Philipp Reiser
Uncertainty-Aware Surrogate-based Amortized Bayesian Inference for Computationally Expensive Models
May 13, 2025Abstract:Bayesian inference typically relies on a large number of model evaluations to estimate posterior distributions. Established methods like Markov Chain Monte Carlo (MCMC) and Amortized Bayesian Inference (ABI) can become computationally challenging. While ABI enables fast inference after training, generating sufficient training data still requires thousands of model simulations, which is infeasible for expensive models. Surrogate models offer a solution by providing approximate simulations at a lower computational cost, allowing the generation of large data sets for training. However, the introduced approximation errors and uncertainties can lead to overconfident posterior estimates. To address this, we propose Uncertainty-Aware Surrogate-based Amortized Bayesian Inference (UA-SABI) - a framework that combines surrogate modeling and ABI while explicitly quantifying and propagating surrogate uncertainties through the inference pipeline. Our experiments show that this approach enables reliable, fast, and repeated Bayesian inference for computationally expensive models, even under tight time constraints.
Bayesian Surrogate Training on Multiple Data Sources: A Hybrid Modeling Strategy
Dec 16, 2024



Abstract:Surrogate models are often used as computationally efficient approximations to complex simulation models, enabling tasks such as solving inverse problems, sensitivity analysis, and probabilistic forward predictions, which would otherwise be computationally infeasible. During training, surrogate parameters are fitted such that the surrogate reproduces the simulation model's outputs as closely as possible. However, the simulation model itself is merely a simplification of the real-world system, often missing relevant processes or suffering from misspecifications e.g., in inputs or boundary conditions. Hints about these might be captured in real-world measurement data, and yet, we typically ignore those hints during surrogate building. In this paper, we propose two novel probabilistic approaches to integrate simulation data and real-world measurement data during surrogate training. The first method trains separate surrogate models for each data source and combines their predictive distributions, while the second incorporates both data sources by training a single surrogate. We show the conceptual differences and benefits of the two approaches through both synthetic and real-world case studies. The results demonstrate the potential of these methods to improve predictive accuracy, predictive coverage, and to diagnose problems in the underlying simulation model. These insights can improve system understanding and future model development.
Uncertainty Quantification and Propagation in Surrogate-based Bayesian Inference
Dec 08, 2023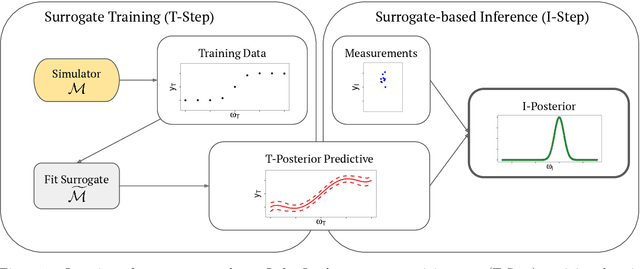
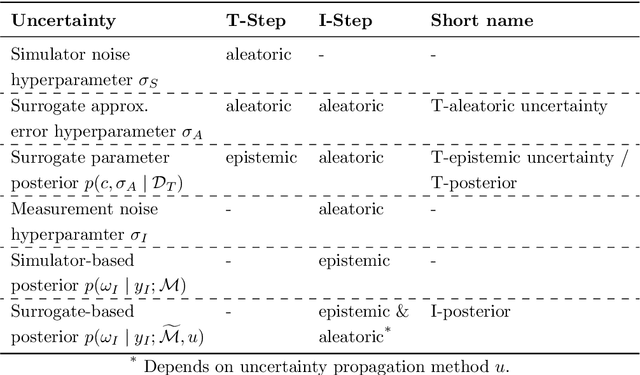
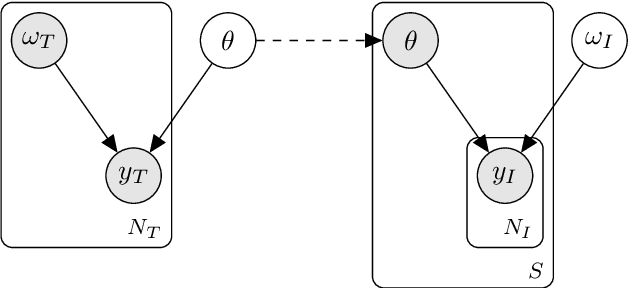
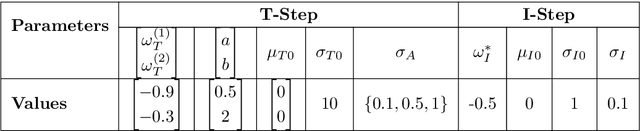
Abstract:Surrogate models are statistical or conceptual approximations for more complex simulation models. In this context, it is crucial to propagate the uncertainty induced by limited simulation budget and surrogate approximation error to predictions, inference, and subsequent decision-relevant quantities. However, quantifying and then propagating the uncertainty of surrogates is usually limited to special analytic cases or is otherwise computationally very expensive. In this paper, we propose a framework enabling a scalable, Bayesian approach to surrogate modeling with thorough uncertainty quantification, propagation, and validation. Specifically, we present three methods for Bayesian inference with surrogate models given measurement data. This is a task where the propagation of surrogate uncertainty is especially relevant, because failing to account for it may lead to biased and/or overconfident estimates of the parameters of interest. We showcase our approach in two detailed case studies for both linear and nonlinear modeling scenarios. Uncertainty propagation in surrogate models enables more reliable and safe approximation of expensive simulators and will therefore be useful in various fields of applications.
uBAM: Unsupervised Behavior Analysis and Magnification using Deep Learning
Dec 16, 2020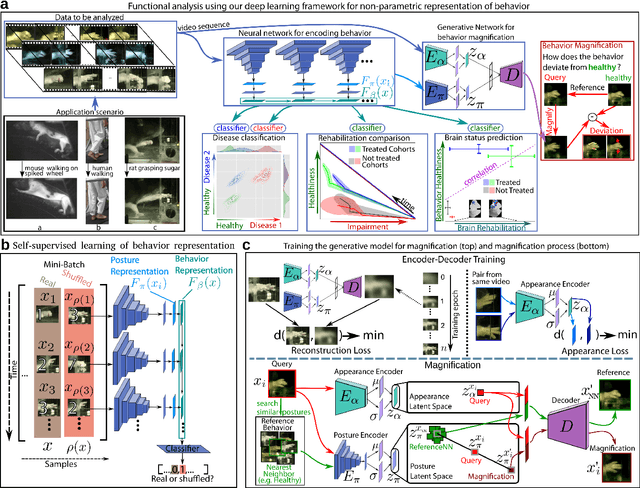
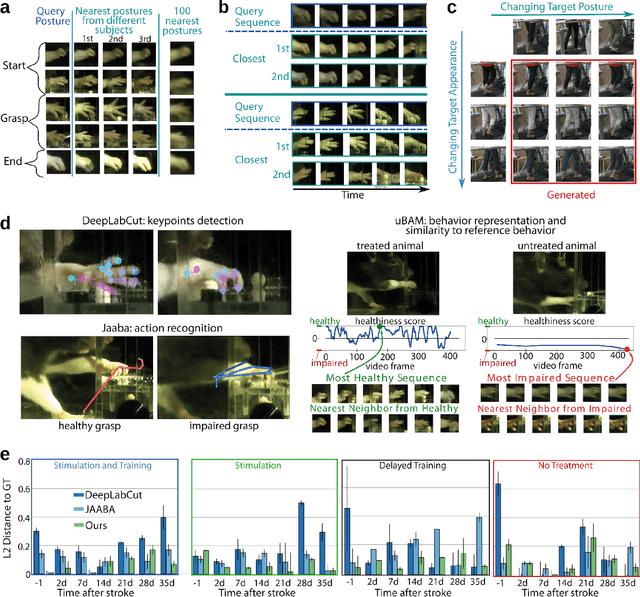
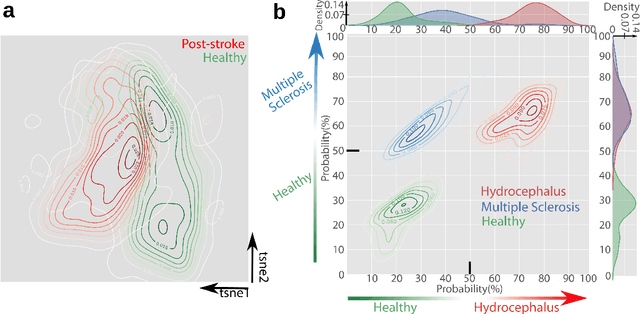
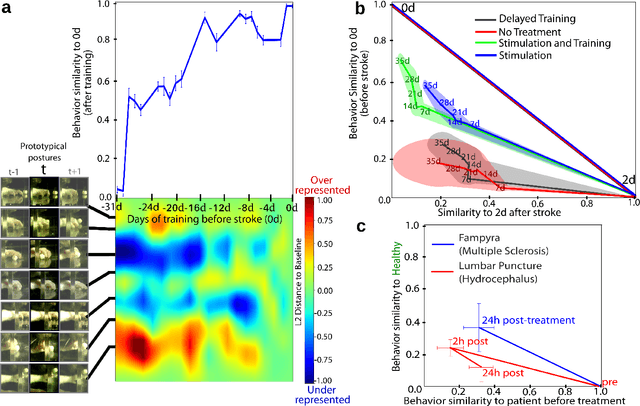
Abstract:Motor behavior analysis is essential to biomedical research and clinical diagnostics as it provides a non-invasive strategy for identifying motor impairment and its change caused by interventions. State-of-the-art instrumented movement analysis is time- and cost-intensive, since it requires placing physical or virtual markers. Besides the effort required for marking keypoints or annotations necessary for training or finetuning a detector, users need to know the interesting behavior beforehand to provide meaningful keypoints. We introduce uBAM, a novel, automatic deep learning algorithm for behavior analysis by discovering and magnifying deviations. We propose an unsupervised learning of posture and behavior representations that enable an objective behavior comparison across subjects. A generative model with novel disentanglement of appearance and behavior magnifies subtle behavior differences across subjects directly in a video without requiring a detour via keypoints or annotations. Evaluations on rodents and human patients with neurological diseases demonstrate the wide applicability of our approach.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge