Pieter Wolfert
Love, Joy, and Autism Robots: A Metareview and Provocatype
Mar 08, 2024Abstract:Previous work has observed how Neurodivergence is often harmfully pathologized in Human-Computer Interaction (HCI) and Human-Robot interaction (HRI) research. We conduct a review of autism robot reviews and find the dominant research direction is Autistic people's second to lowest (24 of 25) research priority: interventions and treatments purporting to 'help' neurodivergent individuals to conform to neurotypical social norms, become better behaved, improve social and emotional skills, and otherwise 'fix' us -- rarely prioritizing the internal experiences that might lead to such differences. Furthermore, a growing body of evidence indicates many of the most popular current approaches risk inflicting lasting trauma and damage on Autistic people. We draw on the principles and findings of the latest Autism research, Feminist HRI, and Robotics to imagine a role reversal, analyze the implications, then conclude with actionable guidance on Autistic-led scientific methods and research directions.
Evaluating gesture-generation in a large-scale open challenge: The GENEA Challenge 2022
Mar 15, 2023Abstract:This paper reports on the second GENEA Challenge to benchmark data-driven automatic co-speech gesture generation. Participating teams used the same speech and motion dataset to build gesture-generation systems. Motion generated by all these systems was rendered to video using a standardised visualisation pipeline and evaluated in several large, crowdsourced user studies. Unlike when comparing different research papers, differences in results are here only due to differences between methods, enabling direct comparison between systems. The dataset was based on 18 hours of full-body motion capture, including fingers, of different persons engaging in a dyadic conversation. Ten teams participated in the challenge across two tiers: full-body and upper-body gesticulation. For each tier, we evaluated both the human-likeness of the gesture motion and its appropriateness for the specific speech signal. Our evaluations decouple human-likeness from gesture appropriateness, which has been a difficult problem in the field. The evaluation results are a revolution, and a revelation. Some synthetic conditions are rated as significantly more human-like than human motion capture. To the best of our knowledge, this has never been shown before on a high-fidelity avatar. On the other hand, all synthetic motion is found to be vastly less appropriate for the speech than the original motion-capture recordings. We also find that conventional objective metrics do not correlate well with subjective human-likeness ratings in this large evaluation. The one exception is the Fr\'echet gesture distance (FGD), which achieves a Kendall's tau rank correlation of around -0.5. Based on the challenge results we formulate numerous recommendations for system building and evaluation.
The GENEA Challenge 2022: A large evaluation of data-driven co-speech gesture generation
Aug 22, 2022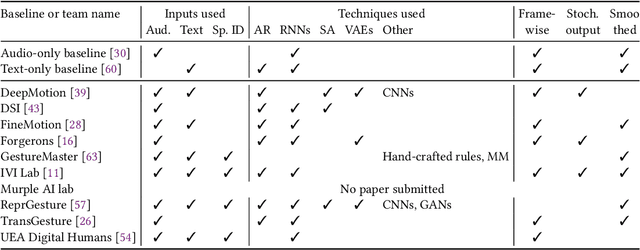
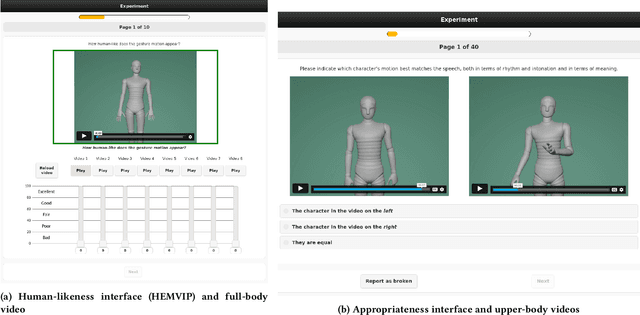

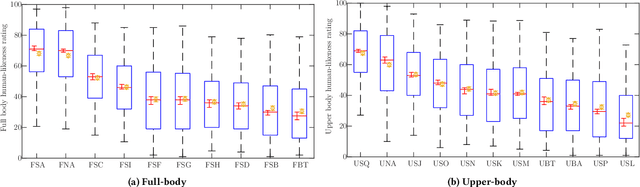
Abstract:This paper reports on the second GENEA Challenge to benchmark data-driven automatic co-speech gesture generation. Participating teams used the same speech and motion dataset to build gesture-generation systems. Motion generated by all these systems was rendered to video using a standardised visualisation pipeline and evaluated in several large, crowdsourced user studies. Unlike when comparing different research papers, differences in results are here only due to differences between methods, enabling direct comparison between systems. This year's dataset was based on 18 hours of full-body motion capture, including fingers, of different persons engaging in dyadic conversation. Ten teams participated in the challenge across two tiers: full-body and upper-body gesticulation. For each tier we evaluated both the human-likeness of the gesture motion and its appropriateness for the specific speech signal. Our evaluations decouple human-likeness from gesture appropriateness, which previously was a major challenge in the field. The evaluation results are a revolution, and a revelation. Some synthetic conditions are rated as significantly more human-like than human motion capture. To the best of our knowledge, this has never been shown before on a high-fidelity avatar. On the other hand, all synthetic motion is found to be vastly less appropriate for the speech than the original motion-capture recordings. Additional material is available via the project website at https://youngwoo-yoon.github.io/GENEAchallenge2022/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge