Nikita Prabhu
A Taxonomy of Deep Convolutional Neural Nets for Computer Vision
Jan 25, 2016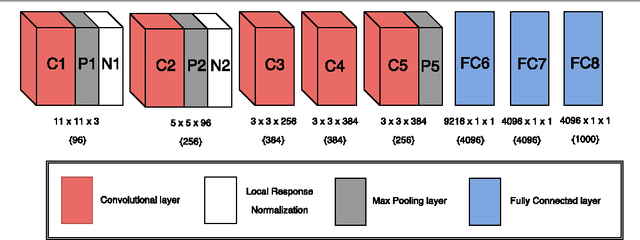
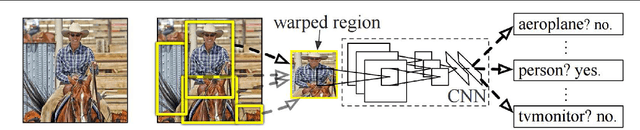
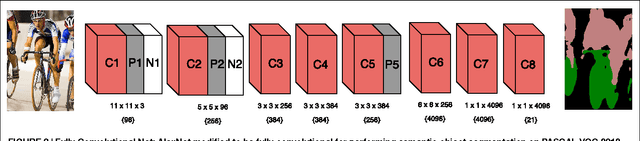
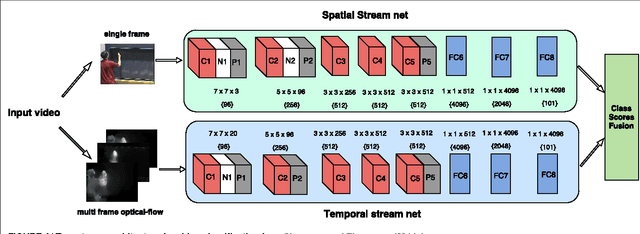
Abstract:Traditional architectures for solving computer vision problems and the degree of success they enjoyed have been heavily reliant on hand-crafted features. However, of late, deep learning techniques have offered a compelling alternative -- that of automatically learning problem-specific features. With this new paradigm, every problem in computer vision is now being re-examined from a deep learning perspective. Therefore, it has become important to understand what kind of deep networks are suitable for a given problem. Although general surveys of this fast-moving paradigm (i.e. deep-networks) exist, a survey specific to computer vision is missing. We specifically consider one form of deep networks widely used in computer vision - convolutional neural networks (CNNs). We start with "AlexNet" as our base CNN and then examine the broad variations proposed over time to suit different applications. We hope that our recipe-style survey will serve as a guide, particularly for novice practitioners intending to use deep-learning techniques for computer vision.
* Published in Frontiers in Robotics and AI (http://goo.gl/6691Bm)
Attribute-Graph: A Graph based approach to Image Ranking
Oct 08, 2015



Abstract:We propose a novel image representation, termed Attribute-Graph, to rank images by their semantic similarity to a given query image. An Attribute-Graph is an undirected fully connected graph, incorporating both local and global image characteristics. The graph nodes characterise objects as well as the overall scene context using mid-level semantic attributes, while the edges capture the object topology. We demonstrate the effectiveness of Attribute-Graphs by applying them to the problem of image ranking. We benchmark the performance of our algorithm on the 'rPascal' and 'rImageNet' datasets, which we have created in order to evaluate the ranking performance on complex queries containing multiple objects. Our experimental evaluation shows that modelling images as Attribute-Graphs results in improved ranking performance over existing techniques.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge