Piotr Aleksander Sokol
On 1/n neural representation and robustness
Dec 08, 2020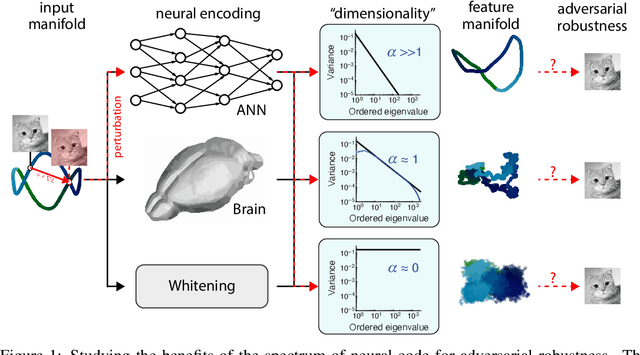
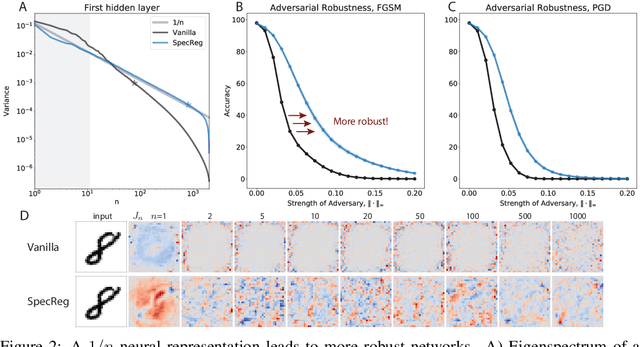
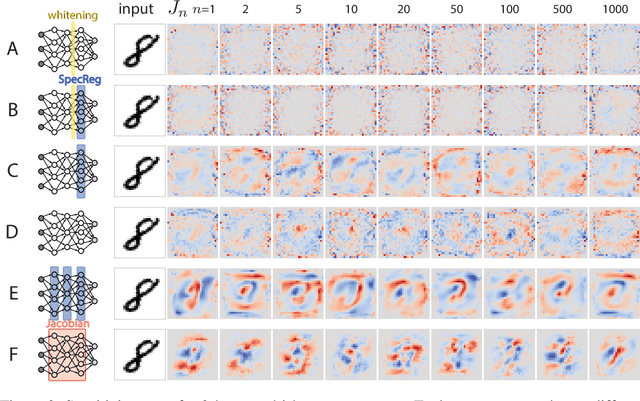
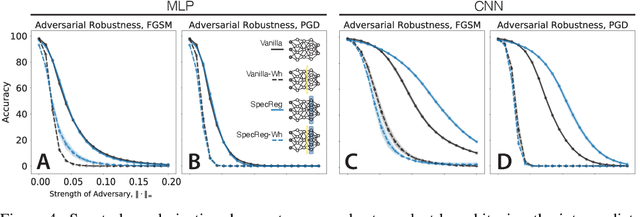
Abstract:Understanding the nature of representation in neural networks is a goal shared by neuroscience and machine learning. It is therefore exciting that both fields converge not only on shared questions but also on similar approaches. A pressing question in these areas is understanding how the structure of the representation used by neural networks affects both their generalization, and robustness to perturbations. In this work, we investigate the latter by juxtaposing experimental results regarding the covariance spectrum of neural representations in the mouse V1 (Stringer et al) with artificial neural networks. We use adversarial robustness to probe Stringer et al's theory regarding the causal role of a 1/n covariance spectrum. We empirically investigate the benefits such a neural code confers in neural networks, and illuminate its role in multi-layer architectures. Our results show that imposing the experimentally observed structure on artificial neural networks makes them more robust to adversarial attacks. Moreover, our findings complement the existing theory relating wide neural networks to kernel methods, by showing the role of intermediate representations.
Gated recurrent units viewed through the lens of continuous time dynamical systems
Jun 03, 2019



Abstract:Gated recurrent units (GRUs) are specialized memory elements for building recurrent neural networks. Despite their incredible success in natural language, speech, and video processing, little is understood about the specific dynamics representable in a GRU network, along with the constraints these dynamics impose when generalizing a specific task. As a result, it is difficult to know a priori how successful a GRU network will perform on a given task. Using a continuous time analysis, we gain intuition on the inner workings of GRU networks. We restrict our presentation to low dimensions to allow for a comprehensive visualization. We found a surprisingly rich repertoire of dynamical features that includes stable limit cycles (nonlinear oscillations), multi-stable dynamics with various topologies, and homoclinic orbits. We contextualize the usefulness of the different kinds of dynamics and experimentally test their existence.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge