Olivier deVel
Improving Ensemble Robustness by Collaboratively Promoting and Demoting Adversarial Robustness
Sep 21, 2020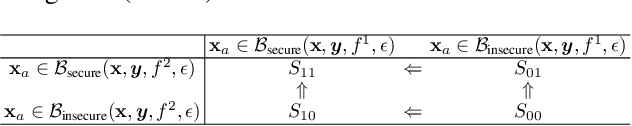
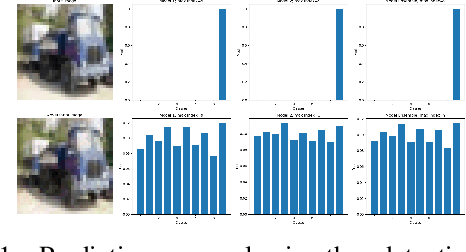
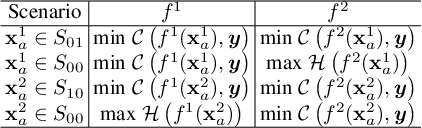
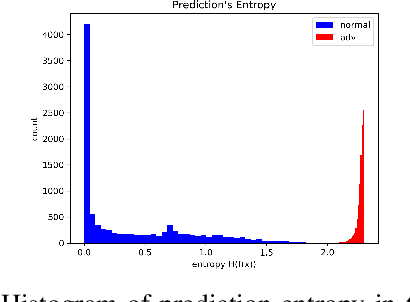
Abstract:Ensemble-based adversarial training is a principled approach to achieve robustness against adversarial attacks. An important technique of this approach is to control the transferability of adversarial examples among ensemble members. We propose in this work a simple yet effective strategy to collaborate among committee models of an ensemble model. This is achieved via the secure and insecure sets defined for each model member on a given sample, hence help us to quantify and regularize the transferability. Consequently, our proposed framework provides the flexibility to reduce the adversarial transferability as well as to promote the diversity of ensemble members, which are two crucial factors for better robustness in our ensemble approach. We conduct extensive and comprehensive experiments to demonstrate that our proposed method outperforms the state-of-the-art ensemble baselines, at the same time can detect a wide range of adversarial examples with a nearly perfect accuracy.
Improving Adversarial Robustness by Enforcing Local and Global Compactness
Jul 10, 2020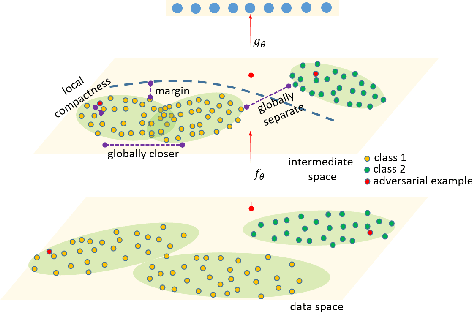
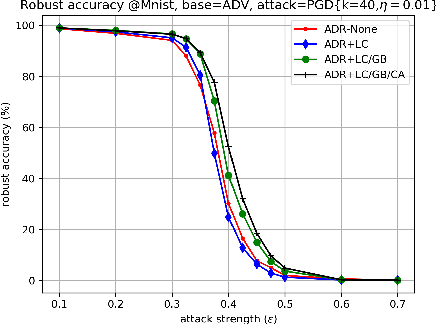
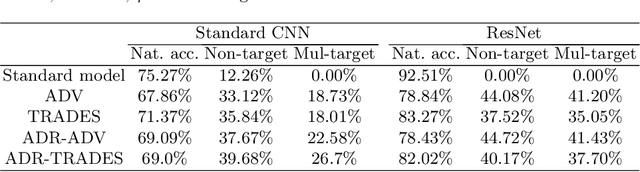
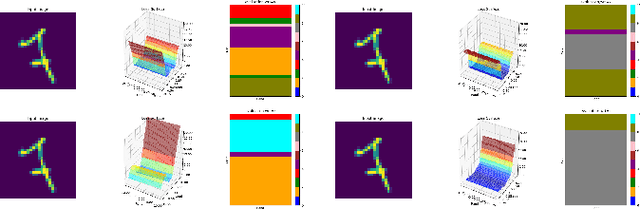
Abstract:The fact that deep neural networks are susceptible to crafted perturbations severely impacts the use of deep learning in certain domains of application. Among many developed defense models against such attacks, adversarial training emerges as the most successful method that consistently resists a wide range of attacks. In this work, based on an observation from a previous study that the representations of a clean data example and its adversarial examples become more divergent in higher layers of a deep neural net, we propose the Adversary Divergence Reduction Network which enforces local/global compactness and the clustering assumption over an intermediate layer of a deep neural network. We conduct comprehensive experiments to understand the isolating behavior of each component (i.e., local/global compactness and the clustering assumption) and compare our proposed model with state-of-the-art adversarial training methods. The experimental results demonstrate that augmenting adversarial training with our proposed components can further improve the robustness of the network, leading to higher unperturbed and adversarial predictive performances.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge