Prafulla Saxena
Cross-Centroid Ripple Pattern for Facial Expression Recognition
Jan 16, 2022



Abstract:In this paper, we propose a new feature descriptor Cross-Centroid Ripple Pattern (CRIP) for facial expression recognition. CRIP encodes the transitional pattern of a facial expression by incorporating cross-centroid relationship between two ripples located at radius r1 and r2 respectively. These ripples are generated by dividing the local neighborhood region into subregions. Thus, CRIP has ability to preserve macro and micro structural variations in an extensive region, which enables it to deal with side views and spontaneous expressions. Furthermore, gradient information between cross centroid ripples provides strenght to captures prominent edge features in active patches: eyes, nose and mouth, that define the disparities between different facial expressions. Cross centroid information also provides robustness to irregular illumination. Moreover, CRIP utilizes the averaging behavior of pixels at subregions that yields robustness to deal with noisy conditions. The performance of proposed descriptor is evaluated on seven comprehensive expression datasets consisting of challenging conditions such as age, pose, ethnicity and illumination variations. The experimental results show that our descriptor consistently achieved better accuracy rate as compared to existing state-of-art approaches.
QUEST: Quadriletral Senary bit Pattern for Facial Expression Recognition
Jul 24, 2018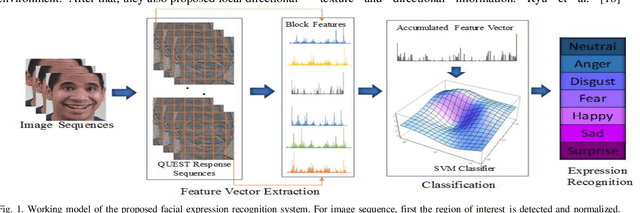
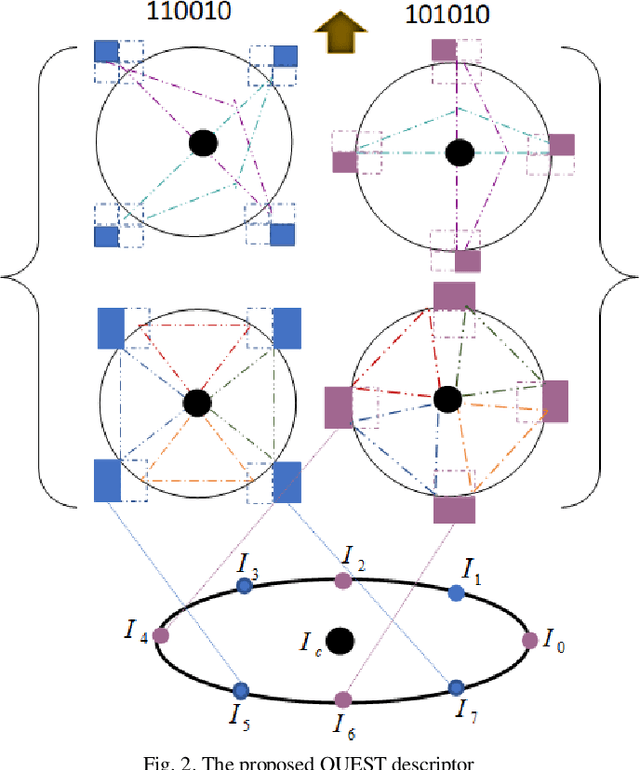
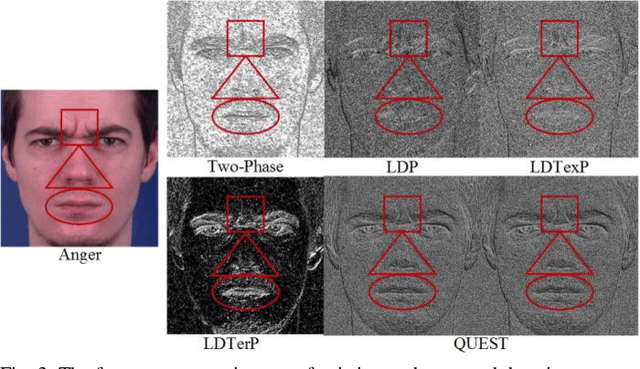
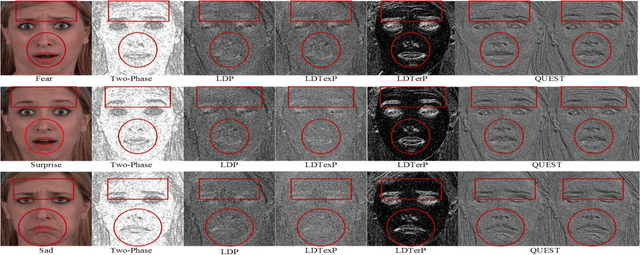
Abstract:Facial expression has a significant role in analyzing human cognitive state. Deriving an accurate facial appearance representation is a critical task for an automatic facial expression recognition application. This paper provides a new feature descriptor named as Quadrilateral Senary bit Pattern for facial expression recognition. The QUEST pattern encoded the intensity changes by emphasizing the relationship between neighboring and reference pixels by dividing them into two quadrilaterals in a local neighborhood. Thus, the resultant gradient edges reveal the transitional variation information, that improves the classification rate by discriminating expression classes. Moreover, it also enhances the capability of the descriptor to deal with viewpoint variations and illumination changes. The trine relationship in a quadrilateral structure helps to extract the expressive edges and suppressing noise elements to enhance the robustness to noisy conditions. The QUEST pattern generates a six-bit compact code, which improves the efficiency of the FER system with more discriminability. The effectiveness of the proposed method is evaluated by conducting several experiments on four benchmark datasets: MMI, GEMEP-FERA, OULU-CASIA, and ISED. The experimental results show better performance of the proposed method as compared to existing state-art-the approaches.
CANDID: Robust Change Dynamics and Deterministic Update Policy for Dynamic Background Subtraction
Apr 19, 2018

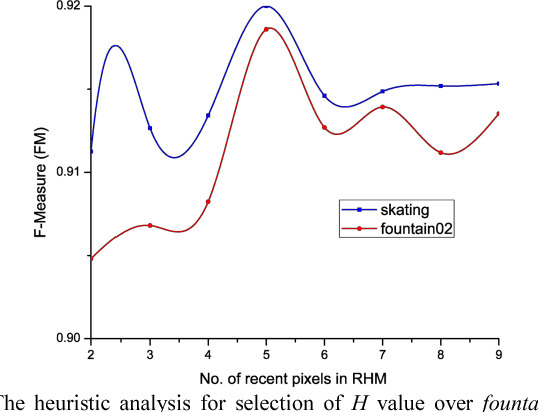

Abstract:Background subtraction in video provides the preliminary information which is essential for many computer vision applications. In this paper, we propose a sequence of approaches named CANDID to handle the change detection problem in challenging video scenarios. The CANDID adaptively initializes the pixel-level distance threshold and update rate. These parameters are updated by computing the change dynamics at a location. Further, the background model is maintained by formulating a deterministic update policy. The performance of the proposed method is evaluated over various challenging scenarios such as dynamic background and extreme weather conditions. The qualitative and quantitative measures of the proposed method outperform the existing state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge