Panagiotis Kanellopoulos
How game complexity affects the playing behavior of synthetic agents
Jul 07, 2018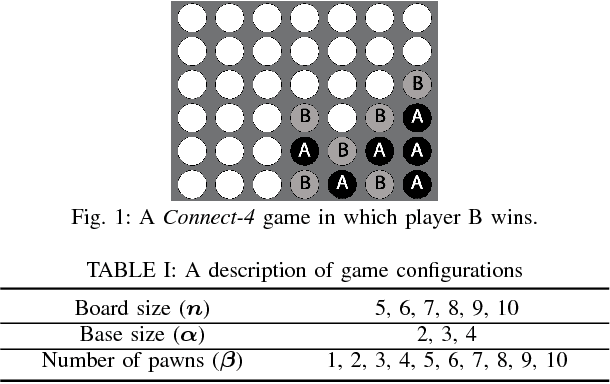
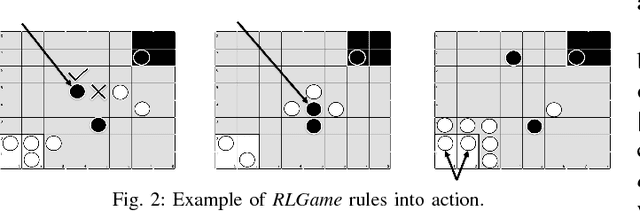
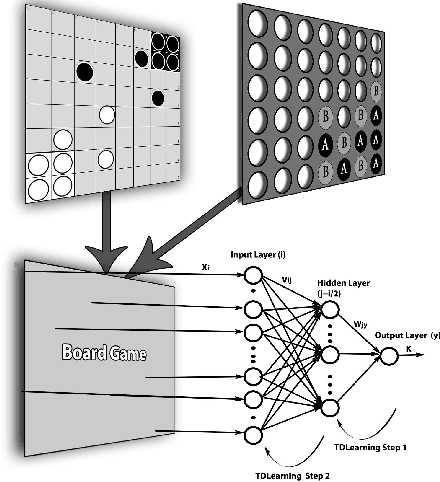
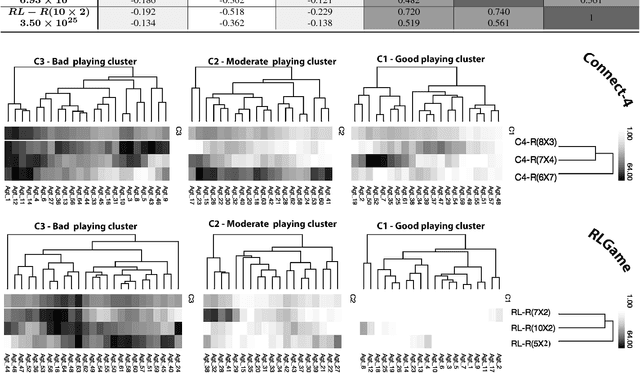
Abstract:Agent based simulation of social organizations, via the investigation of agents' training and learning tactics and strategies, has been inspired by the ability of humans to learn from social environments which are rich in agents, interactions and partial or hidden information. Such richness is a source of complexity that an effective learner has to be able to navigate. This paper focuses on the investigation of the impact of the environmental complexity on the game playing-and-learning behavior of synthetic agents. We demonstrate our approach using two independent turn-based zero-sum games as the basis of forming social events which are characterized both by competition and cooperation. The paper's key highlight is that as the complexity of a social environment changes, an effective player has to adapt its learning and playing profile to maintain a given performance profile
Efficiency and complexity of price competition among single-product vendors
Mar 06, 2017
Abstract:Motivated by recent progress on pricing in the AI literature, we study marketplaces that contain multiple vendors offering identical or similar products and unit-demand buyers with different valuations on these vendors. The objective of each vendor is to set the price of its product to a fixed value so that its profit is maximized. The profit depends on the vendor's price itself and the total volume of buyers that find the particular price more attractive than the price of the vendor's competitors. We model the behaviour of buyers and vendors as a two-stage full-information game and study a series of questions related to the existence, efficiency (price of anarchy) and computational complexity of equilibria in this game. To overcome situations where equilibria do not exist or exist but are highly inefficient, we consider the scenario where some of the vendors are subsidized in order to keep prices low and buyers highly satisfied.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge