Nimrod Kruger
Optical Linear Systems Framework for Event Sensing and Computational Neuromorphic Imaging
Jan 20, 2026Abstract:Event vision sensors (neuromorphic cameras) output sparse, asynchronous ON/OFF events triggered by log-intensity threshold crossings, enabling microsecond-scale sensing with high dynamic range and low data bandwidth. As a nonlinear system, this event representation does not readily integrate with the linear forward models that underpin most computational imaging and optical system design. We present a physics-grounded processing pipeline that maps event streams to estimates of per-pixel log-intensity and intensity derivatives, and embeds these measurements in a dynamic linear systems model with a time-varying point spread function. This enables inverse filtering directly from event data, using frequency-domain Wiener deconvolution with a known (or parameterised) dynamic transfer function. We validate the approach in simulation for single and overlapping point sources under modulated defocus, and on real event data from a tunable-focus telescope imaging a star field, demonstrating source localisation and separability. The proposed framework provides a practical bridge between event sensing and model-based computational imaging for dynamic optical systems.
Seeing like a Cephalopod: Colour Vision with a Monochrome Event Camera
Apr 15, 2025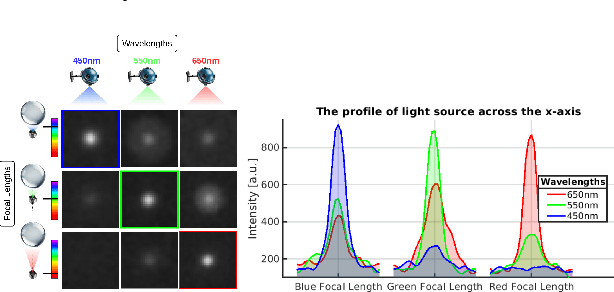
Abstract:Cephalopods exhibit unique colour discrimination capabilities despite having one type of photoreceptor, relying instead on chromatic aberration induced by their ocular optics and pupil shapes to perceive spectral information. We took inspiration from this biological mechanism to design a spectral imaging system that combines a ball lens with an event-based camera. Our approach relies on a motorised system that shifts the focal position, mirroring the adaptive lens motion in cephalopods. This approach has enabled us to achieve wavelength-dependent focusing across the visible light and near-infrared spectrum, making the event a spectral sensor. We characterise chromatic aberration effects, using both event-based and conventional frame-based sensors, validating the effectiveness of bio-inspired spectral discrimination both in simulation and in a real setup as well as assessing the spectral discrimination performance. Our proposed approach provides a robust spectral sensing capability without conventional colour filters or computational demosaicing. This approach opens new pathways toward new spectral sensing systems inspired by nature's evolutionary solutions. Code and analysis are available at: https://samiarja.github.io/neuromorphic_octopus_eye/
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge