Nicholas LaHaye
Development and Application of Self-Supervised Machine Learning for Smoke Plume and Active Fire Identification from the FIREX-AQ Datasets
Jan 25, 2025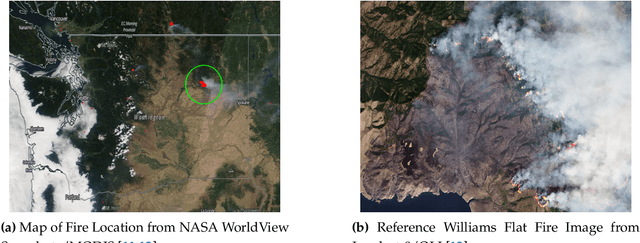
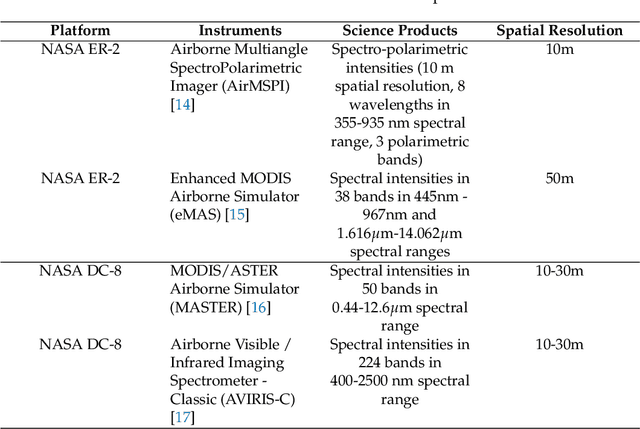
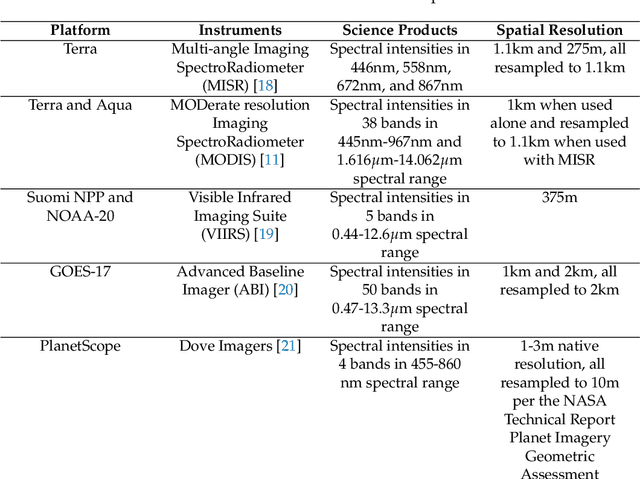
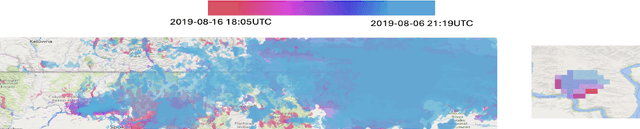
Abstract:Fire Influence on Regional to Global Environments and Air Quality (FIREX-AQ) was a field campaign aimed at better understanding the impact of wildfires and agricultural fires on air quality and climate. The FIREX-AQ campaign took place in August 2019 and involved two aircraft and multiple coordinated satellite observations. This study applied and evaluated a self-supervised machine learning (ML) method for the active fire and smoke plume identification and tracking in the satellite and sub-orbital remote sensing datasets collected during the campaign. Our unique methodology combines remote sensing observations with different spatial and spectral resolutions. The demonstrated approach successfully differentiates fire pixels and smoke plumes from background imagery, enabling the generation of a per-instrument smoke and fire mask product, as well as smoke and fire masks created from the fusion of selected data from independent instruments. This ML approach has a potential to enhance operational wildfire monitoring systems and improve decision-making in air quality management through fast smoke plume identification12 and tracking and could improve climate impact studies through fusion data from independent instruments.
Learning in the Machine: To Share or Not to Share?
Oct 04, 2019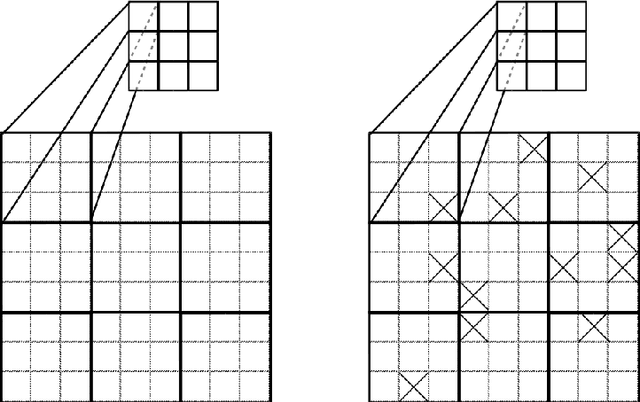
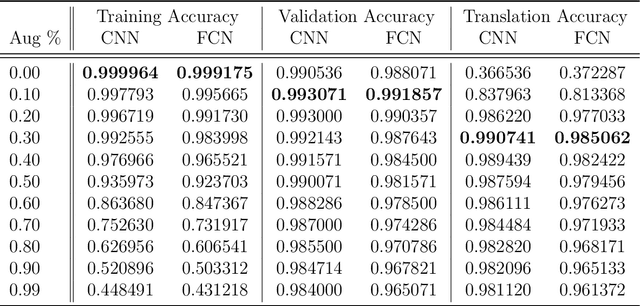
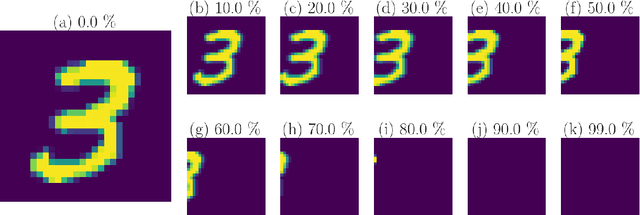
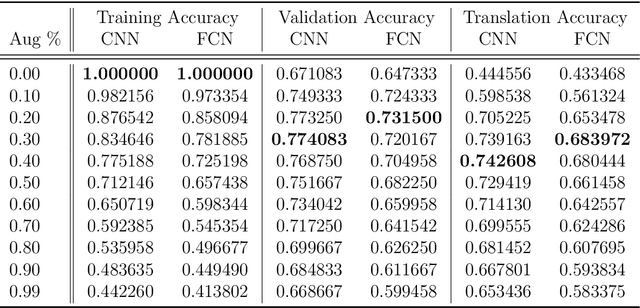
Abstract:Weight-sharing is one of the pillars behind Convolutional Neural Networks and their successes. However, in physical neural systems such as the brain, weight-sharing is implausible. This discrepancy raises the fundamental question of whether weight-sharing is necessary. If so, to which degree of precision? If not, what are the alternatives? The goal of this study is to investigate these questions, primarily through simulations where the weight-sharing assumption is relaxed. Taking inspiration from neural circuitry, we explore the use of Free Convolutional Networks and neurons with variable connection patterns. Using Free Convolutional Networks, we show that while weight-sharing is a pragmatic optimization approach, it is not a necessity in computer vision applications. Furthermore, Free Convolutional Networks match the performance observed in standard architectures when trained using properly translated data (akin to video). Under the assumption of translationally augmented data, Free Convolutional Networks learn translationally invariant representations that yield an approximate form of weight sharing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge