Nazar Zaki
Scalable Graph Attention-based Instance Selection via Mini-Batch Sampling and Hierarchical Hashing
Feb 27, 2025Abstract:Instance selection (IS) is important in machine learning for reducing dataset size while keeping key characteristics. Current IS methods often struggle with capturing complex relationships in high-dimensional spaces and scale with large datasets. This paper introduces a graph attention-based instance selection (GAIS) method that uses attention mechanisms to identify informative instances through their structural relationships in graph representations. We present two approaches for scalable graph construction: a distance-based mini-batch sampling technique that reduces computation through strategic batch processing, and a hierarchical hashing approach that allows for efficient similarity computation through random projections. The mini-batch approach keeps class distributions through stratified sampling, while the hierarchical hashing method captures relationships at multiple granularities through single-level, multi-level, and multi-view variants. Experiments across 39 datasets show that GAIS achieves reduction rates above 96\% while maintaining or improving model performance relative to state-of-the-art IS methods. The findings shows that the distance-based mini-batch approach offers an optimal balance of efficiency and effectiveness for large-scale datasets, while multi-view variants provide superior performance for complex, high-dimensional data, demonstrating that attention-based importance scoring can effectively identify instances crucial for maintaining decision boundaries without requiring exhaustive pairwise comparisons.
GAIS: A Novel Approach to Instance Selection with Graph Attention Networks
Dec 26, 2024



Abstract:Instance selection (IS) is a crucial technique in machine learning that aims to reduce dataset size while maintaining model performance. This paper introduces a novel method called Graph Attention-based Instance Selection (GAIS), which leverages Graph Attention Networks (GATs) to identify the most informative instances in a dataset. GAIS represents the data as a graph and uses GATs to learn node representations, enabling it to capture complex relationships between instances. The method processes data in chunks, applies random masking and similarity thresholding during graph construction, and selects instances based on confidence scores from the trained GAT model. Experiments on 13 diverse datasets demonstrate that GAIS consistently outperforms traditional IS methods in terms of effectiveness, achieving high reduction rates (average 96\%) while maintaining or improving model performance. Although GAIS exhibits slightly higher computational costs, its superior performance in maintaining accuracy with significantly reduced training data makes it a promising approach for graph-based data selection.
GAT-RWOS: Graph Attention-Guided Random Walk Oversampling for Imbalanced Data Classification
Dec 20, 2024Abstract:Class imbalance poses a significant challenge in machine learning (ML), often leading to biased models favouring the majority class. In this paper, we propose GAT-RWOS, a novel graph-based oversampling method that combines the strengths of Graph Attention Networks (GATs) and random walk-based oversampling. GAT-RWOS leverages the attention mechanism of GATs to guide the random walk process, focusing on the most informative neighbourhoods for each minority node. By performing attention-guided random walks and interpolating features along the traversed paths, GAT-RWOS generates synthetic minority samples that expand class boundaries while preserving the original data distribution. Extensive experiments on a diverse set of imbalanced datasets demonstrate the effectiveness of GAT-RWOS in improving classification performance, outperforming state-of-the-art oversampling techniques. The proposed method has the potential to significantly improve the performance of ML models on imbalanced datasets and contribute to the development of more reliable classification systems.
Unsupervised Automatic Speech Recognition: A Review
Jun 09, 2021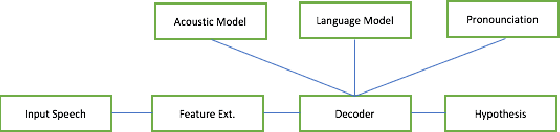
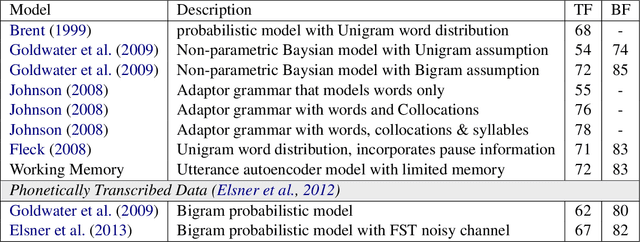

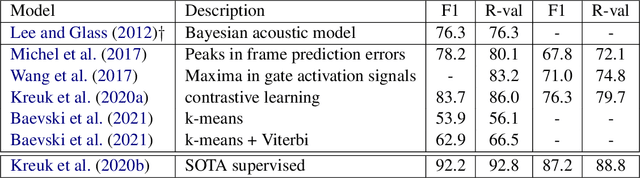
Abstract:Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) systems can be trained to achieve remarkable performance given large amounts of manually transcribed speech, but large labeled data sets can be difficult or expensive to acquire for all languages of interest. In this paper, we review the research literature to identify models and ideas that could lead to fully unsupervised ASR, including unsupervised segmentation of the speech signal, unsupervised mapping from speech segments to text, and semi-supervised models with nominal amounts of labeled examples. The objective of the study is to identify the limitations of what can be learned from speech data alone and to understand the minimum requirements for speech recognition. Identifying these limitations would help optimize the resources and efforts in ASR development for low-resource languages.
A Novel Image Segmentation Enhancement Technique based on Active Contour and Topological Alignments
Jun 02, 2011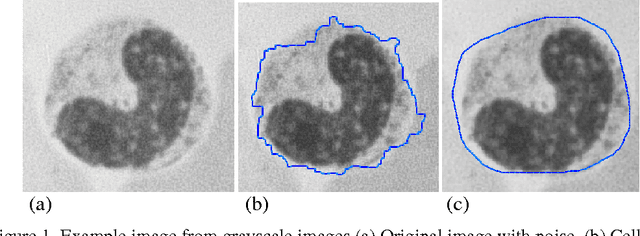
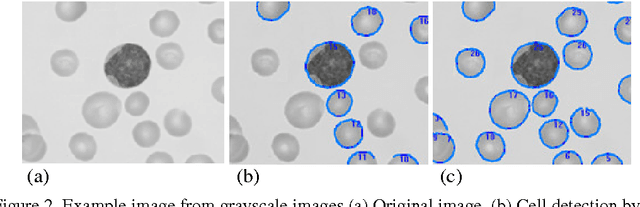
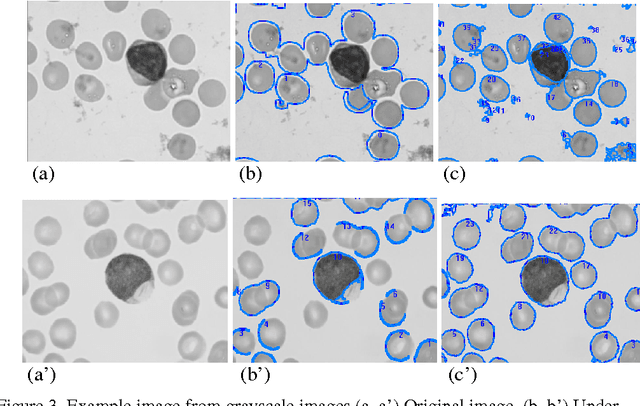
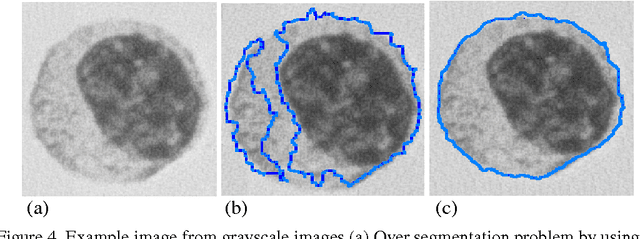
Abstract:Topological alignments and snakes are used in image processing, particularly in locating object boundaries. Both of them have their own advantages and limitations. To improve the overall image boundary detection system, we focused on developing a novel algorithm for image processing. The algorithm we propose to develop will based on the active contour method in conjunction with topological alignments method to enhance the image detection approach. The algorithm presents novel technique to incorporate the advantages of both Topological Alignments and snakes. Where the initial segmentation by Topological Alignments is firstly transformed into the input of the snake model and begins its evolvement to the interested object boundary. The results show that the algorithm can deal with low contrast images and shape cells, demonstrate the segmentation accuracy under weak image boundaries, which responsible for lacking accuracy in image detecting techniques. We have achieved better segmentation and boundary detecting for the image, also the ability of the system to improve the low contrast and deal with over and under segmentation.
* 7 pages
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge