Nikhil Abhyankar
RUST-BENCH: Benchmarking LLM Reasoning on Unstructured Text within Structured Tables
Nov 06, 2025Abstract:Existing tabular reasoning benchmarks mostly test models on small, uniform tables, underrepresenting the complexity of real-world data and giving an incomplete view of Large Language Models' (LLMs) reasoning abilities. Real tables are long, heterogeneous, and domain-specific, mixing structured fields with free text and requiring multi-hop reasoning across thousands of tokens. To address this gap, we introduce RUST-BENCH, a benchmark of 7966 questions from 2031 real-world tables spanning two domains: i) RB-Science (NSF grant records) and ii) RB-Sports (NBA statistics). Unlike prior work, RUST-BENCH evaluates LLMs jointly across scale, heterogeneity, domain specificity, and reasoning complexity. Experiments with open-source and proprietary models show that LLMs struggle with heterogeneous schemas and complex multi-hop inference, revealing persistent weaknesses in current architectures and prompting strategies. RUST-BENCH establishes a challenging new testbed for advancing tabular reasoning research.
Accelerating Materials Design via LLM-Guided Evolutionary Search
Oct 26, 2025Abstract:Materials discovery requires navigating vast chemical and structural spaces while satisfying multiple, often conflicting, objectives. We present LLM-guided Evolution for MAterials design (LLEMA), a unified framework that couples the scientific knowledge embedded in large language models with chemistry-informed evolutionary rules and memory-based refinement. At each iteration, an LLM proposes crystallographically specified candidates under explicit property constraints; a surrogate-augmented oracle estimates physicochemical properties; and a multi-objective scorer updates success/failure memories to guide subsequent generations. Evaluated on 14 realistic tasks spanning electronics, energy, coatings, optics, and aerospace, LLEMA discovers candidates that are chemically plausible, thermodynamically stable, and property-aligned, achieving higher hit-rates and stronger Pareto fronts than generative and LLM-only baselines. Ablation studies confirm the importance of rule-guided generation, memory-based refinement, and surrogate prediction. By enforcing synthesizability and multi-objective trade-offs, LLEMA delivers a principled pathway to accelerate practical materials discovery. Code: https://github.com/scientific-discovery/LLEMA
LLM-FE: Automated Feature Engineering for Tabular Data with LLMs as Evolutionary Optimizers
Mar 18, 2025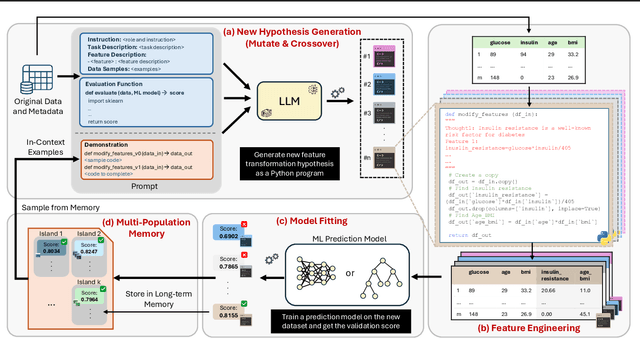
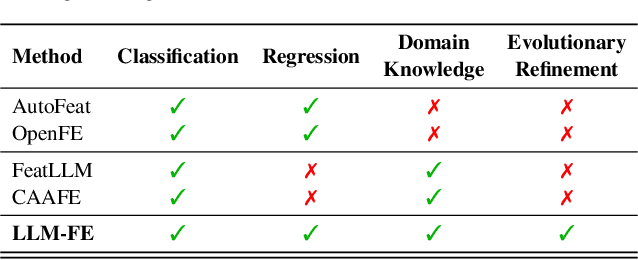
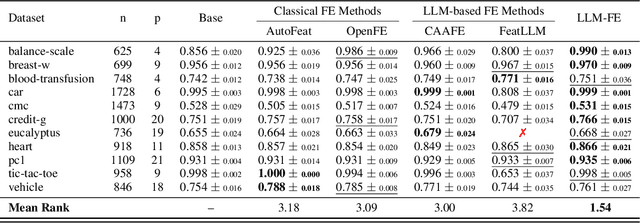
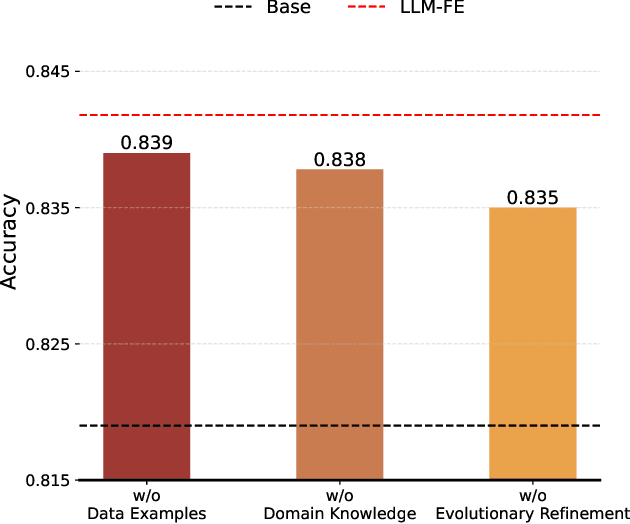
Abstract:Automated feature engineering plays a critical role in improving predictive model performance for tabular learning tasks. Traditional automated feature engineering methods are limited by their reliance on pre-defined transformations within fixed, manually designed search spaces, often neglecting domain knowledge. Recent advances using Large Language Models (LLMs) have enabled the integration of domain knowledge into the feature engineering process. However, existing LLM-based approaches use direct prompting or rely solely on validation scores for feature selection, failing to leverage insights from prior feature discovery experiments or establish meaningful reasoning between feature generation and data-driven performance. To address these challenges, we propose LLM-FE, a novel framework that combines evolutionary search with the domain knowledge and reasoning capabilities of LLMs to automatically discover effective features for tabular learning tasks. LLM-FE formulates feature engineering as a program search problem, where LLMs propose new feature transformation programs iteratively, and data-driven feedback guides the search process. Our results demonstrate that LLM-FE consistently outperforms state-of-the-art baselines, significantly enhancing the performance of tabular prediction models across diverse classification and regression benchmarks.
H-STAR: LLM-driven Hybrid SQL-Text Adaptive Reasoning on Tables
Jun 29, 2024Abstract:Tabular reasoning involves interpreting unstructured queries against structured tables, requiring a synthesis of textual understanding and symbolic reasoning. Existing methods rely on either of the approaches and are constrained by their respective limitations. Textual reasoning excels in semantic interpretation unlike symbolic reasoning (SQL logic), but falls short in mathematical reasoning where SQL excels. In this paper, we introduce a novel algorithm H-STAR, comprising table extraction and adaptive reasoning, integrating both symbolic and semantic (text-based) approaches. To enhance evidence extraction, H-STAR employs a multi-view approach, incorporating step-by-step row and column retrieval. It also adapts reasoning strategies based on question types, utilizing symbolic reasoning for quantitative and logical tasks, and semantic reasoning for direct lookup and complex lexical queries. Our extensive experiments demonstrate that H-STAR significantly outperforms state-of-the-art methods across three tabular question-answering (QA) and fact-verification datasets, underscoring its effectiveness and efficiency.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge