Philipp Seeberger
Towards Multi-Level Transcript Segmentation: LoRA Fine-Tuning for Table-of-Contents Generation
Jan 05, 2026Abstract:Segmenting speech transcripts into thematic sections benefits both downstream processing and users who depend on written text for accessibility. We introduce a novel approach to hierarchical topic segmentation in transcripts, generating multi-level tables of contents that capture both topic and subtopic boundaries. We compare zero-shot prompting and LoRA fine-tuning on large language models, while also exploring the integration of high-level speech pause features. Evaluations on English meeting recordings and multilingual lecture transcripts (Portuguese, German) show significant improvements over established topic segmentation baselines. Additionally, we adapt a common evaluation measure for multi-level segmentation, taking into account all hierarchical levels within one metric.
* Published in Proceedings of Interspeech 2025. Please cite the proceedings version (DOI: 10.21437/Interspeech.2025-2792)
Generalizing to Unseen Disaster Events: A Causal View
Nov 13, 2025Abstract:Due to the rapid growth of social media platforms, these tools have become essential for monitoring information during ongoing disaster events. However, extracting valuable insights requires real-time processing of vast amounts of data. A major challenge in existing systems is their exposure to event-related biases, which negatively affects their ability to generalize to emerging events. While recent advancements in debiasing and causal learning offer promising solutions, they remain underexplored in the disaster event domain. In this work, we approach bias mitigation through a causal lens and propose a method to reduce event- and domain-related biases, enhancing generalization to future events. Our approach outperforms multiple baselines by up to +1.9% F1 and significantly improves a PLM-based classifier across three disaster classification tasks.
MMUTF: Multimodal Multimedia Event Argument Extraction with Unified Template Filling
Jun 18, 2024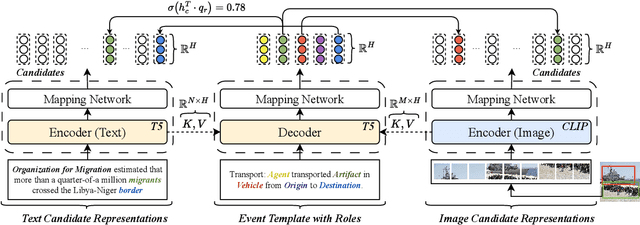
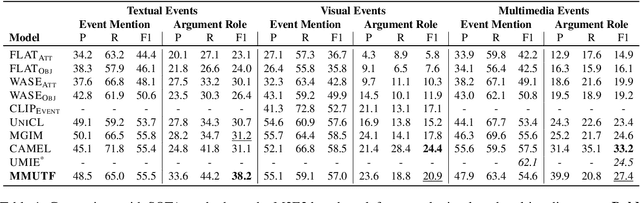
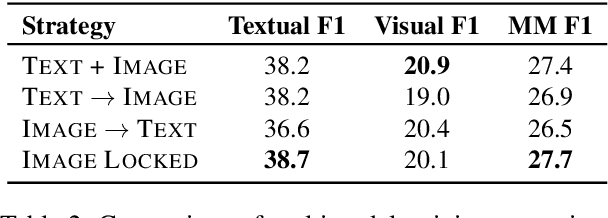
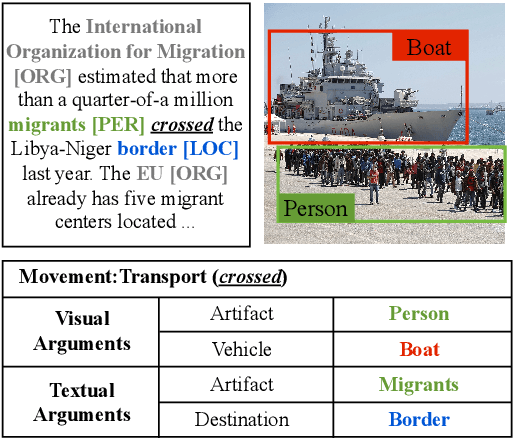
Abstract:With the advancement of multimedia technologies, news documents and user-generated content are often represented as multiple modalities, making Multimedia Event Extraction (MEE) an increasingly important challenge. However, recent MEE methods employ weak alignment strategies and data augmentation with simple classification models, which ignore the capabilities of natural language-formulated event templates for the challenging Event Argument Extraction (EAE) task. In this work, we focus on EAE and address this issue by introducing a unified template filling model that connects the textual and visual modalities via textual prompts. This approach enables the exploitation of cross-ontology transfer and the incorporation of event-specific semantics. Experiments on the M2E2 benchmark demonstrate the effectiveness of our approach. Our system surpasses the current SOTA on textual EAE by +7% F1, and performs generally better than the second-best systems for multimedia EAE.
Optimized Speculative Sampling for GPU Hardware Accelerators
Jun 16, 2024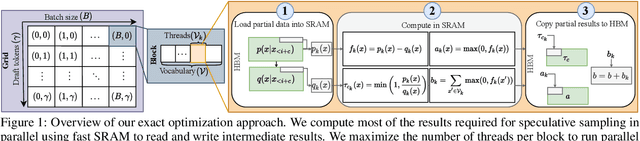
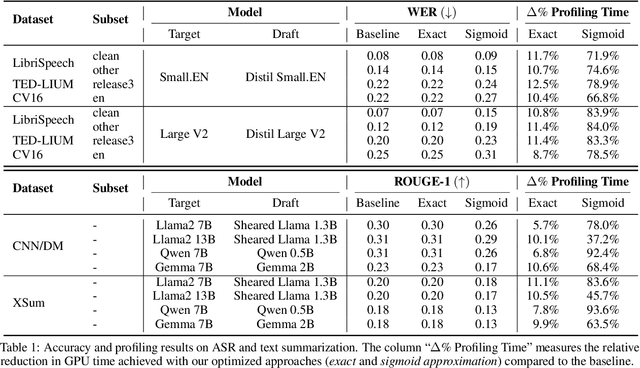


Abstract:In this work, we optimize speculative sampling for parallel hardware accelerators to improve sampling speed. We notice that substantial portions of the intermediate matrices necessary for speculative sampling can be computed concurrently. This allows us to distribute the workload across multiple GPU threads, enabling simultaneous operations on matrix segments within thread blocks. Additionally, we use fast on-chip memory to store intermediate results, thereby minimizing the frequency of slow read and write operations across different types of memory. This results in profiling time improvements ranging from 6% to 13% relative to the baseline implementation, without compromising accuracy. To further accelerate speculative sampling, probability distributions parameterized by softmax are approximated by sigmoid. This approximation approach results in significantly greater relative improvements in profiling time, ranging from 37% to 94%, with a slight decline in accuracy. We conduct extensive experiments on both automatic speech recognition and summarization tasks to validate the effectiveness of our optimization methods.
Multi-Query Focused Disaster Summarization via Instruction-Based Prompting
Feb 14, 2024Abstract:Automatic summarization of mass-emergency events plays a critical role in disaster management. The second edition of CrisisFACTS aims to advance disaster summarization based on multi-stream fact-finding with a focus on web sources such as Twitter, Reddit, Facebook, and Webnews. Here, participants are asked to develop systems that can extract key facts from several disaster-related events, which ultimately serve as a summary. This paper describes our method to tackle this challenging task. We follow previous work and propose to use a combination of retrieval, reranking, and an embarrassingly simple instruction-following summarization. The two-stage retrieval pipeline relies on BM25 and MonoT5, while the summarizer module is based on the open-source Large Language Model (LLM) LLaMA-13b. For summarization, we explore a Question Answering (QA)-motivated prompting approach and find the evidence useful for extracting query-relevant facts. The automatic metrics and human evaluation show strong results but also highlight the gap between open-source and proprietary systems.
Information Type Classification with Contrastive Task-Specialized Sentence Encoders
Dec 18, 2023Abstract:User-generated information content has become an important information source in crisis situations. However, classification models suffer from noise and event-related biases which still poses a challenging task and requires sophisticated task-adaptation. To address these challenges, we propose the use of contrastive task-specialized sentence encoders for downstream classification. We apply the task-specialization on the CrisisLex, HumAID, and TrecIS information type classification tasks and show performance gains w.r.t. F1-score. Furthermore, we analyse the cross-corpus and cross-lingual capabilities for two German event relevancy classification datasets.
Combining Deep Neural Reranking and Unsupervised Extraction for Multi-Query Focused Summarization
Feb 02, 2023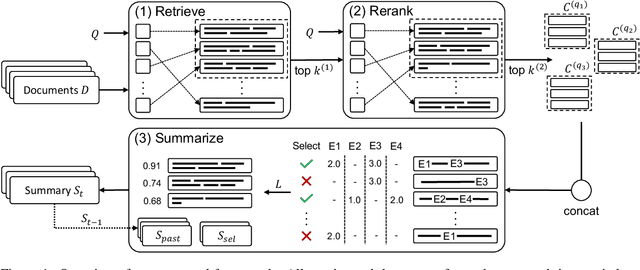
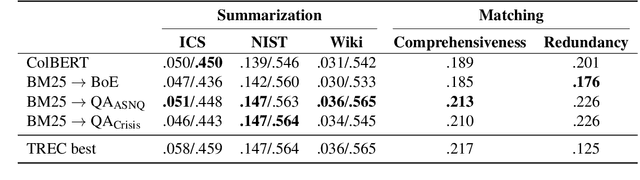
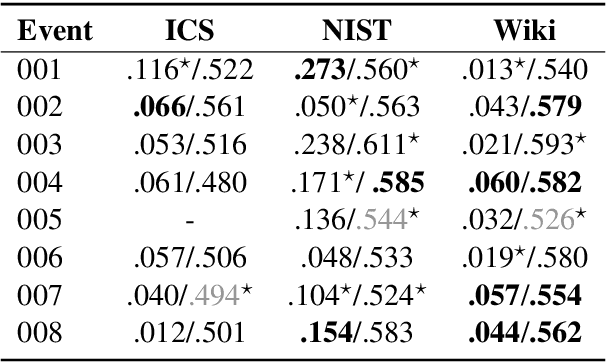
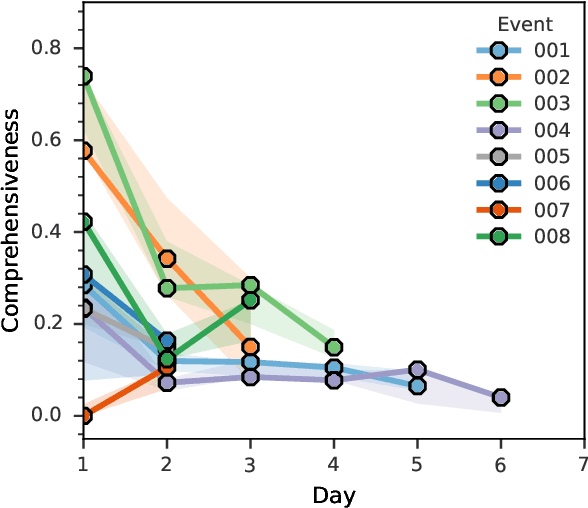
Abstract:The CrisisFACTS Track aims to tackle challenges such as multi-stream fact-finding in the domain of event tracking; participants' systems extract important facts from several disaster-related events while incorporating the temporal order. We propose a combination of retrieval, reranking, and the well-known Integer Linear Programming (ILP) and Maximal Marginal Relevance (MMR) frameworks. In the former two modules, we explore various methods including an entity-based baseline, pre-trained and fine-tuned Question Answering systems, and ColBERT. We then use the latter module as an extractive summarization component by taking diversity and novelty criteria into account. The automatic scoring runs show strong results across the evaluation setups but also reveal shortcomings and challenges.
Enhancing Crisis-Related Tweet Classification with Entity-Masked Language Modeling and Multi-Task Learning
Nov 21, 2022Abstract:Social media has become an important information source for crisis management and provides quick access to ongoing developments and critical information. However, classification models suffer from event-related biases and highly imbalanced label distributions which still poses a challenging task. To address these challenges, we propose a combination of entity-masked language modeling and hierarchical multi-label classification as a multi-task learning problem. We evaluate our method on tweets from the TREC-IS dataset and show an absolute performance gain w.r.t. F1-score of up to 10% for actionable information types. Moreover, we found that entity-masking reduces the effect of overfitting to in-domain events and enables improvements in cross-event generalization.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge