Ning Zou
Effects of Different Prompts on the Quality of GPT-4 Responses to Dementia Care Questions
Apr 05, 2024


Abstract:Evidence suggests that different prompts lead large language models (LLMs) to generate responses with varying quality. Yet, little is known about prompts' effects on response quality in healthcare domains. In this exploratory study, we address this gap, focusing on a specific healthcare domain: dementia caregiving. We first developed an innovative prompt template with three components: (1) system prompts (SPs) featuring 4 different roles; (2) an initialization prompt; and (3) task prompts (TPs) specifying different levels of details, totaling 12 prompt combinations. Next, we selected 3 social media posts containing complicated, real-world questions about dementia caregivers' challenges in 3 areas: memory loss and confusion, aggression, and driving. We then entered these posts into GPT-4, with our 12 prompts, to generate 12 responses per post, totaling 36 responses. We compared the word count of the 36 responses to explore potential differences in response length. Two experienced dementia care clinicians on our team assessed the response quality using a rating scale with 5 quality indicators: factual, interpretation, application, synthesis, and comprehensiveness (scoring range: 0-5; higher scores indicate higher quality).
User independent Emotion Recognition with Residual Signal-Image Network
Aug 10, 2019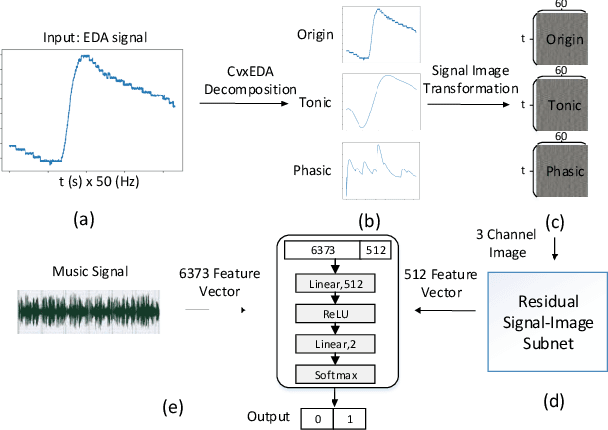
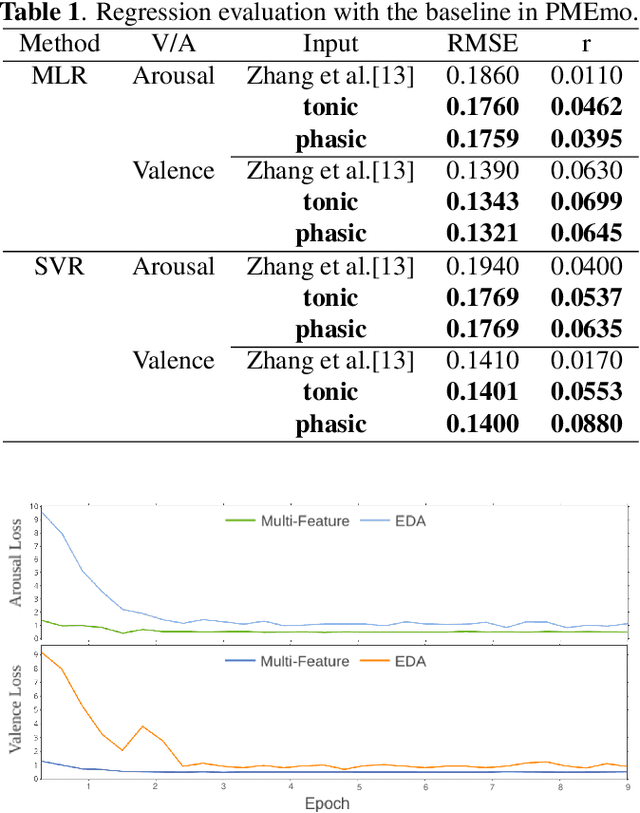
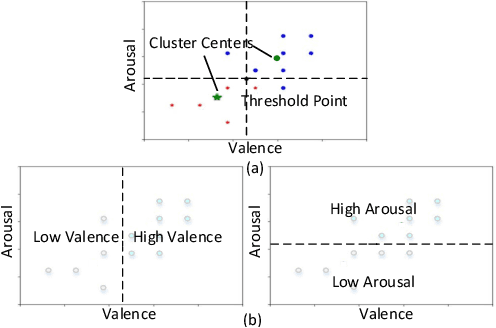
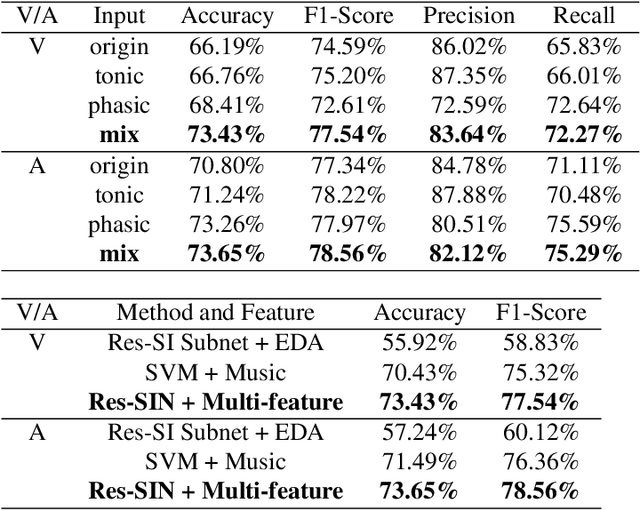
Abstract:User independent emotion recognition with large scale physiological signals is a tough problem. There exist many advanced methods but they are conducted under relatively small datasets with dozens of subjects. Here, we propose Res-SIN, a novel end-to-end framework using Electrodermal Activity(EDA) signal images to classify human emotion. We first apply convex optimization-based EDA (cvxEDA) to decompose signals and mine the static and dynamic emotion changes. Then, we transform decomposed signals to images so that they can be effectively processed by CNN frameworks. The Res-SIN combines individual emotion features and external emotion benchmarks to accelerate convergence. We evaluate our approach on the PMEmo dataset, the currently largest emotional dataset containing music and EDA signals. To the best of author's knowledge, our method is the first attempt to classify large scale subject-independent emotion with 7962 pieces of EDA signals from 457 subjects. Experimental results demonstrate the reliability of our model and the binary classification accuracy of 73.65% and 73.43% on arousal and valence dimension can be used as a baseline.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge