Nana Kankam Gyimah
Analyzing Factors Influencing Driver Willingness to Accept Advanced Driver Assistance Systems
Feb 23, 2025Abstract:Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS) enhance highway safety by improving environmental perception and reducing human errors. However, misconceptions, trust issues, and knowledge gaps hinder widespread adoption. This study examines driver perceptions, knowledge sources, and usage patterns of ADAS in passenger vehicles. A nationwide survey collected data from a diverse sample of U.S. drivers. Machine learning models predicted ADAS adoption, with SHAP (SHapley Additive Explanations) identifying key influencing factors. Findings indicate that higher trust levels correlate with increased ADAS usage, while concerns about reliability remain a barrier. Specific features, such as Forward Collision Warning and Driver Monitoring Systems, significantly influence adoption likelihood. Demographic factors (age, gender) and driving habits (experience, frequency) also shape ADAS acceptance. Findings emphasize the influence of socioeconomic, demographic, and behavioral factors on ADAS adoption, offering guidance for automakers, policymakers, and safety advocates to improve awareness, trust, and usability.
An AutoML-based approach for Network Intrusion Detection
Nov 24, 2024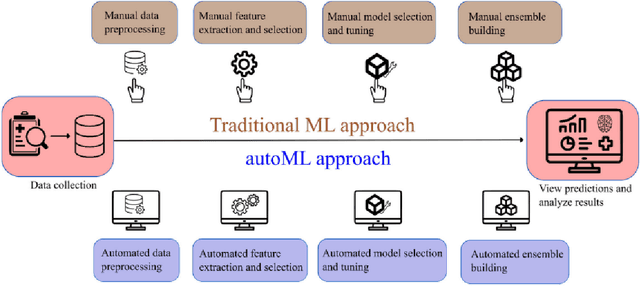
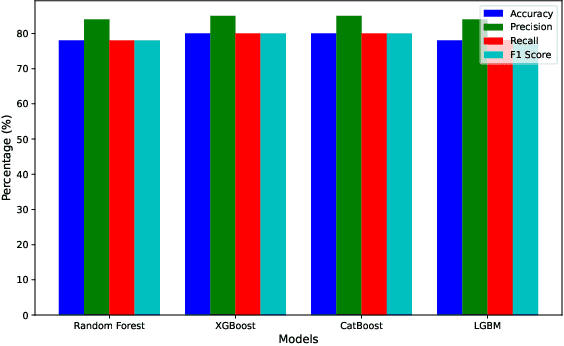
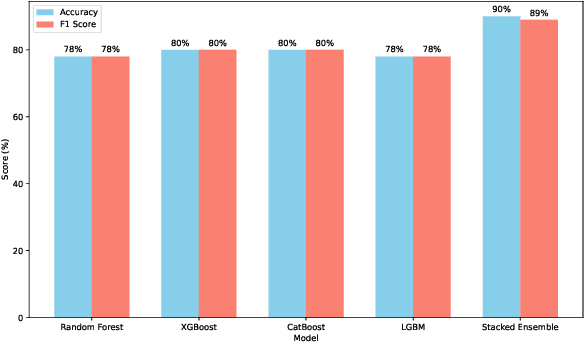

Abstract:In this paper, we present an automated machine learning (AutoML) approach for network intrusion detection, leveraging a stacked ensemble model developed using the MLJAR AutoML framework. Our methodology combines multiple machine learning algorithms, including LightGBM, CatBoost, and XGBoost, to enhance detection accuracy and robustness. By automating model selection, feature engineering, and hyperparameter tuning, our approach reduces the manual overhead typically associated with traditional machine learning methods. Extensive experimentation on the NSL-KDD dataset demonstrates that the stacked ensemble model outperforms individual models, achieving high accuracy and minimizing false positives. Our findings underscore the benefits of using AutoML for network intrusion detection, as the AutoML-driven stacked ensemble achieved the highest performance with 90\% accuracy and an 89\% F1 score, outperforming individual models like Random Forest (78\% accuracy, 78\% F1 score), XGBoost and CatBoost (both 80\% accuracy, 80\% F1 score), and LightGBM (78\% accuracy, 78\% F1 score), providing a more adaptable and efficient solution for network security applications.
A Robust Completed Local Binary Pattern for Surface Defect Detection
Dec 07, 2021
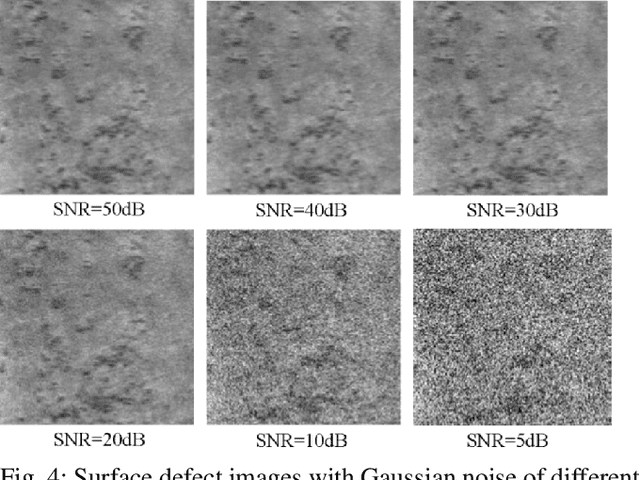



Abstract:In this paper, we present a Robust Completed Local Binary Pattern (RCLBP) framework for a surface defect detection task. Our approach uses a combination of Non-Local (NL) means filter with wavelet thresholding and Completed Local Binary Pattern (CLBP) to extract robust features which are fed into classifiers for surface defects detection. This paper combines three components: A denoising technique based on Non-Local (NL) means filter with wavelet thresholding is established to denoise the noisy image while preserving the textures and edges. Second, discriminative features are extracted using the CLBP technique. Finally, the discriminative features are fed into the classifiers to build the detection model and evaluate the performance of the proposed framework. The performance of the defect detection models are evaluated using a real-world steel surface defect database from Northeastern University (NEU). Experimental results demonstrate that the proposed approach RCLBP is noise robust and can be applied for surface defect detection under varying conditions of intra-class and inter-class changes and with illumination changes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge