Nicholas Santavas
Meeting SLOs, Slashing Hours: Automated Enterprise LLM Optimization with OptiKIT
Jan 28, 2026Abstract:Enterprise LLM deployment faces a critical scalability challenge: organizations must optimize models systematically to scale AI initiatives within constrained compute budgets, yet the specialized expertise required for manual optimization remains a niche and scarce skillset. This challenge is particularly evident in managing GPU utilization across heterogeneous infrastructure while enabling teams with diverse workloads and limited LLM optimization experience to deploy models efficiently. We present OptiKIT, a distributed LLM optimization framework that democratizes model compression and tuning by automating complex optimization workflows for non-expert teams. OptiKIT provides dynamic resource allocation, staged pipeline execution with automatic cleanup, and seamless enterprise integration. In production, it delivers more than 2x GPU throughput improvement while empowering application teams to achieve consistent performance improvements without deep LLM optimization expertise. We share both the platform design and key engineering insights into resource allocation algorithms, pipeline orchestration, and integration patterns that enable large-scale, production-grade democratization of model optimization. Finally, we open-source the system to enable external contributions and broader reproducibility.
HASeparator: Hyperplane-Assisted Softmax
Aug 08, 2020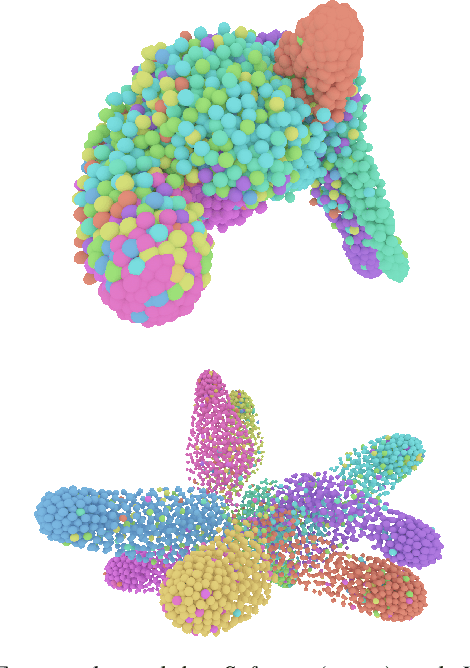
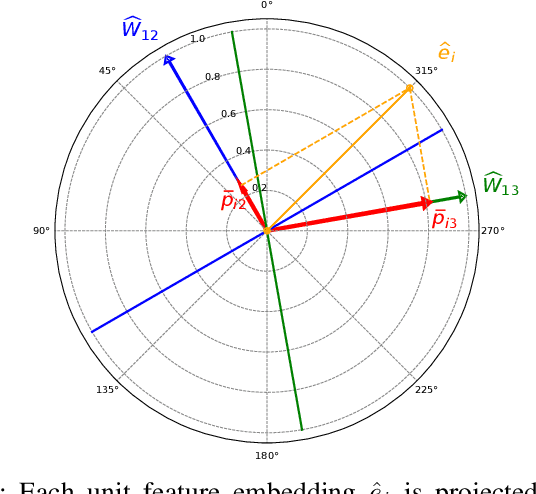
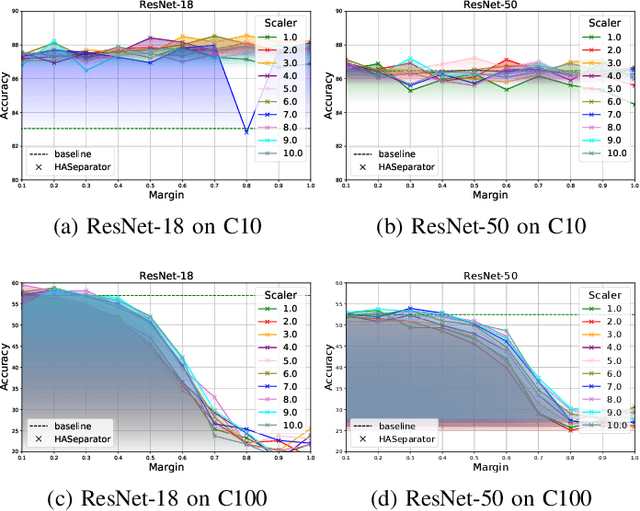
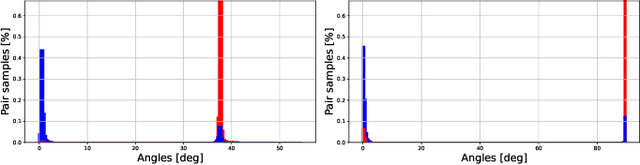
Abstract:Efficient feature learning with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) constitutes an increasingly imperative property since several challenging tasks of computer vision tend to require cascade schemes and modalities fusion. Feature learning aims at CNN models capable of extracting embeddings, exhibiting high discrimination among the different classes, as well as intra-class compactness. In this paper, a novel approach is introduced that has separator, which focuses on an effective hyperplane-based segregation of the classes instead of the common class centers separation scheme. Accordingly, an innovatory separator, namely the Hyperplane-Assisted Softmax separator (HASeparator), is proposed that demonstrates superior discrimination capabilities, as evaluated on popular image classification benchmarks.
Attention! A Lightweight 2D Hand Pose Estimation Approach
Jan 22, 2020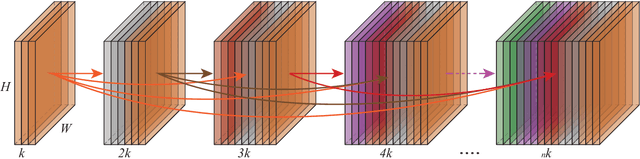
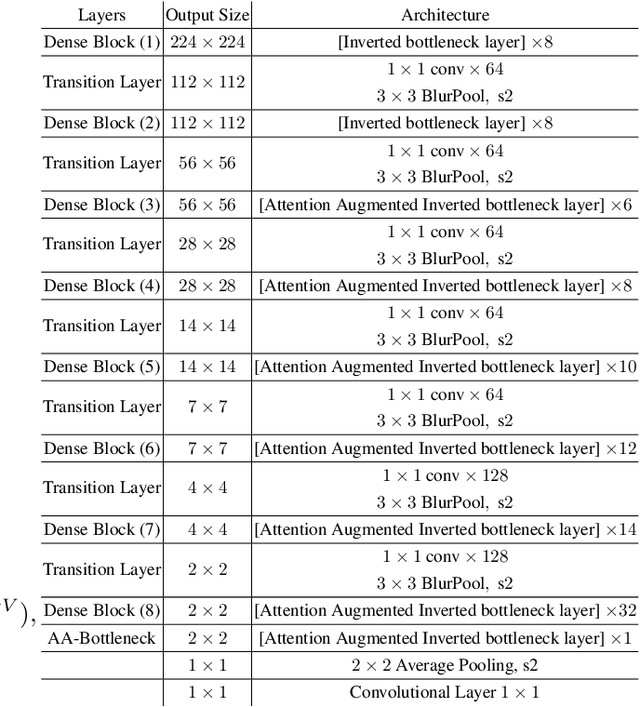
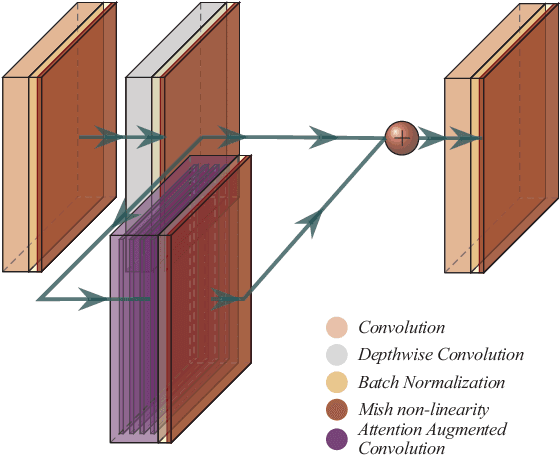
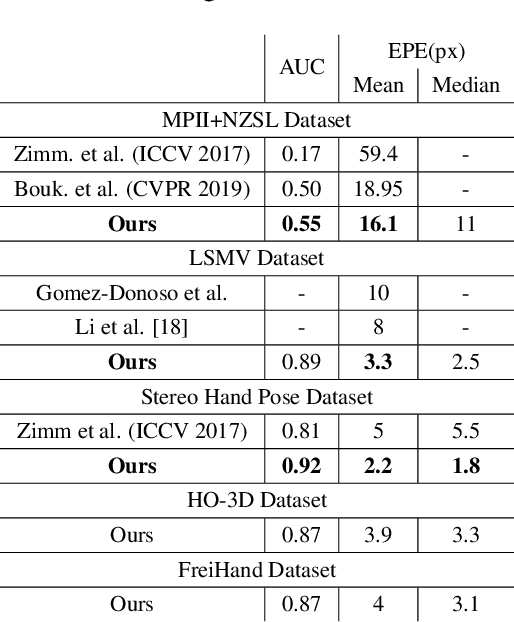
Abstract:Vision based human pose estimation is an non-invasive technology for Human-Computer Interaction (HCI). Direct use of the hand as an input device provides an attractive interaction method, with no need for specialized sensing equipment, such as exoskeletons, gloves etc, but a camera. Traditionally, HCI is employed in various applications spreading in areas including manufacturing, surgery, entertainment industry and architecture, to mention a few. Deployment of vision based human pose estimation algorithms can give a breath of innovation to these applications. In this letter, we present a novel Convolutional Neural Network architecture, reinforced with a Self-Attention module that it can be deployed on an embedded system, due to its lightweight nature, with just 1.9 Million parameters. The source code and qualitative results are publicly available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge