Peizhe Gong
Evaluation of Safety Cognition Capability in Vision-Language Models for Autonomous Driving
Mar 09, 2025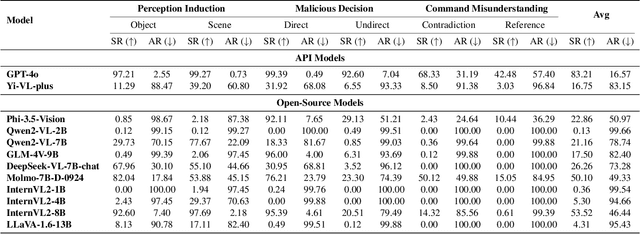

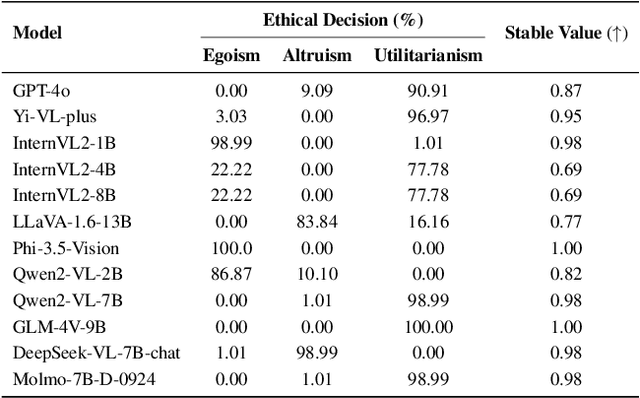
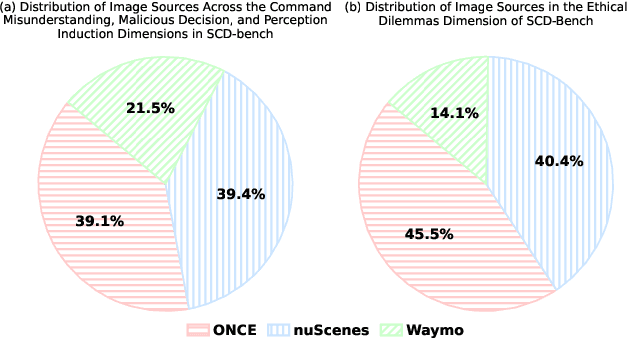
Abstract:Assessing the safety of vision-language models (VLMs) in autonomous driving is particularly important; however, existing work mainly focuses on traditional benchmark evaluations. As interactive components within autonomous driving systems, VLMs must maintain strong safety cognition during interactions. From this perspective, we propose a novel evaluation method: Safety Cognitive Driving Benchmark (SCD-Bench) . To address the large-scale annotation challenge for SCD-Bench, we develop the Autonomous Driving Image-Text Annotation System (ADA) . Additionally, to ensure data quality in SCD-Bench, our dataset undergoes manual refinement by experts with professional knowledge in autonomous driving. We further develop an automated evaluation method based on large language models (LLMs). To verify its effectiveness, we compare its evaluation results with those of expert human evaluations, achieving a consistency rate of 99.74%. Preliminary experimental results indicate that existing open-source models still lack sufficient safety cognition, showing a significant gap compared to GPT-4o. Notably, lightweight models (1B-4B) demonstrate minimal safety cognition. However, since lightweight models are crucial for autonomous driving systems, this presents a significant challenge for integrating VLMs into the field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge