Noriko Takemura
Enhancing Ambiguous Dynamic Facial Expression Recognition with Soft Label-based Data Augmentation
Jun 25, 2025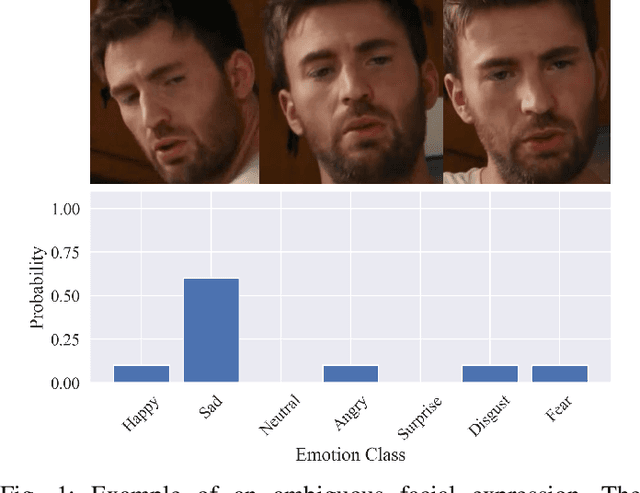
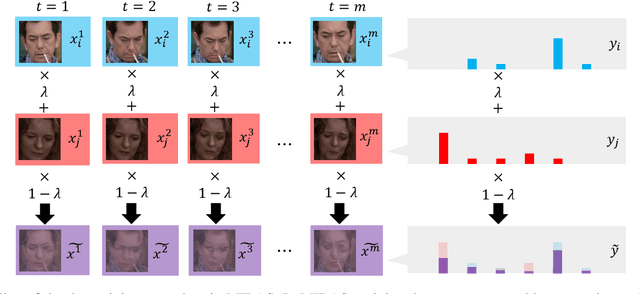
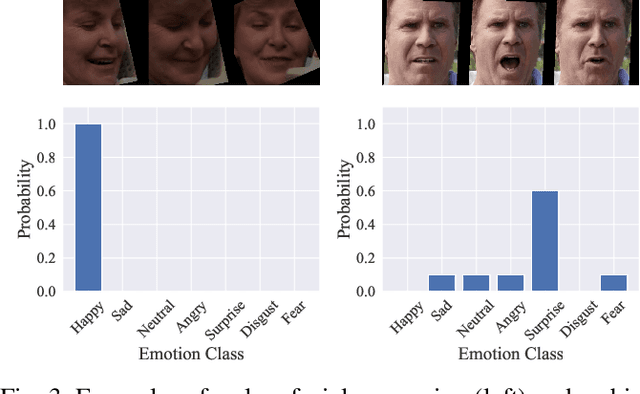
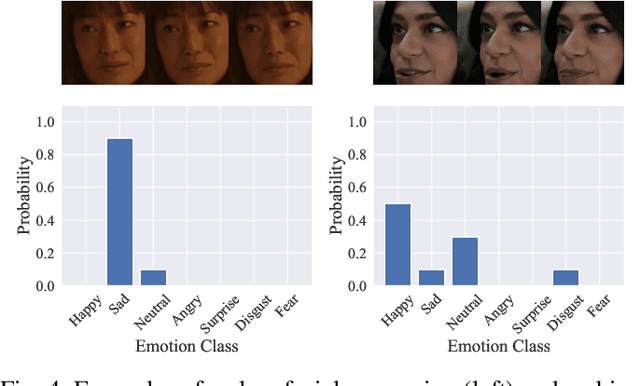
Abstract:Dynamic facial expression recognition (DFER) is a task that estimates emotions from facial expression video sequences. For practical applications, accurately recognizing ambiguous facial expressions -- frequently encountered in in-the-wild data -- is essential. In this study, we propose MIDAS, a data augmentation method designed to enhance DFER performance for ambiguous facial expression data using soft labels representing probabilities of multiple emotion classes. MIDAS augments training data by convexly combining pairs of video frames and their corresponding emotion class labels. This approach extends mixup to soft-labeled video data, offering a simple yet highly effective method for handling ambiguity in DFER. To evaluate MIDAS, we conducted experiments on both the DFEW dataset and FERV39k-Plus, a newly constructed dataset that assigns soft labels to an existing DFER dataset. The results demonstrate that models trained with MIDAS-augmented data achieve superior performance compared to the state-of-the-art method trained on the original dataset.
DRIV100: In-The-Wild Multi-Domain Dataset and Evaluation for Real-World Domain Adaptation of Semantic Segmentation
Feb 25, 2021
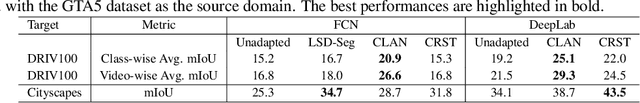

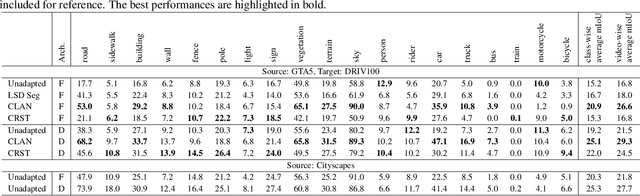
Abstract:Together with the recent advances in semantic segmentation, many domain adaptation methods have been proposed to overcome the domain gap between training and deployment environments. However, most previous studies use limited combinations of source/target datasets, and domain adaptation techniques have never been thoroughly evaluated in a more challenging and diverse set of target domains. This work presents a new multi-domain dataset DRIV100 for benchmarking domain adaptation techniques on in-the-wild road-scene videos collected from the Internet. The dataset consists of pixel-level annotations for 100 videos selected to cover diverse scenes/domains based on two criteria; human subjective judgment and an anomaly score judged using an existing road-scene dataset. We provide multiple manually labeled ground-truth frames for each video, enabling a thorough evaluation of video-level domain adaptation where each video independently serves as the target domain. Using the dataset, we quantify domain adaptation performances of state-of-the-art methods and clarify the potential and novel challenges of domain adaptation techniques. The dataset is available at https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4389243.
Development of a Vertex Finding Algorithm using Recurrent Neural Network
Jan 28, 2021

Abstract:Deep learning is a rapidly-evolving technology with possibility to significantly improve physics reach of collider experiments. In this study we developed a novel algorithm of vertex finding for future lepton colliders such as the International Linear Collider. We deploy two networks; one is simple fully-connected layers to look for vertex seeds from track pairs, and the other is a customized Recurrent Neural Network with an attention mechanism and an encoder-decoder structure to associate tracks to the vertex seeds. The performance of the vertex finder is compared with the standard ILC reconstruction algorithm.
Procams-Based Cybernetics
Oct 09, 2015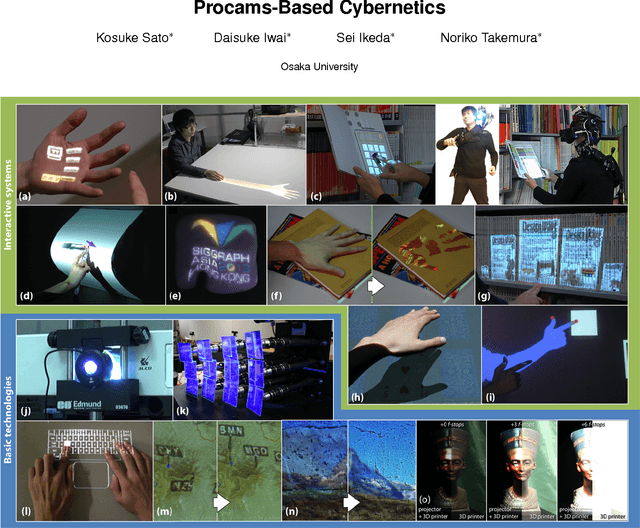

Abstract:Procams-based cybernetics is a unique, emerging research field, which aims at enhancing and supporting our activities by naturally connecting human and computers/machines as a cooperative integrated system via projector-camera systems (procams). It rests on various research domains such as virtual/augmented reality, computer vision, computer graphics, projection display, human computer interface, human robot interaction and so on. This laboratory presentation provides a brief history including recent achievements of our procams-based cybernetics project.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge