Hour-Ahead Load Forecasting Using AMI Data
Paper and Code
Jan 08, 2020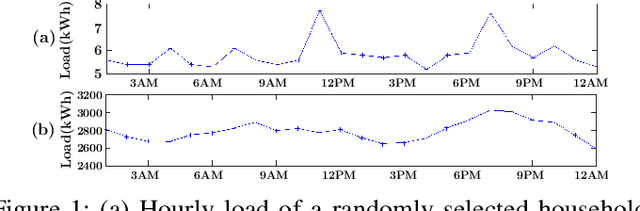
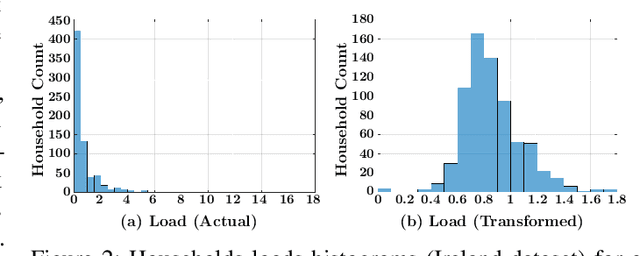
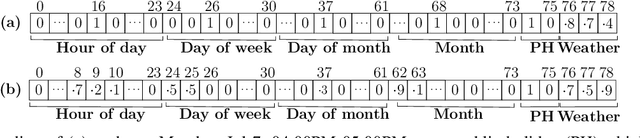

Accurate short-term load forecasting is essential for efficient operation of the power sector. Predicting load at a fine granularity such as individual households or buildings is challenging due to higher volatility and uncertainty in the load. In aggregate loads such as at grids level, the inherent stochasticity and fluctuations are averaged-out, the problem becomes substantially easier. We propose an approach for short-term load forecasting at individual consumers (households) level, called Forecasting using Matrix Factorization (FMF). FMF does not use any consumers' demographic or activity patterns information. Therefore, it can be applied to any locality with the readily available smart meters and weather data. We perform extensive experiments on three benchmark datasets and demonstrate that FMF significantly outperforms the computationally expensive state-of-the-art methods for this problem. We achieve up to 26.5% and 24.4 % improvement in RMSE over Regression Tree and Support Vector Machine, respectively and up to 36% and 73.2% improvement in MAPE over Random Forest and Long Short-Term Memory neural network, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge