Numan Khurshid
Cross-View Image Retrieval -- Ground to Aerial Image Retrieval through Deep Learning
May 02, 2020


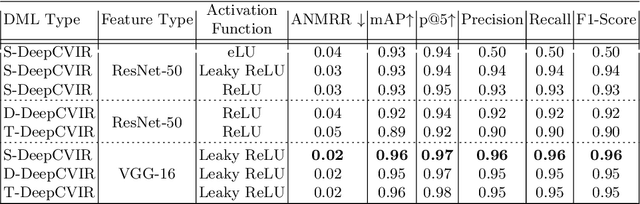
Abstract:Cross-modal retrieval aims to measure the content similarity between different types of data. The idea has been previously applied to visual, text, and speech data. In this paper, we present a novel cross-modal retrieval method specifically for multi-view images, called Cross-view Image Retrieval CVIR. Our approach aims to find a feature space as well as an embedding space in which samples from street-view images are compared directly to satellite-view images (and vice-versa). For this comparison, a novel deep metric learning based solution "DeepCVIR" has been proposed. Previous cross-view image datasets are deficient in that they (1) lack class information; (2) were originally collected for cross-view image geolocalization task with coupled images; (3) do not include any images from off-street locations. To train, compare, and evaluate the performance of cross-view image retrieval, we present a new 6 class cross-view image dataset termed as CrossViewRet which comprises of images including freeway, mountain, palace, river, ship, and stadium with 700 high-resolution dual-view images for each class. Results show that the proposed DeepCVIR outperforms conventional matching approaches on the CVIR task for the given dataset and would also serve as the baseline for future research.
Patch-based Generative Adversarial Network Towards Retinal Vessel Segmentation
Dec 22, 2019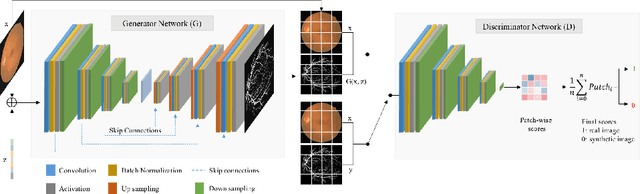
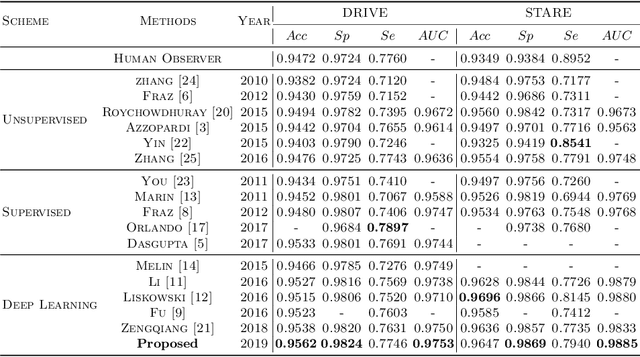
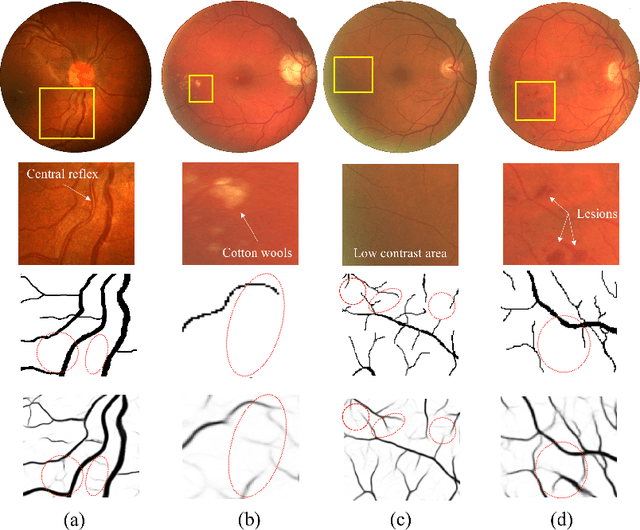
Abstract:Retinal blood vessels are considered to be the reliable diagnostic biomarkers of ophthalmologic and diabetic retinopathy. Monitoring and diagnosis totally depends on expert analysis of both thin and thick retinal vessels which has recently been carried out by various artificial intelligent techniques. Existing deep learning methods attempt to segment retinal vessels using a unified loss function optimized for both thin and thick vessels with equal importance. Due to variable thickness, biased distribution, and difference in spatial features of thin and thick vessels, unified loss function are more influential towards identification of thick vessels resulting in weak segmentation. To address this problem, a conditional patch-based generative adversarial network is proposed which utilizes a generator network and a patch-based discriminator network conditioned on the sample data with an additional loss function to learn both thin and thick vessels. Experiments are conducted on publicly available STARE and DRIVE datasets which show that the proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art methods.
Tiny-Inception-ResNet-v2: Using Deep Learning for Eliminating Bonded Labors of Brick Kilns in South Asia
Jul 12, 2019
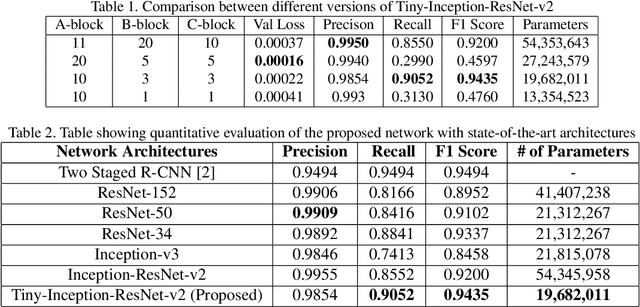
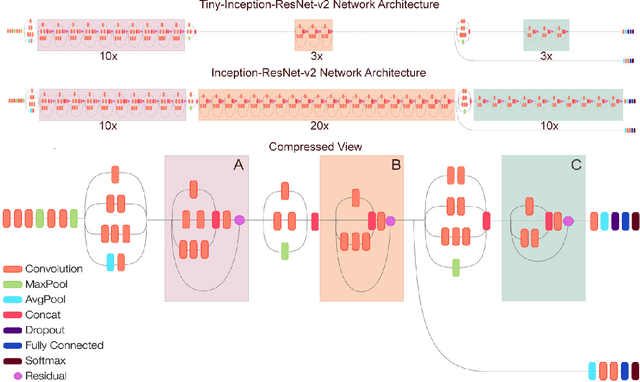
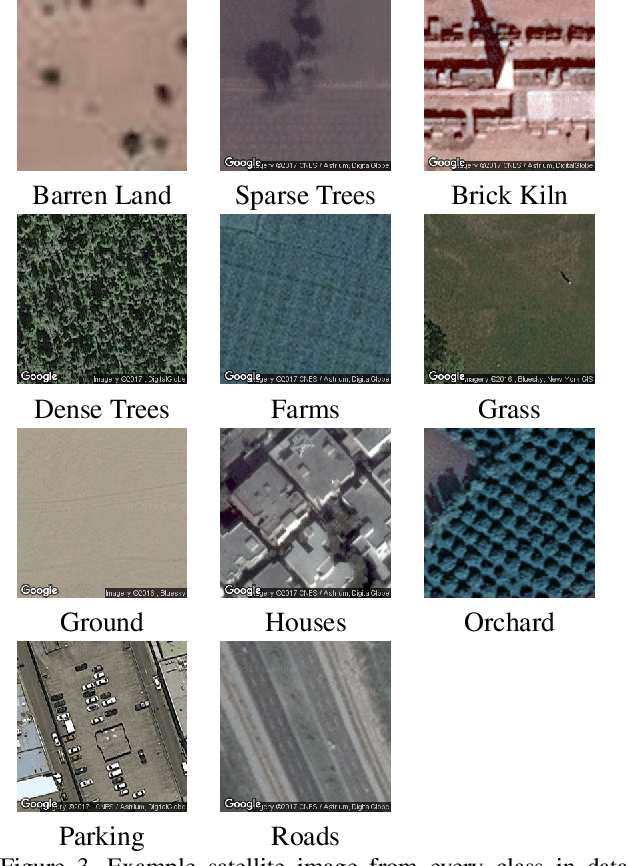
Abstract:This paper proposes to employ a Inception-ResNet inspired deep learning architecture called Tiny-Inception-ResNet-v2 to eliminate bonded labor by identifying brick kilns within "Brick-Kiln-Belt" of South Asia. The framework is developed by training a network on the satellite imagery consisting of 11 different classes of South Asian region. The dataset developed during the process includes the geo-referenced images of brick kilns, houses, roads, tennis courts, farms, sparse trees, dense trees, orchards, parking lots, parks and barren lands. The dataset is made publicly available for further research. Our proposed network architecture with very fewer learning parameters outperforms all state-of-the-art architectures employed for recognition of brick kilns. Our proposed solution would enable regional monitoring and evaluation mechanisms for the Sustainable Development Goals.
Unsupervised Deep Features for Remote Sensing Image Matching via Discriminator Network
Oct 15, 2018


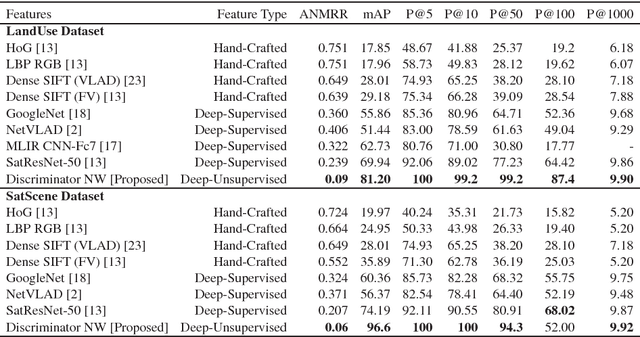
Abstract:The advent of deep perceptual networks brought about a paradigm shift in machine vision and image perception. Image apprehension lately carried out by hand-crafted features in the latent space have been replaced by deep features acquired from supervised networks for improved understanding. However, such deep networks require strict supervision with a substantial amount of the labeled data for authentic training process. These methods perform poorly in domains lacking labeled data especially in case of remote sensing image retrieval. Resolving this, we propose an unsupervised encoder-decoder feature for remote sensing image matching (RSIM). Moreover, we replace the conventional distance metrics with a deep discriminator network to identify the similarity of the image pairs. To the best of our knowledge, discriminator network has never been used before for solving RSIM problem. Results have been validated with two publicly available benchmark remote sensing image datasets. The technique has also been investigated for content-based remote sensing image retrieval (CBRSIR); one of the widely used applications of RSIM. Results demonstrate that our technique supersedes the state-of-the-art methods used for unsupervised image matching with mean average precision (mAP) of 81%, and image retrieval with an overall improvement in mAP score of about 12%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge