Ngoc-Dung T. Tieu
Identifying Computer-Translated Paragraphs using Coherence Features
Dec 28, 2018
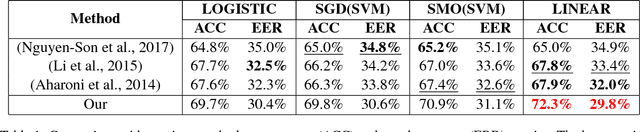

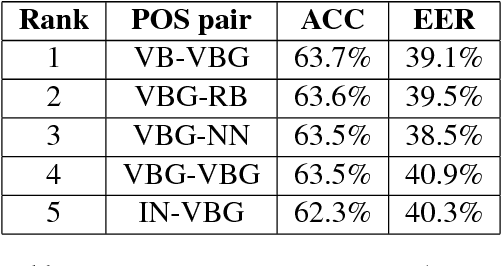
Abstract:We have developed a method for extracting the coherence features from a paragraph by matching similar words in its sentences. We conducted an experiment with a parallel German corpus containing 2000 human-created and 2000 machine-translated paragraphs. The result showed that our method achieved the best performance (accuracy = 72.3%, equal error rate = 29.8%) when it is compared with previous methods on various computer-generated text including translation and paper generation (best accuracy = 67.9%, equal error rate = 32.0%). Experiments on Dutch, another rich resource language, and a low resource one (Japanese) attained similar performances. It demonstrated the efficiency of the coherence features at distinguishing computer-translated from human-created paragraphs on diverse languages.
Transformation on Computer-Generated Facial Image to Avoid Detection by Spoofing Detector
Apr 12, 2018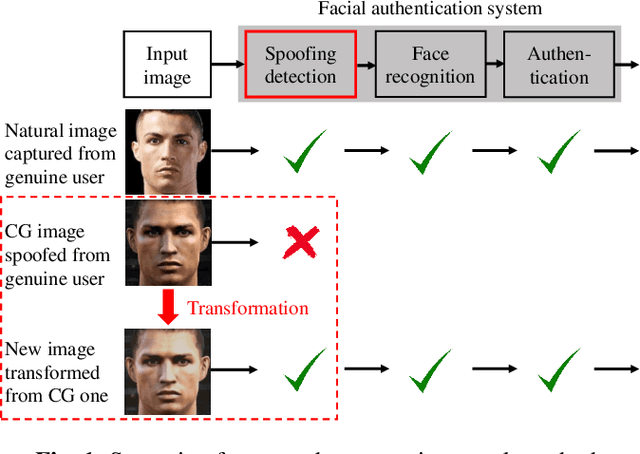
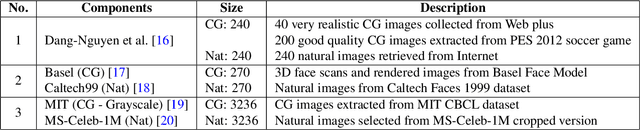
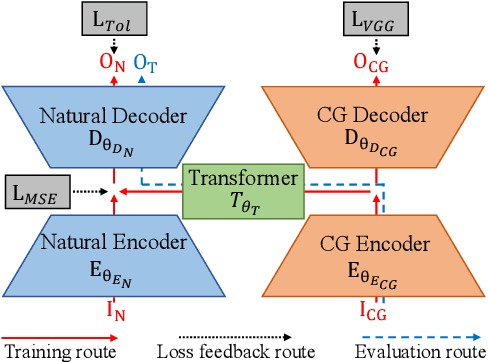
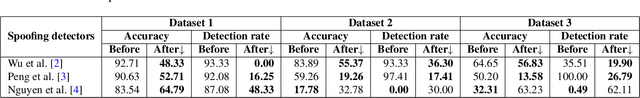
Abstract:Making computer-generated (CG) images more difficult to detect is an interesting problem in computer graphics and security. While most approaches focus on the image rendering phase, this paper presents a method based on increasing the naturalness of CG facial images from the perspective of spoofing detectors. The proposed method is implemented using a convolutional neural network (CNN) comprising two autoencoders and a transformer and is trained using a black-box discriminator without gradient information. Over 50% of the transformed CG images were not detected by three state-of-the-art spoofing detectors. This capability raises an alarm regarding the reliability of facial authentication systems, which are becoming widely used in daily life.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge