Ngot Bui
Matryoshka Model Learning for Improved Elastic Student Models
May 29, 2025Abstract:Industry-grade ML models are carefully designed to meet rapidly evolving serving constraints, which requires significant resources for model development. In this paper, we propose MatTA, a framework for training multiple accurate Student models using a novel Teacher-TA-Student recipe. TA models are larger versions of the Student models with higher capacity, and thus allow Student models to better relate to the Teacher model and also bring in more domain-specific expertise. Furthermore, multiple accurate Student models can be extracted from the TA model. Therefore, despite only one training run, our methodology provides multiple servable options to trade off accuracy for lower serving cost. We demonstrate the proposed method, MatTA, on proprietary datasets and models. Its practical efficacy is underscored by live A/B tests within a production ML system, demonstrating 20% improvement on a key metric. We also demonstrate our method on GPT-2 Medium, a public model, and achieve relative improvements of over 24% on SAT Math and over 10% on the LAMBADA benchmark.
Multi-View Network Embedding Via Graph Factorization Clustering and Co-Regularized Multi-View Agreement
Nov 08, 2018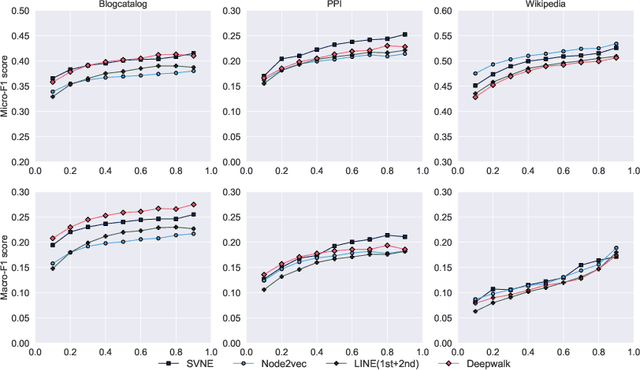
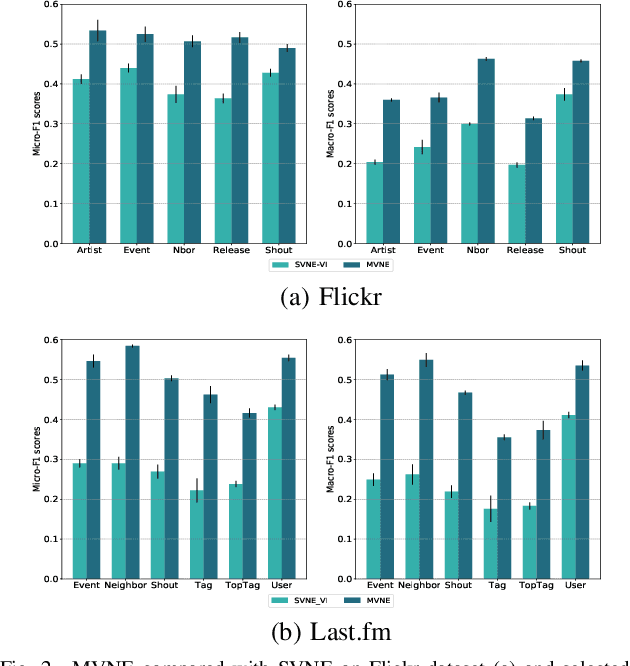
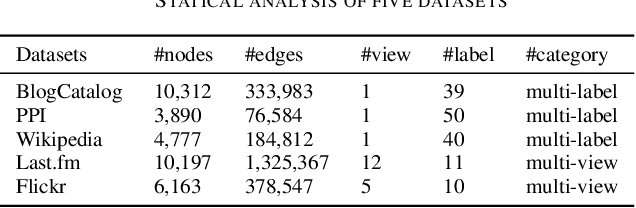
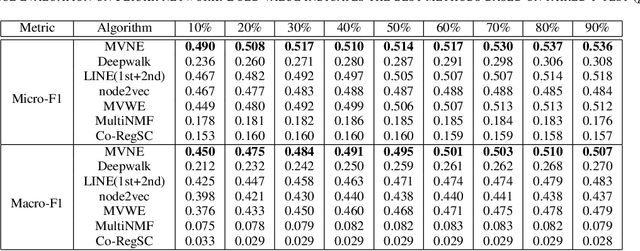
Abstract:Real-world social networks and digital platforms are comprised of individuals (nodes) that are linked to other individuals or entities through multiple types of relationships (links). Sub-networks of such a network based on each type of link correspond to distinct views of the underlying network. In real-world applications, each node is typically linked to only a small subset of other nodes. Hence, practical approaches to problems such as node labeling have to cope with the resulting sparse networks. While low-dimensional network embeddings offer a promising approach to this problem, most of the current network embedding methods focus primarily on single view networks. We introduce a novel multi-view network embedding (MVNE) algorithm for constructing low-dimensional node embeddings from multi-view networks. MVNE adapts and extends an approach to single view network embedding (SVNE) using graph factorization clustering (GFC) to the multi-view setting using an objective function that maximizes the agreement between views based on both the local and global structure of the underlying multi-view graph. Our experiments with several benchmark real-world single view networks show that GFC-based SVNE yields network embeddings that are competitive with or superior to those produced by the state-of-the-art single view network embedding methods when the embeddings are used for labeling unlabeled nodes in the networks. Our experiments with several multi-view networks show that MVNE substantially outperforms the single view methods on integrated view and the state-of-the-art multi-view methods. We further show that even when the goal is to predict labels of nodes within a single target view, MVNE outperforms its single-view counterpart suggesting that the MVNE is able to extract the information that is useful for labeling nodes in the target view from the all of the views.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge