Pooya Moradi
Interrogating the Explanatory Power of Attention in Neural Machine Translation
Sep 30, 2019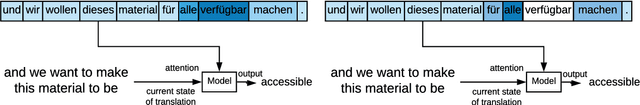

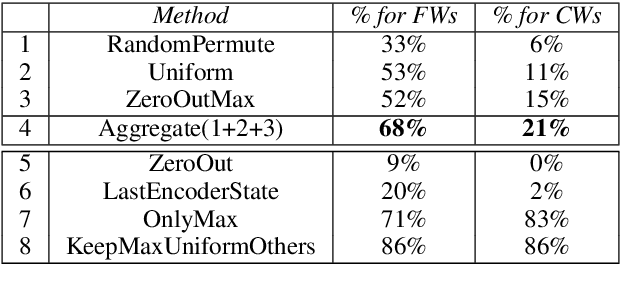
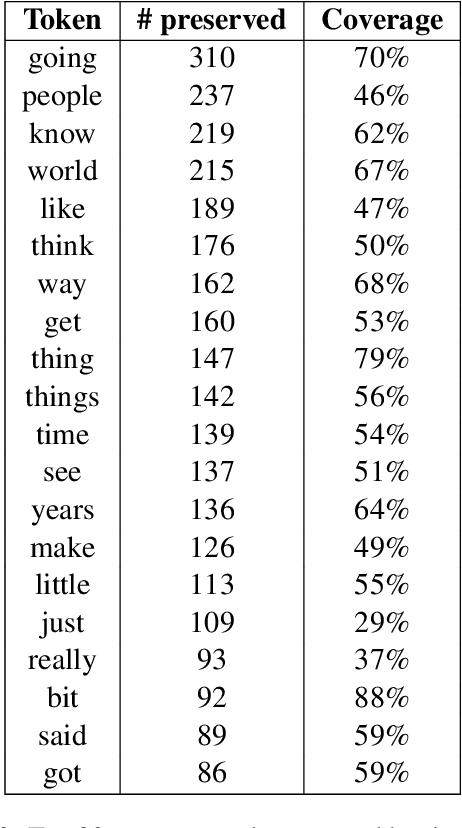
Abstract:Attention models have become a crucial component in neural machine translation (NMT). They are often implicitly or explicitly used to justify the model's decision in generating a specific token but it has not yet been rigorously established to what extent attention is a reliable source of information in NMT. To evaluate the explanatory power of attention for NMT, we examine the possibility of yielding the same prediction but with counterfactual attention models that modify crucial aspects of the trained attention model. Using these counterfactual attention mechanisms we assess the extent to which they still preserve the generation of function and content words in the translation process. Compared to a state of the art attention model, our counterfactual attention models produce 68% of function words and 21% of content words in our German-English dataset. Our experiments demonstrate that attention models by themselves cannot reliably explain the decisions made by a NMT model.
Regression and Learning to Rank Aggregation for User Engagement Evaluation
Jan 29, 2015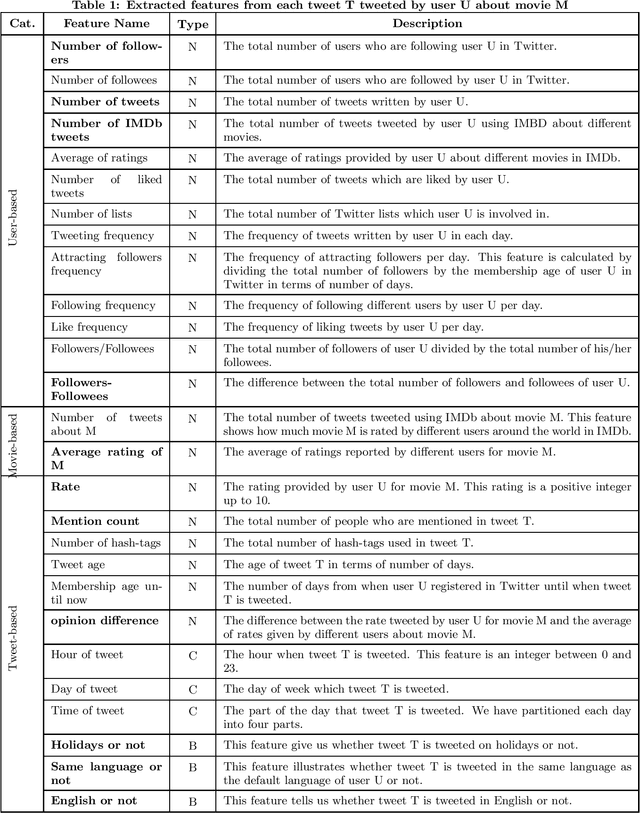
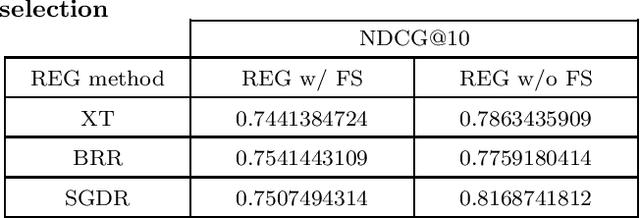
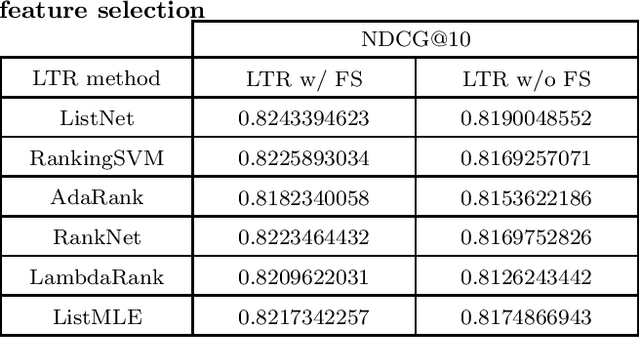
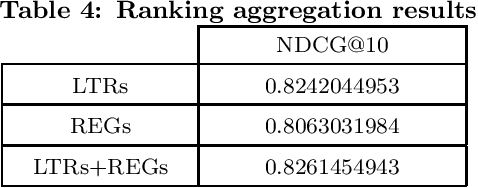
Abstract:User engagement refers to the amount of interaction an instance (e.g., tweet, news, and forum post) achieves. Ranking the items in social media websites based on the amount of user participation in them, can be used in different applications, such as recommender systems. In this paper, we consider a tweet containing a rating for a movie as an instance and focus on ranking the instances of each user based on their engagement, i.e., the total number of retweets and favorites it will gain. For this task, we define several features which can be extracted from the meta-data of each tweet. The features are partitioned into three categories: user-based, movie-based, and tweet-based. We show that in order to obtain good results, features from all categories should be considered. We exploit regression and learning to rank methods to rank the tweets and propose to aggregate the results of regression and learning to rank methods to achieve better performance. We have run our experiments on an extended version of MovieTweeting dataset provided by ACM RecSys Challenge 2014. The results show that learning to rank approach outperforms most of the regression models and the combination can improve the performance significantly.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge