Mohbat Tharani
Attention Neural Network for Trash Detection on Water Channels
Jul 09, 2020
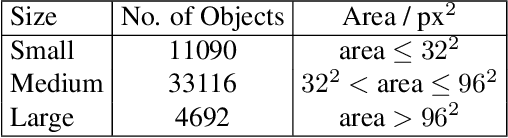

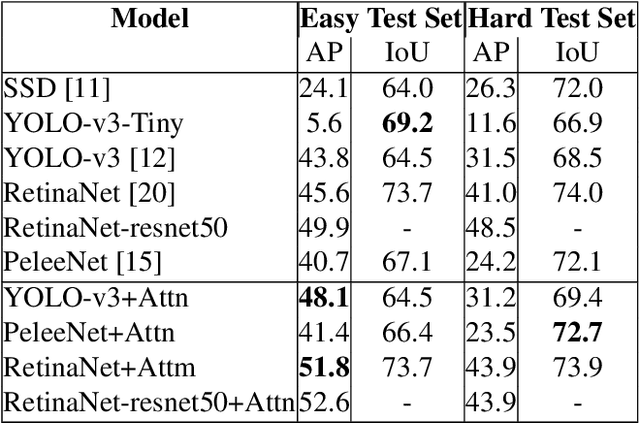
Abstract:Rivers and canals flowing through cities are often used illegally for dumping the trash. This contaminates freshwater channels as well as causes blockage in sewerage resulting in urban flooding. When this contaminated water reaches agricultural fields, it results in degradation of soil and poses critical environmental as well as economic threats. The dumped trash is often found floating on the water surface. The trash could be disfigured, partially submerged, decomposed into smaller pieces, clumped together with other objects which obscure its shape and creates a challenging detection problem. This paper proposes a method for the detection of visible trash floating on the water surface of the canals in urban areas. We also provide a large dataset, first of its kind, trash in water channels that contains object-level annotations. A novel attention layer is proposed that improves the detection of smaller objects. Towards the end of this paper, we provide a detailed comparison of our method with state-of-the-art object detectors and show that our method significantly improves the detection of smaller objects. The dataset will be made publicly available.
Cross-View Image Retrieval -- Ground to Aerial Image Retrieval through Deep Learning
May 02, 2020


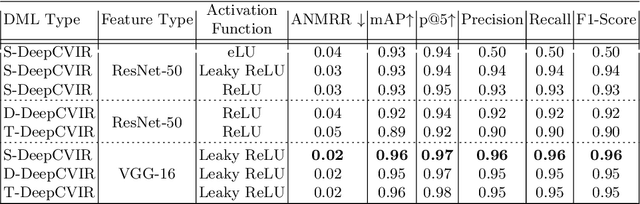
Abstract:Cross-modal retrieval aims to measure the content similarity between different types of data. The idea has been previously applied to visual, text, and speech data. In this paper, we present a novel cross-modal retrieval method specifically for multi-view images, called Cross-view Image Retrieval CVIR. Our approach aims to find a feature space as well as an embedding space in which samples from street-view images are compared directly to satellite-view images (and vice-versa). For this comparison, a novel deep metric learning based solution "DeepCVIR" has been proposed. Previous cross-view image datasets are deficient in that they (1) lack class information; (2) were originally collected for cross-view image geolocalization task with coupled images; (3) do not include any images from off-street locations. To train, compare, and evaluate the performance of cross-view image retrieval, we present a new 6 class cross-view image dataset termed as CrossViewRet which comprises of images including freeway, mountain, palace, river, ship, and stadium with 700 high-resolution dual-view images for each class. Results show that the proposed DeepCVIR outperforms conventional matching approaches on the CVIR task for the given dataset and would also serve as the baseline for future research.
Teacher-Class Network: A Neural Network Compression Mechanism
Apr 07, 2020



Abstract:To solve the problem of the overwhelming size of Deep Neural Networks (DNN) several compression schemes have been proposed, one of them is teacher-student. Teacher-student tries to transfer knowledge from a complex teacher network to a simple student network. In this paper, we propose a novel method called a teacher-class network consisting of a single teacher and multiple student networks (i.e. class of students). Instead of transferring knowledge to one student only, the proposed method transfers a chunk of knowledge about the entire solution to each student. Our students are not trained for problem-specific logits, they are trained to mimic knowledge (dense representation) learned by the teacher network. Thus unlike the logits-based single student approach, the combined knowledge learned by the class of students can be used to solve other problems as well. These students can be designed to satisfy a given budget, e.g. for comparative purposes we kept the collective parameters of all the students less than or equivalent to that of a single student in the teacher-student approach . These small student networks are trained independently, making it possible to train and deploy models on memory deficient devices as well as on parallel processing systems such as data centers. The proposed teacher-class architecture is evaluated on several benchmark datasets including MNIST, FashionMNIST, IMDB Movie Reviews and CAMVid on multiple tasks including classification, sentiment classification and segmentation. Our approach outperforms the state-of-the-art single student approach in terms of accuracy as well as computational cost and in many cases it achieves an accuracy equivalent to the teacher network while having 10-30 times fewer parameters.
Unsupervised Deep Features for Remote Sensing Image Matching via Discriminator Network
Oct 15, 2018


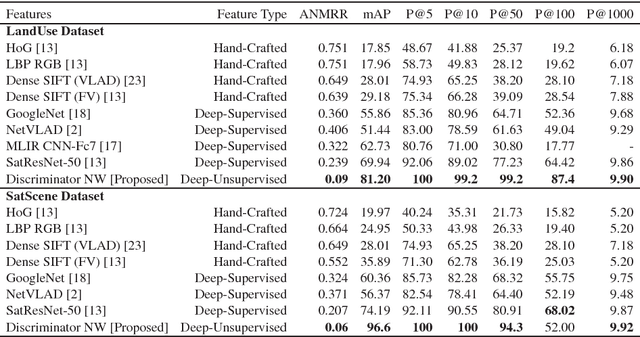
Abstract:The advent of deep perceptual networks brought about a paradigm shift in machine vision and image perception. Image apprehension lately carried out by hand-crafted features in the latent space have been replaced by deep features acquired from supervised networks for improved understanding. However, such deep networks require strict supervision with a substantial amount of the labeled data for authentic training process. These methods perform poorly in domains lacking labeled data especially in case of remote sensing image retrieval. Resolving this, we propose an unsupervised encoder-decoder feature for remote sensing image matching (RSIM). Moreover, we replace the conventional distance metrics with a deep discriminator network to identify the similarity of the image pairs. To the best of our knowledge, discriminator network has never been used before for solving RSIM problem. Results have been validated with two publicly available benchmark remote sensing image datasets. The technique has also been investigated for content-based remote sensing image retrieval (CBRSIR); one of the widely used applications of RSIM. Results demonstrate that our technique supersedes the state-of-the-art methods used for unsupervised image matching with mean average precision (mAP) of 81%, and image retrieval with an overall improvement in mAP score of about 12%.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge