Parisa Ghanad Torshizi
Large Language Models for Virtual Human Gesture Selection
Mar 18, 2025Abstract:Co-speech gestures convey a wide variety of meanings and play an important role in face-to-face human interactions. These gestures significantly influence the addressee's engagement, recall, comprehension, and attitudes toward the speaker. Similarly, they impact interactions between humans and embodied virtual agents. The process of selecting and animating meaningful gestures has thus become a key focus in the design of these agents. However, automating this gesture selection process poses a significant challenge. Prior gesture generation techniques have varied from fully automated, data-driven methods, which often struggle to produce contextually meaningful gestures, to more manual approaches that require crafting specific gesture expertise and are time-consuming and lack generalizability. In this paper, we leverage the semantic capabilities of Large Language Models to develop a gesture selection approach that suggests meaningful, appropriate co-speech gestures. We first describe how information on gestures is encoded into GPT-4. Then, we conduct a study to evaluate alternative prompting approaches for their ability to select meaningful, contextually relevant gestures and to align them appropriately with the co-speech utterance. Finally, we detail and demonstrate how this approach has been implemented within a virtual agent system, automating the selection and subsequent animation of the selected gestures for enhanced human-agent interactions.
Investigating Large Language Models' Perception of Emotion Using Appraisal Theory
Oct 03, 2023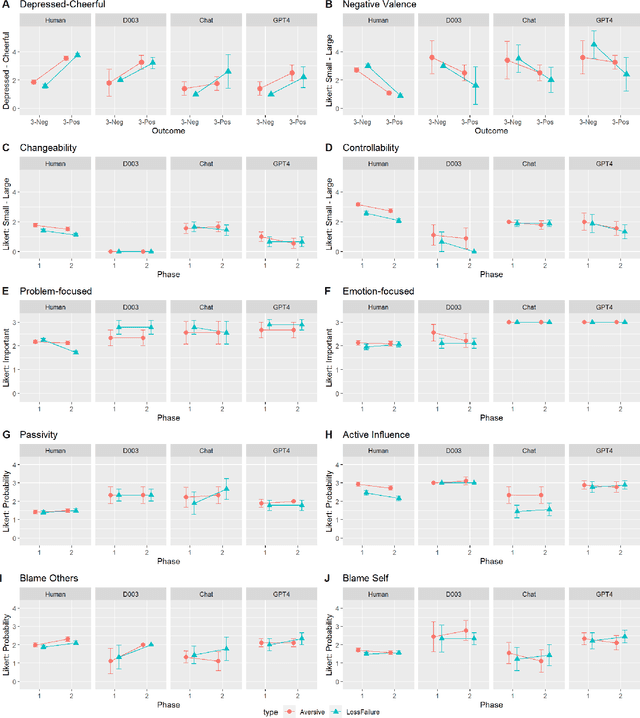
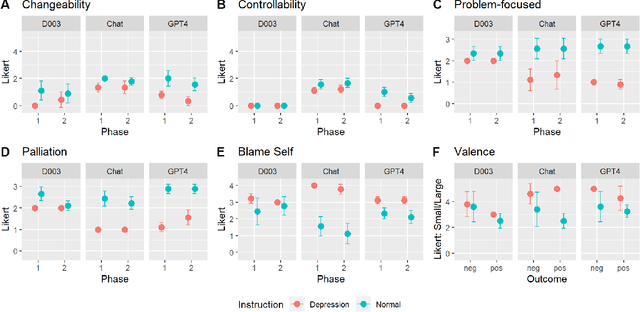
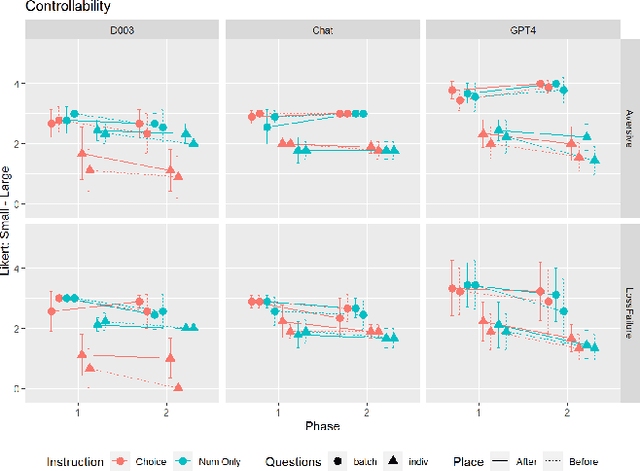
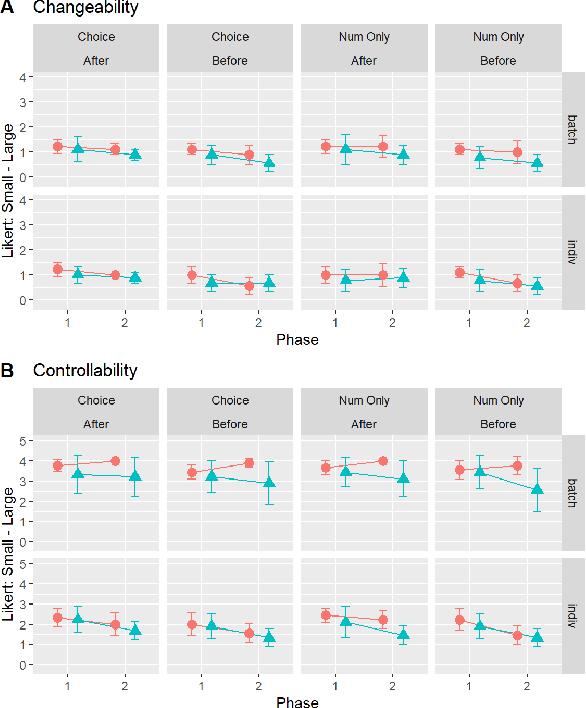
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLM) like ChatGPT have significantly advanced in recent years and are now being used by the general public. As more people interact with these systems, improving our understanding of these black box models is crucial, especially regarding their understanding of human psychological aspects. In this work, we investigate their emotion perception through the lens of appraisal and coping theory using the Stress and Coping Process Questionaire (SCPQ). SCPQ is a validated clinical instrument consisting of multiple stories that evolve over time and differ in key appraisal variables such as controllability and changeability. We applied SCPQ to three recent LLMs from OpenAI, davinci-003, ChatGPT, and GPT-4 and compared the results with predictions from the appraisal theory and human data. The results show that LLMs' responses are similar to humans in terms of dynamics of appraisal and coping, but their responses did not differ along key appraisal dimensions as predicted by the theory and data. The magnitude of their responses is also quite different from humans in several variables. We also found that GPTs can be quite sensitive to instruction and how questions are asked. This work adds to the growing literature evaluating the psychological aspects of LLMs and helps enrich our understanding of the current models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge