Naveed Arshad
Fair Allocation Based Soft Load Shedding
Feb 02, 2020
Abstract:Renewable sources are taking center stage in electricity generation. Due to the intermittent nature of these renewable resources, the problem of the demand-supply gap arises. To solve this problem, several techniques have been proposed in the literature in terms of cost (adding peaker plants), availability of data (Demand Side Management "DSM"), hardware infrastructure (appliance controlling DSM) and safety (voltage reduction). However, these solutions are not fair in terms of electricity distribution. In many cases, although the available supply may not match the demand in peak hours, however, the total aggregated demand remains less than the total supply for the whole day. Load shedding (complete blackout) is a commonly used solution to deal with the demand-supply gap, which can cause substantial economic losses. To solve the demand-supply gap problem, we propose a solution called Soft Load Shedding (SLS), which assigns electricity quota to each household in a fair way. We measure the fairness of SLS by defining a function for household satisfaction level. We model the household utilities by parametric function and formulate the problem of SLS as a social welfare problem. We also consider revenue generated from the fair allocation as a performance measure. To evaluate our approach, extensive experiments have been performed on both synthetic and real-world datasets, and our model is compared with several baselines to show its effectiveness in terms of fair allocation and revenue generation.
Hour-Ahead Load Forecasting Using AMI Data
Jan 08, 2020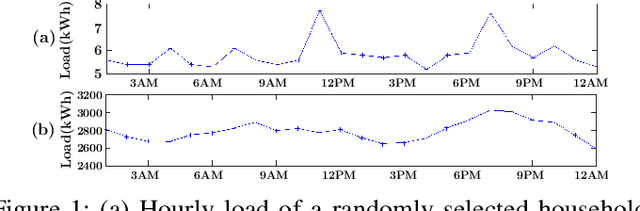
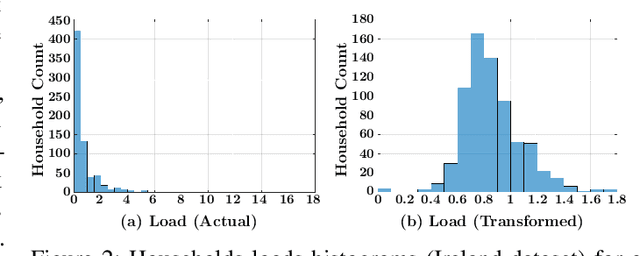
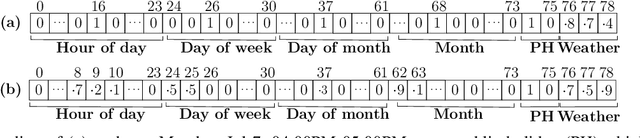

Abstract:Accurate short-term load forecasting is essential for efficient operation of the power sector. Predicting load at a fine granularity such as individual households or buildings is challenging due to higher volatility and uncertainty in the load. In aggregate loads such as at grids level, the inherent stochasticity and fluctuations are averaged-out, the problem becomes substantially easier. We propose an approach for short-term load forecasting at individual consumers (households) level, called Forecasting using Matrix Factorization (FMF). FMF does not use any consumers' demographic or activity patterns information. Therefore, it can be applied to any locality with the readily available smart meters and weather data. We perform extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets and demonstrate that FMF significantly outperforms the computationally expensive state-of-the-art methods for this problem. We achieve up to 26.5% and 24.4 % improvement in RMSE over Regression Tree and Support Vector Machine, respectively and up to 36% and 73.2% improvement in MAPE over Random Forest and Long Short-Term Memory neural network, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge