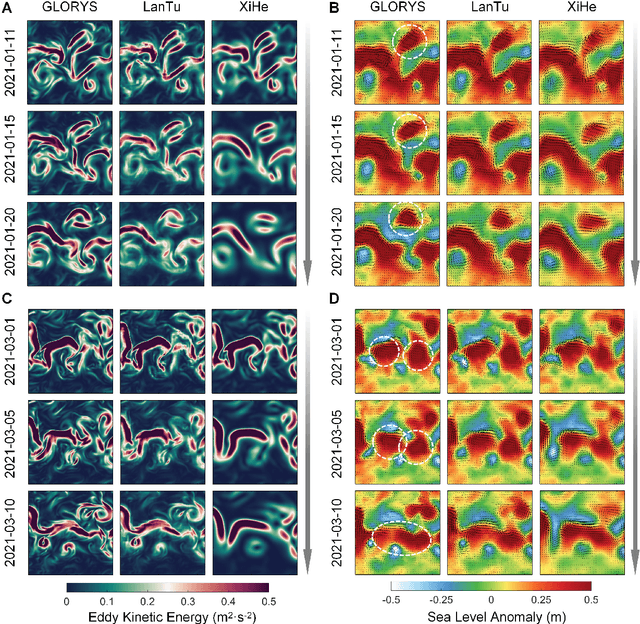
Abstract:Mesoscale eddies dominate the spatiotemporal multiscale variability of the ocean, and their impact on the energy cascade of the global ocean cannot be ignored. Eddy-resolving ocean forecasting is providing more reliable protection for fisheries and navigational safety, but also presents significant scientific challenges and high computational costs for traditional numerical models. Artificial intelligence (AI)-based weather and ocean forecasting systems are becoming powerful tools that balance forecast performance with computational efficiency. However, the complex multiscale features in the ocean dynamical system make AI models still face many challenges in mesoscale eddy forecasting (especially regional modelling). Here, we develop LanTu, a regional eddy-resolving ocean forecasting system based on dynamics-enhanced deep learning. We incorporate cross-scale interactions into LanTu and construct multiscale physical constraint for optimising LanTu guided by knowledge of eddy dynamics in order to improve the forecasting skill of LanTu for mesoscale evolution. The results show that LanTu outperforms the existing advanced operational numerical ocean forecasting system (NOFS) and AI-based ocean forecasting system (AI-OFS) in temperature, salinity, sea level anomaly and current prediction, with a lead time of more than 10 days. Our study highlights that dynamics-enhanced deep learning (LanTu) can be a powerful paradigm for eddy-resolving ocean forecasting.
Portable, High-Frequency, and High-Voltage Control Circuits for Untethered Miniature Robots Driven by Dielectric Elastomer Actuators
Feb 10, 2025



Abstract:In this work, we propose a high-voltage, high-frequency control circuit for the untethered applications of dielectric elastomer actuators (DEAs). The circuit board leverages low-voltage resistive components connected in series to control voltages of up to 1.8 kV within a compact size, suitable for frequencies ranging from 0 to 1 kHz. A single-channel control board weighs only 2.5 g. We tested the performance of the control circuit under different load conditions and power supplies. Based on this control circuit, along with a commercial miniature high-voltage power converter, we construct an untethered crawling robot driven by a cylindrical DEA. The 42-g untethered robots successfully obtained crawling locomotion on a bench and within a pipeline at a driving frequency of 15 Hz, while simultaneously transmitting real-time video data via an onboard camera and antenna. Our work provides a practical way to use low-voltage control electronics to achieve the untethered driving of DEAs, and therefore portable and wearable devices.
Generating Unseen Nonlinear Evolution in Sea Surface Temperature Using a Deep Learning-Based Latent Space Data Assimilation Framework
Dec 18, 2024



Abstract:Advances in data assimilation (DA) methods have greatly improved the accuracy of Earth system predictions. To fuse multi-source data and reconstruct the nonlinear evolution missing from observations, geoscientists are developing future-oriented DA methods. In this paper, we redesign a purely data-driven latent space DA framework (DeepDA) that employs a generative artificial intelligence model to capture the nonlinear evolution in sea surface temperature. Under variational constraints, DeepDA embedded with nonlinear features can effectively fuse heterogeneous data. The results show that DeepDA remains highly stable in capturing and generating nonlinear evolutions even when a large amount of observational information is missing. It can be found that when only 10% of the observation information is available, the error increase of DeepDA does not exceed 40%. Furthermore, DeepDA has been shown to be robust in the fusion of real observations and ensemble simulations. In particular, this paper provides a mechanism analysis of the nonlinear evolution generated by DeepDA from the perspective of physical patterns, which reveals the inherent explainability of our DL model in capturing multi-scale ocean signals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge