Pablo Monteagudo-Lago
MixQuant: Pushing the Limits of Block Rotations in Post-Training Quantization
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:Recent post-training quantization (PTQ) methods have adopted block rotations to diffuse outliers prior to rounding. While this reduces the overhead of full-vector rotations, the effect of block structure on outlier suppression remains poorly understood. To fill this gap, we present the first systematic, non-asymptotic analysis of outlier suppression for block Hadamard rotations. Our analysis reveals that outlier suppression is fundamentally limited by the geometry of the input vector. In particular, post-rotation outliers are deterministically minimized when the pre-rotation $\ell_1$ norm mass is evenly distributed across blocks. Guided by these insights, we introduce MixQuant, a block rotation-aware PTQ framework that redistributes activation mass via permutations prior to rotation. We propose a greedy mass diffusion algorithm to calibrate permutations by equalizing the expected blockwise $\ell_1$ norms. To avoid adding inference overhead, we identify permutation-equivariant regions in transformer architectures to merge the resulting permutations into model weights before deployment. Experiments show that MixQuant consistently improves accuracy across all block sizes, recovering up to 90% of the full-vector rotation perplexity when quantizing Llama3 1B to INT4 with block size 16, compared to 46% without permutations.
Encoder-Decoder Model for Suffix Prediction in Predictive Monitoring
Nov 29, 2022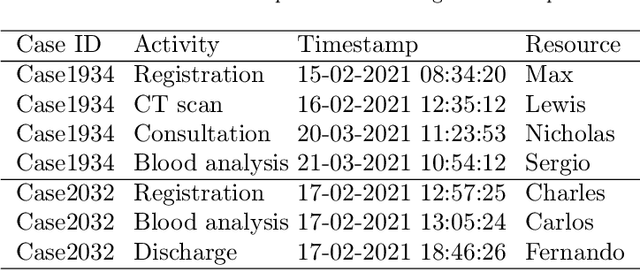
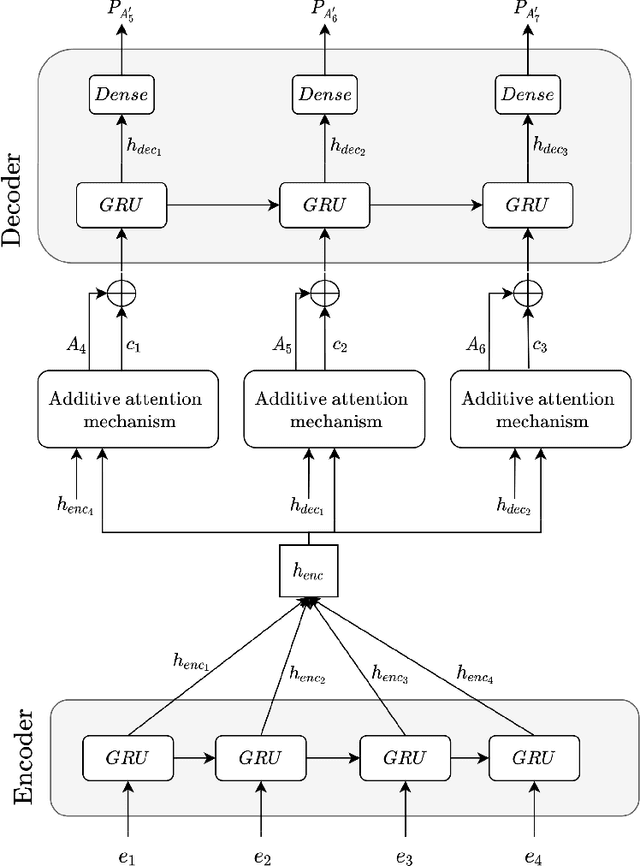
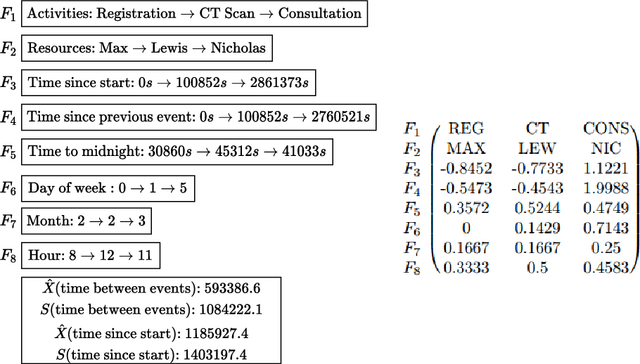
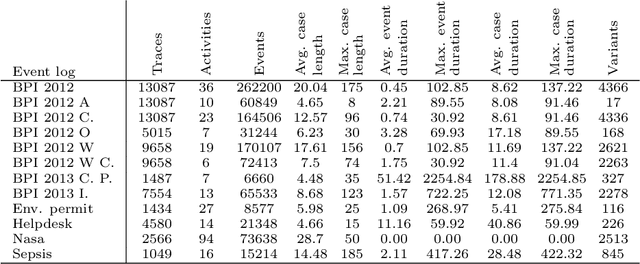
Abstract:Predictive monitoring is a subfield of process mining that aims to predict how a running case will unfold in the future. One of its main challenges is forecasting the sequence of activities that will occur from a given point in time -- suffix prediction -- . Most approaches to the suffix prediction problem learn to predict the suffix by learning how to predict the next activity only, not learning from the whole suffix during the training phase. This paper proposes a novel architecture based on an encoder-decoder model with an attention mechanism that decouples the representation learning of the prefixes from the inference phase, predicting only the activities of the suffix. During the inference phase, this architecture is extended with a heuristic search algorithm that improves the selection of the activity for each index of the suffix. Our approach has been tested using 12 public event logs against 6 different state-of-the-art proposals, showing that it significantly outperforms these proposals.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge