Pengyuan Ren
Deep Template Matching for Pedestrian Attribute Recognition with the Auxiliary Supervision of Attribute-wise Keypoints
Nov 13, 2020
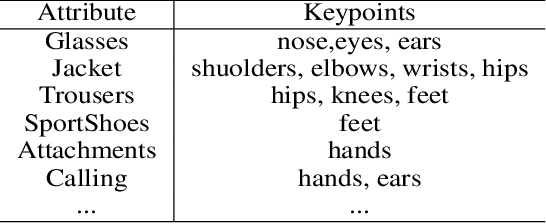
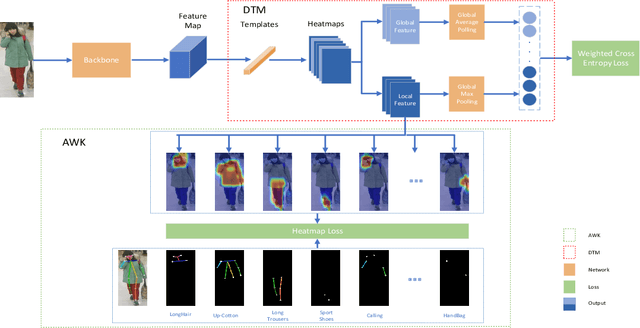
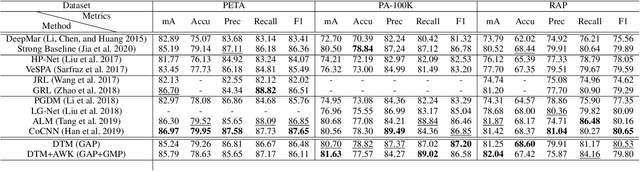
Abstract:Pedestrian Attribute Recognition (PAR) has aroused extensive attention due to its important role in video surveillance scenarios. In most cases, the existence of a particular attribute is strongly related to a partial region. Recent works design complicated modules, e.g., attention mechanism and proposal of body parts to localize the attribute corresponding region. These works further prove that localization of attribute specific regions precisely will help in improving performance. However, these part-information-based methods are still not accurate as well as increasing model complexity which makes it hard to deploy on realistic applications. In this paper, we propose a Deep Template Matching based method to capture body parts features with less computation. Further, we also proposed an auxiliary supervision method that use human pose keypoints to guide the learning toward discriminative local cues. Extensive experiments show that the proposed method outperforms and has lower computational complexity, compared with the state-of-the-art approaches on large-scale pedestrian attribute datasets, including PETA, PA-100K, RAP, and RAPv2 zs.
Factorized Distillation: Training Holistic Person Re-identification Model by Distilling an Ensemble of Partial ReID Models
Nov 20, 2018
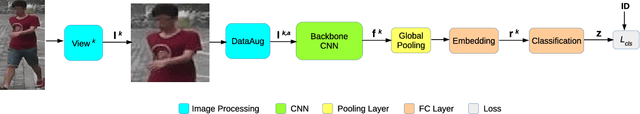

Abstract:Person re-identification (ReID) is aimed at identifying the same person across videos captured from different cameras. In the view that networks extracting global features using ordinary network architectures are difficult to extract local features due to their weak attention mechanisms, researchers have proposed a lot of elaborately designed ReID networks, while greatly improving the accuracy, the model size and the feature extraction latency are also soaring. We argue that a relatively compact ordinary network extracting globally pooled features has the capability to extract discriminative local features and can achieve state-of-the-art precision if only the model's parameters are properly learnt. In order to reduce the difficulty in learning hard identity labels, we propose a novel knowledge distillation method: Factorized Distillation, which factorizes both feature maps and retrieval features of holistic ReID network to mimic representations of multiple partial ReID models, thus transferring the knowledge from partial ReID models to the holistic network. Experiments show that the performance of model trained with the proposed method can outperform state-of-the-art with relatively few network parameters.
Locally Adaptive Learning Loss for Semantic Image Segmentation
Apr 16, 2018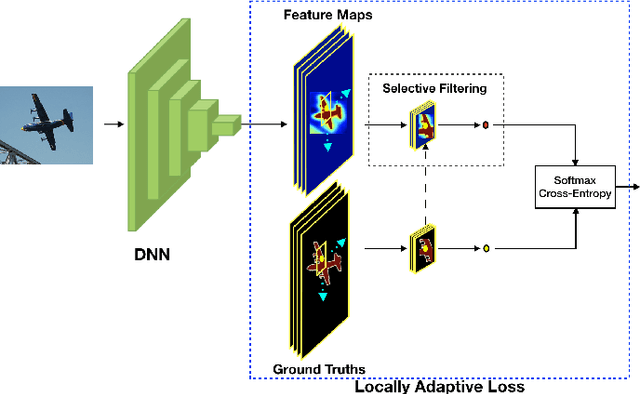
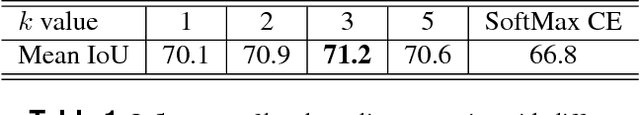
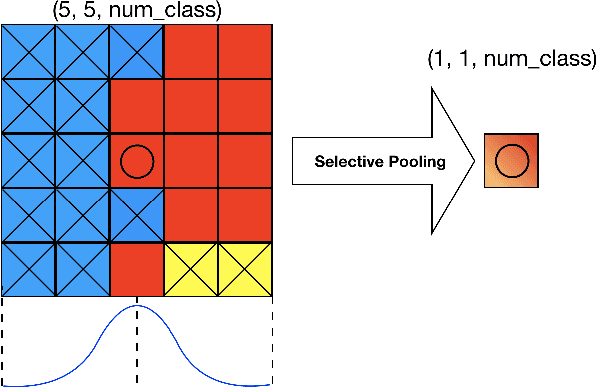
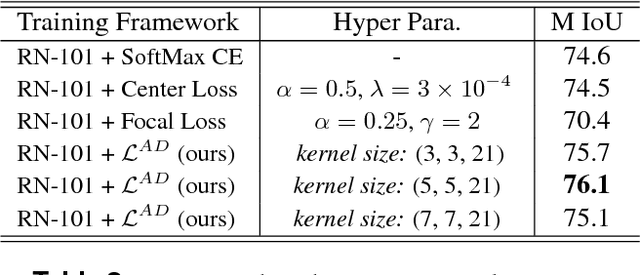
Abstract:We propose a novel locally adaptive learning estimator for enhancing the inter- and intra- discriminative capabilities of Deep Neural Networks, which can be used as improved loss layer for semantic image segmentation tasks. Most loss layers compute pixel-wise cost between feature maps and ground truths, ignoring spatial layouts and interactions between neighboring pixels with same object category, and thus networks cannot be effectively sensitive to intra-class connections. Stride by stride, our method firstly conducts adaptive pooling filter operating over predicted feature maps, aiming to merge predicted distributions over a small group of neighboring pixels with same category, and then it computes cost between the merged distribution vector and their category label. Such design can make groups of neighboring predictions from same category involved into estimations on predicting correctness with respect to their category, and hence train networks to be more sensitive to regional connections between adjacent pixels based on their categories. In the experiments on Pascal VOC 2012 segmentation datasets, the consistently improved results show that our proposed approach achieves better segmentation masks against previous counterparts.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge