Nil Biescas
LayeredDoc: Domain Adaptive Document Restoration with a Layer Separation Approach
Jun 12, 2024



Abstract:The rapid evolution of intelligent document processing systems demands robust solutions that adapt to diverse domains without extensive retraining. Traditional methods often falter with variable document types, leading to poor performance. To overcome these limitations, this paper introduces a text-graphic layer separation approach that enhances domain adaptability in document image restoration (DIR) systems. We propose LayeredDoc, which utilizes two layers of information: the first targets coarse-grained graphic components, while the second refines machine-printed textual content. This hierarchical DIR framework dynamically adjusts to the characteristics of the input document, facilitating effective domain adaptation. We evaluated our approach both qualitatively and quantitatively using a new real-world dataset, LayeredDocDB, developed for this study. Initially trained on a synthetically generated dataset, our model demonstrates strong generalization capabilities for the DIR task, offering a promising solution for handling variability in real-world data. Our code is accessible on GitHub.
GeoContrastNet: Contrastive Key-Value Edge Learning for Language-Agnostic Document Understanding
May 06, 2024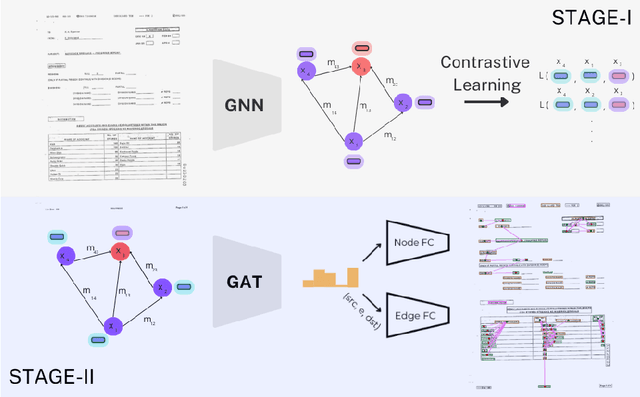
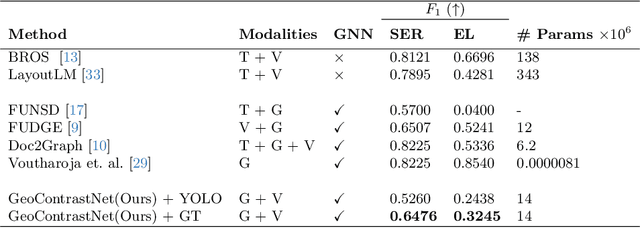
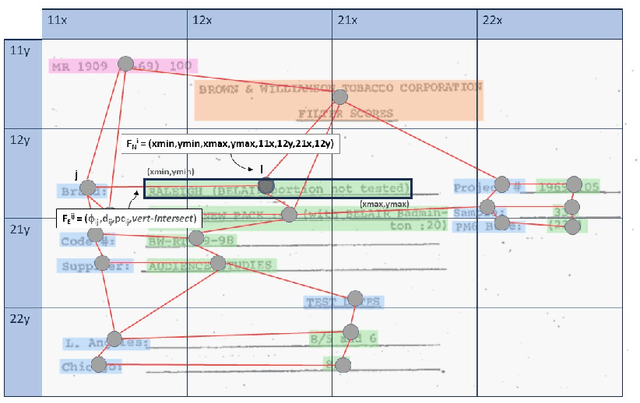
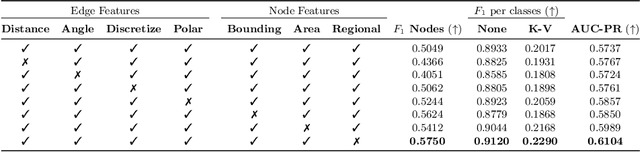
Abstract:This paper presents GeoContrastNet, a language-agnostic framework to structured document understanding (DU) by integrating a contrastive learning objective with graph attention networks (GATs), emphasizing the significant role of geometric features. We propose a novel methodology that combines geometric edge features with visual features within an overall two-staged GAT-based framework, demonstrating promising results in both link prediction and semantic entity recognition performance. Our findings reveal that combining both geometric and visual features could match the capabilities of large DU models that rely heavily on Optical Character Recognition (OCR) features in terms of performance accuracy and efficiency. This approach underscores the critical importance of relational layout information between the named text entities in a semi-structured layout of a page. Specifically, our results highlight the model's proficiency in identifying key-value relationships within the FUNSD dataset for forms and also discovering the spatial relationships in table-structured layouts for RVLCDIP business invoices. Our code and pretrained models will be accessible on our official GitHub.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge