Nina Kerstin Wenke
Privacy-preserving Artificial Intelligence Techniques in Biomedicine
Jul 22, 2020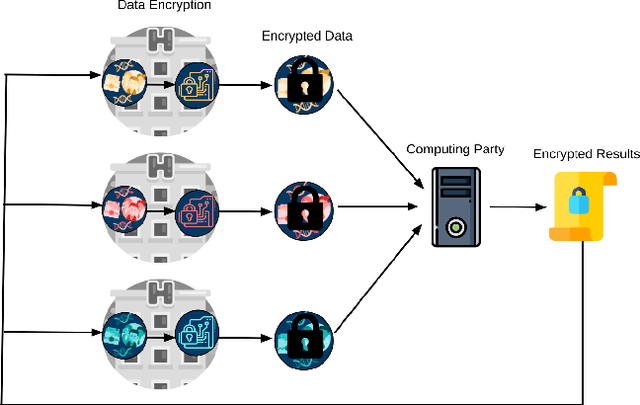
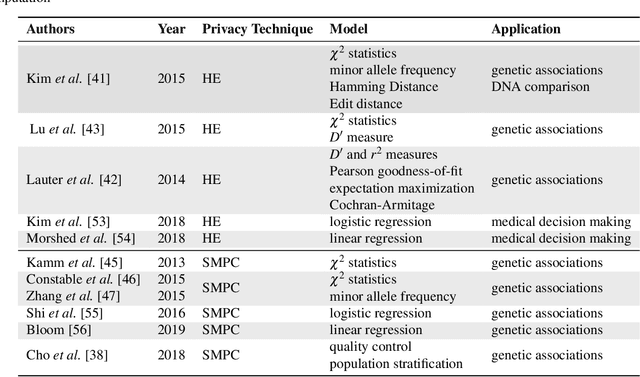
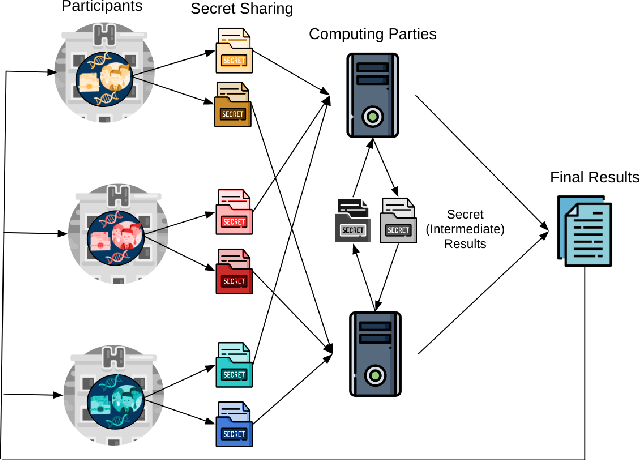
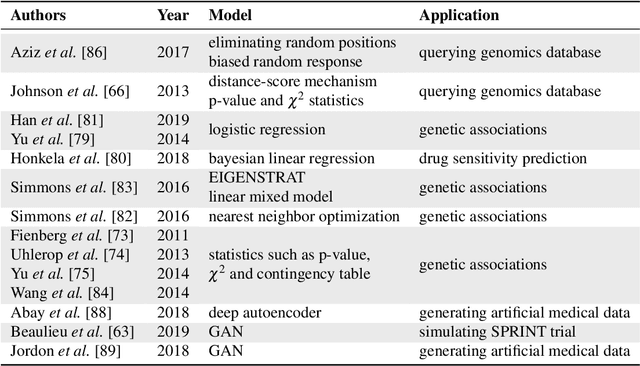
Abstract:Artificial intelligence (AI) has been successfully applied in numerous scientific domains including biomedicine and healthcare. Here, it has led to several breakthroughs ranging from clinical decision support systems, image analysis to whole genome sequencing. However, training an AI model on sensitive data raises also concerns about the privacy of individual participants. Adversary AIs, for example, can abuse even summary statistics of a study to determine the presence or absence of an individual in a given dataset. This has resulted in increasing restrictions to access biomedical data, which in turn is detrimental for collaborative research and impedes scientific progress. Hence there has been an explosive growth in efforts to harness the power of AI for learning from sensitive data while protecting patients' privacy. This paper provides a structured overview of recent advances in privacy-preserving AI techniques in biomedicine. It places the most important state-of-the-art approaches within a unified taxonomy, and discusses their strengths, limitations, and open problems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge