Oliver Y. Feng
Learning the score under shape constraints
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Score estimation has recently emerged as a key modern statistical challenge, due to its pivotal role in generative modelling via diffusion models. Moreover, it is an essential ingredient in a new approach to linear regression via convex $M$-estimation, where the corresponding error densities are projected onto the log-concave class. Motivated by these applications, we study the minimax risk of score estimation with respect to squared $L^2(P_0)$-loss, where $P_0$ denotes an underlying log-concave distribution on $\mathbb{R}$. Such distributions have decreasing score functions, but on its own, this shape constraint is insufficient to guarantee a finite minimax risk. We therefore define subclasses of log-concave densities that capture two fundamental aspects of the estimation problem. First, we establish the crucial impact of tail behaviour on score estimation by determining the minimax rate over a class of log-concave densities whose score function exhibits controlled growth relative to the quantile levels. Second, we explore the interplay between smoothness and log-concavity by considering the class of log-concave densities with a scale restriction and a $(β,L)$-Hölder assumption on the log-density for some $β\in [1,2]$. We show that the minimax risk over this latter class is of order $L^{2/(2β+1)}n^{-β/(2β+1)}$ up to poly-logarithmic factors, where $n$ denotes the sample size. When $β< 2$, this rate is faster than could be obtained under either the shape constraint or the smoothness assumption alone. Our upper bounds are attained by a locally adaptive, multiscale estimator constructed from a uniform confidence band for the score function. This study highlights intriguing differences between the score estimation and density estimation problems over this shape-constrained class.
Optimal convex $M$-estimation via score matching
Mar 25, 2024
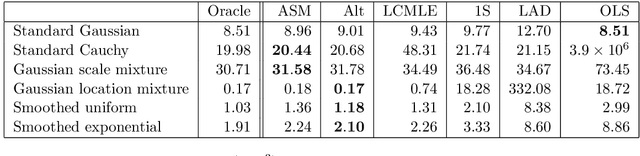

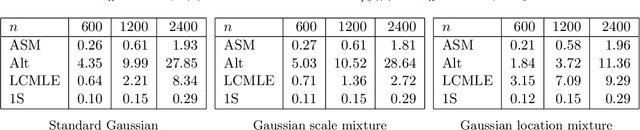
Abstract:In the context of linear regression, we construct a data-driven convex loss function with respect to which empirical risk minimisation yields optimal asymptotic variance in the downstream estimation of the regression coefficients. Our semiparametric approach targets the best decreasing approximation of the derivative of the log-density of the noise distribution. At the population level, this fitting process is a nonparametric extension of score matching, corresponding to a log-concave projection of the noise distribution with respect to the Fisher divergence. The procedure is computationally efficient, and we prove that our procedure attains the minimal asymptotic covariance among all convex $M$-estimators. As an example of a non-log-concave setting, for Cauchy errors, the optimal convex loss function is Huber-like, and our procedure yields an asymptotic efficiency greater than 0.87 relative to the oracle maximum likelihood estimator of the regression coefficients that uses knowledge of this error distribution; in this sense, we obtain robustness without sacrificing much efficiency. Numerical experiments confirm the practical merits of our proposal.
A unifying tutorial on Approximate Message Passing
May 05, 2021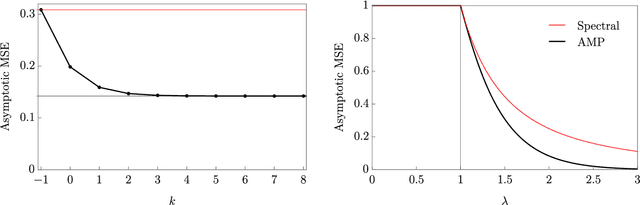

Abstract:Over the last decade or so, Approximate Message Passing (AMP) algorithms have become extremely popular in various structured high-dimensional statistical problems. The fact that the origins of these techniques can be traced back to notions of belief propagation in the statistical physics literature lends a certain mystique to the area for many statisticians. Our goal in this work is to present the main ideas of AMP from a statistical perspective, to illustrate the power and flexibility of the AMP framework. Along the way, we strengthen and unify many of the results in the existing literature.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge