Paul Guerrier
SolderNet: Towards Trustworthy Visual Inspection of Solder Joints in Electronics Manufacturing Using Explainable Artificial Intelligence
Nov 18, 2022Abstract:In electronics manufacturing, solder joint defects are a common problem affecting a variety of printed circuit board components. To identify and correct solder joint defects, the solder joints on a circuit board are typically inspected manually by trained human inspectors, which is a very time-consuming and error-prone process. To improve both inspection efficiency and accuracy, in this work we describe an explainable deep learning-based visual quality inspection system tailored for visual inspection of solder joints in electronics manufacturing environments. At the core of this system is an explainable solder joint defect identification system called SolderNet which we design and implement with trust and transparency in mind. While several challenges remain before the full system can be developed and deployed, this study presents important progress towards trustworthy visual inspection of solder joints in electronics manufacturing.
Automated Copper Alloy Grain Size Evaluation Using a Deep-learning CNN
May 20, 2020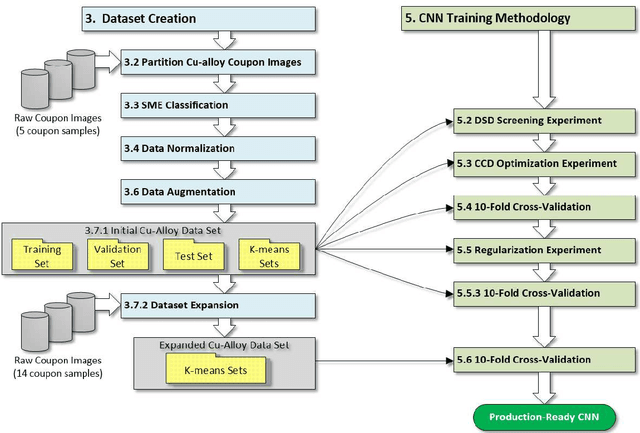
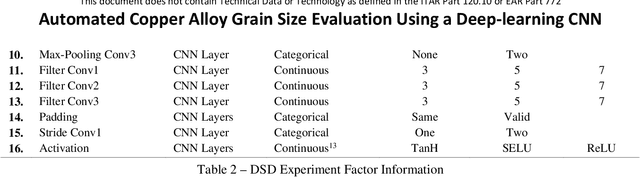
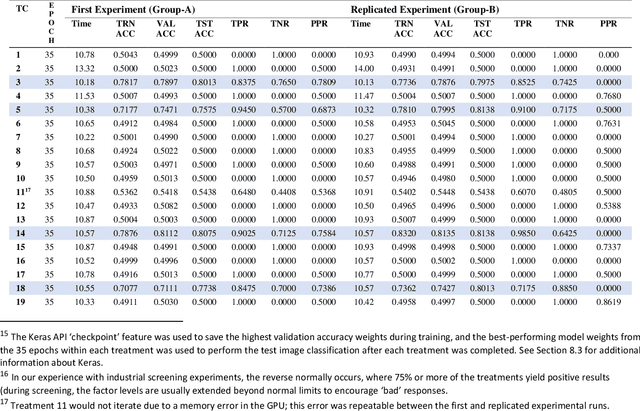
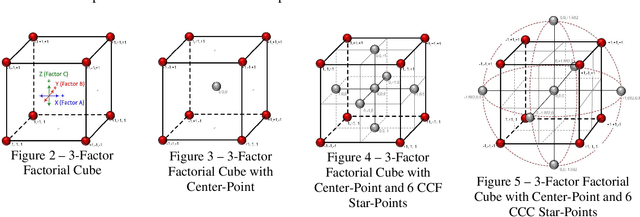
Abstract:Moog Inc. has automated the evaluation of copper (Cu) alloy grain size using a deep-learning convolutional neural network (CNN). The proof-of-concept automated image acquisition and batch-wise image processing offers the potential for significantly reduced labor, improved accuracy of grain evaluation, and decreased overall turnaround times for approving Cu alloy bar stock for use in flight critical aircraft hardware. A classification accuracy of 91.1% on individual sub-images of the Cu alloy coupons was achieved. Process development included minimizing the variation in acquired image color, brightness, and resolution to create a dataset with 12300 sub-images, and then optimizing the CNN hyperparameters on this dataset using statistical design of experiments (DoE). Over the development of the automated Cu alloy grain size evaluation, a degree of "explainability" in the artificial intelligence (XAI) output was realized, based on the decomposition of the large raw images into many smaller dataset sub-images, through the ability to explain the CNN ensemble image output via inspection of the classification results from the individual smaller sub-images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge