Nurul H. Mahmood
6G Resilience -- White Paper
Sep 10, 2025
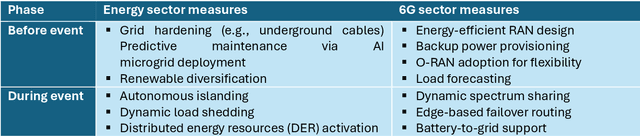


Abstract:6G must be designed to withstand, adapt to, and evolve amid prolonged, complex disruptions. Mobile networks' shift from efficiency-first to sustainability-aware has motivated this white paper to assert that resilience is a primary design goal, alongside sustainability and efficiency, encompassing technology, architecture, and economics. We promote resilience by analysing dependencies between mobile networks and other critical systems, such as energy, transport, and emergency services, and illustrate how cascading failures spread through infrastructures. We formalise resilience using the 3R framework: reliability, robustness, resilience. Subsequently, we translate this into measurable capabilities: graceful degradation, situational awareness, rapid reconfiguration, and learning-driven improvement and recovery. Architecturally, we promote edge-native and locality-aware designs, open interfaces, and programmability to enable islanded operations, fallback modes, and multi-layer diversity (radio, compute, energy, timing). Key enablers include AI-native control loops with verifiable behaviour, zero-trust security rooted in hardware and supply-chain integrity, and networking techniques that prioritise critical traffic, time-sensitive flows, and inter-domain coordination. Resilience also has a techno-economic aspect: open platforms and high-quality complementors generate ecosystem externalities that enhance resilience while opening new markets. We identify nine business-model groups and several patterns aligned with the 3R objectives, and we outline governance and standardisation. This white paper serves as an initial step and catalyst for 6G resilience. It aims to inspire researchers, professionals, government officials, and the public, providing them with the essential components to understand and shape the development of 6G resilience.
On the Robustness of RSMA to Adversarial BD-RIS-Induced Interference
May 26, 2025Abstract:This article investigates the robustness of rate-splitting multiple access (RSMA) in multi-user multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems to interference attacks against channel acquisition induced by beyond-diagonal RISs (BD-RISs). Two primary attack strategies, random and aligned interference, are proposed for fully connected and group-connected BD-RIS architectures. Valid random reflection coefficients are generated exploiting the Takagi factorization, while potent aligned interference attacks are achieved through optimization strategies based on a quadratically constrained quadratic program (QCQP) reformulation followed by projections onto the unitary manifold. Our numerical findings reveal that, when perfect channel state information (CSI) is available, RSMA behaves similarly to space-division multiple access (SDMA) and thus is highly susceptible to the attack, with BD-RIS inducing severe performance loss and significantly outperforming diagonal RIS. However, under imperfect CSI, RSMA consistently demonstrates significantly greater robustness than SDMA, particularly as the system's transmit power increases.
A Deep-Unfolding Approach to RIS Phase Shift Optimization Via Transformer-Based Channel Prediction
Feb 25, 2025Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs) have emerged as a promising solution that can provide dynamic control over the propagation of electromagnetic waves. The RIS technology is envisioned as a key enabler of sixth-generation networks by offering the ability to adaptively manipulate signal propagation through the smart configuration of its phase shift coefficients, thereby optimizing signal strength, coverage, and capacity. However, the realization of this technology's full potential hinges on the accurate acquisition of channel state information (CSI). In this paper, we propose an efficient CSI prediction framework for a RIS-assisted communication system based on the machine learning (ML) transformer architecture. Architectural modifications are introduced to the vanilla transformer for multivariate time series forecasting to achieve high prediction accuracy. The predicted channel coefficients are then used to optimize the RIS phase shifts. Simulation results present a comprehensive analysis of key performance metrics, including data rate and outage probability. Our results confirm the effectiveness of the proposed ML approach and demonstrate its superiority over other baseline ML-based CSI prediction schemes such as conventional deep neural networks and long short-term memory architectures, albeit at the cost of slightly increased complexity.
* Accepted for Scandinavian Simulation Society(SIMS) EUROSIM 2024
Beyond Diagonal RIS for Multi-Band Multi-Cell MIMO Networks: A Practical Frequency-Dependent Model and Performance Analysis
Jan 12, 2024



Abstract:This paper delves into the unexplored frequency-dependent characteristics of beyond diagonal reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (BD-RISs). A generalized practical frequency-dependent reflection model is proposed as a fundamental framework for configuring fully-connected and group-connected RISs in a multi-band multi-base station (BS) multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) network. Leveraging this practical model, multi-objective optimization strategies are formulated to maximize the received power at multiple users connected to different BSs, each operating under a distinct carrier frequency. By relying on matrix theory and exploiting the symmetric structure of the reflection matrices inherent to BD-RISs, closed-form relaxed solutions for the challenging optimization problems are derived. The ideal solutions are then combined with codebook-based approaches to configure the practical capacitance values for the BD-RISs. Simulation results reveal the frequency-dependent behaviors of different RIS architectures and demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed schemes. Notably, BD-RISs exhibit superior resilience to frequency deviations compared to conventional single-connected RISs. Moreover, the proposed optimization approaches prove effective in enabling the targeted operation of BD-RISs across one or more carrier frequencies. The results also shed light on the potential for harmful interference in the absence of proper synchronization between RISs and adjacent BSs.
Reconfigurable Intelligent Surfaces: The New Frontier of Next G Security
Dec 09, 2022



Abstract:RIS is one of the significant technological advancements that will mark next-generation wireless. RIS technology also opens up the possibility of new security threats, since the reflection of impinging signals can be used for malicious purposes. This article introduces the basic concept for a RIS-assisted attack that re-uses the legitimate signal towards a malicious objective. Specific attacks are identified from this base scenario, and the RIS-assisted signal cancellation attack is selected for evaluation as an attack that inherently exploits RIS capabilities. The key takeaway from the evaluation is that an effective attack requires accurate channel information, a RIS deployed in a favorable location (from the point of view of the attacker), and it disproportionately affects legitimate links that already suffer from reduced path loss. These observations motivate specific security solutions and recommendations for future work.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge