Navjot Kaur
Separation of Unconscious Robots with Obstructed Visibility
Oct 25, 2025



Abstract:We study a recently introduced \textit{unconscious} mobile robot model, where each robot is associated with a \textit{color}, which is visible to other robots but not to itself. The robots are autonomous, anonymous, oblivious and silent, operating in the Euclidean plane under the conventional \textit{Look-Compute-Move} cycle. A primary task in this model is the \textit{separation problem}, where unconscious robots sharing the same color must separate from others, forming recognizable geometric shapes such as circles, points, or lines. All prior works model the robots as \textit{transparent}, enabling each to know the positions and colors of all other robots. In contrast, we model the robots as \textit{opaque}, where a robot can obstruct the visibility of two other robots, if it lies on the line segment between them. Under this obstructed visibility, we consider a variant of the separation problem in which robots, starting from any arbitrary initial configuration, are required to separate into concentric semicircles. We present a collision-free algorithm that solves the separation problem under a semi-synchronous scheduler in $O(n)$ epochs, where $n$ is the number of robots. The robots agree on one coordinate axis but have no knowledge of $n$.
Time out of Mind: Generating Rate of Speech conditioned on emotion and speaker
Jan 31, 2023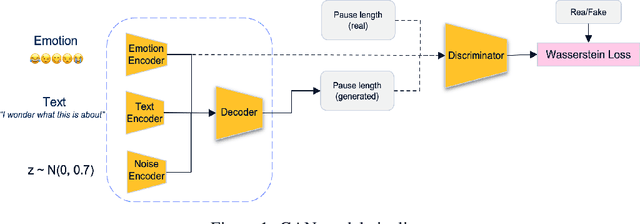
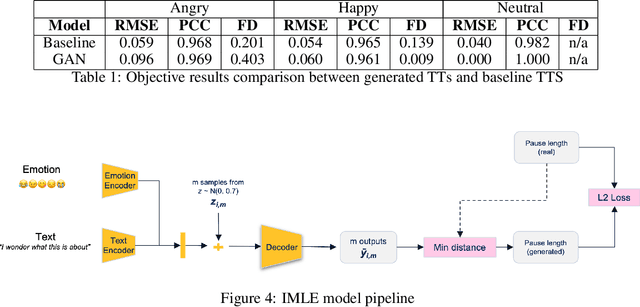
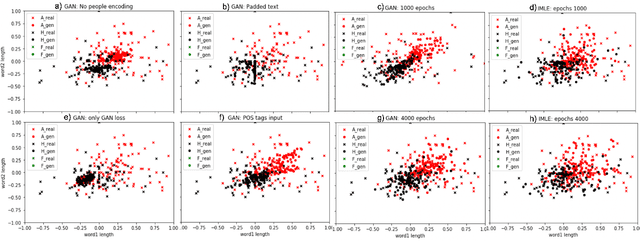
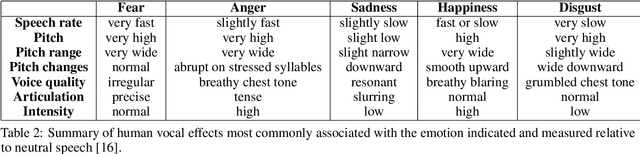
Abstract:Voice synthesis has seen significant improvements in the past decade resulting in highly intelligible voices. Further investigations have resulted in models that can produce variable speech, including conditional emotional expression. The problem lies, however, in a focus on phrase-level modifications and prosodic vocal features. Using the CREMA-D dataset we have trained a GAN conditioned on emotion to generate worth lengths for a given input text. These word lengths are relative to neutral speech and can be provided, through speech synthesis markup language (SSML) to a text-to-speech (TTS) system to generate more expressive speech. Additionally, a generative model is also trained using implicit maximum likelihood estimation (IMLE) and a comparative analysis with GANs is included. We were able to achieve better performances on objective measures for neutral speech, and better time alignment for happy speech when compared to an out-of-box model. However, further investigation of subjective evaluation is required.
DAHiTrA: Damage Assessment Using a Novel Hierarchical Transformer Architecture
Aug 03, 2022


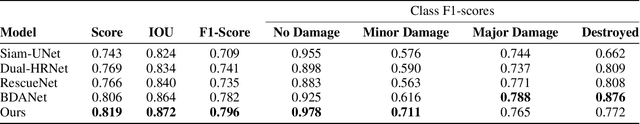
Abstract:This paper presents DAHiTrA, a novel deep-learning model with hierarchical transformers to classify building damages based on satellite images in the aftermath of hurricanes. An automated building damage assessment provides critical information for decision making and resource allocation for rapid emergency response. Satellite imagery provides real-time, high-coverage information and offers opportunities to inform large-scale post-disaster building damage assessment. In addition, deep-learning methods have shown to be promising in classifying building damage. In this work, a novel transformer-based network is proposed for assessing building damage. This network leverages hierarchical spatial features of multiple resolutions and captures temporal difference in the feature domain after applying a transformer encoder on the spatial features. The proposed network achieves state-of-the-art-performance when tested on a large-scale disaster damage dataset (xBD) for building localization and damage classification, as well as on LEVIR-CD dataset for change detection tasks. In addition, we introduce a new high-resolution satellite imagery dataset, Ida-BD (related to the 2021 Hurricane Ida in Louisiana in 2021, for domain adaptation to further evaluate the capability of the model to be applied to newly damaged areas with scarce data. The domain adaptation results indicate that the proposed model can be adapted to a new event with only limited fine-tuning. Hence, the proposed model advances the current state of the art through better performance and domain adaptation. Also, Ida-BD provides a higher-resolution annotated dataset for future studies in this field.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge