Nael Alsheikh
Khalifa University of Science and Technology, Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates
Integrating Features for Recognizing Human Activities through Optimized Parameters in Graph Convolutional Networks and Transformer Architectures
Aug 29, 2024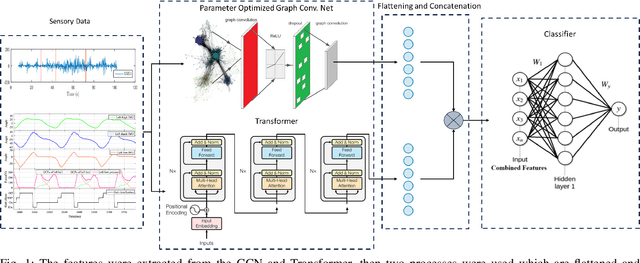
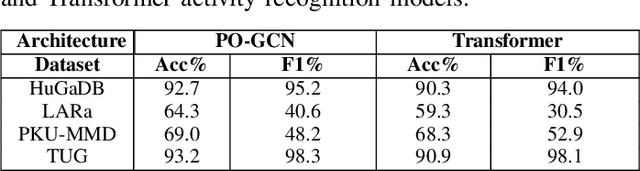
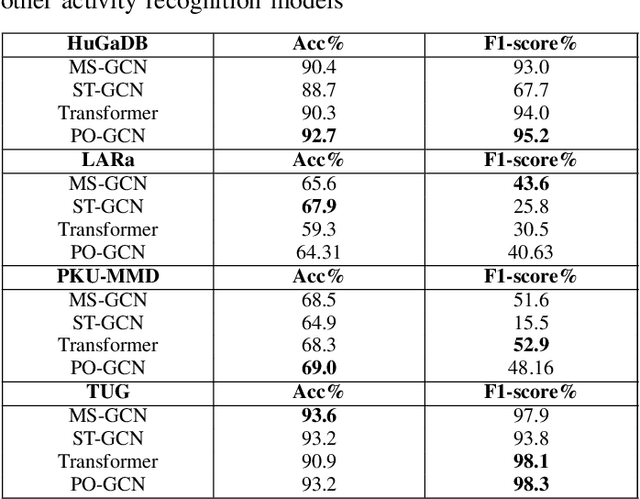

Abstract:Human activity recognition is a major field of study that employs computer vision, machine vision, and deep learning techniques to categorize human actions. The field of deep learning has made significant progress, with architectures that are extremely effective at capturing human dynamics. This study emphasizes the influence of feature fusion on the accuracy of activity recognition. This technique addresses the limitation of conventional models, which face difficulties in identifying activities because of their limited capacity to understand spatial and temporal features. The technique employs sensory data obtained from four publicly available datasets: HuGaDB, PKU-MMD, LARa, and TUG. The accuracy and F1-score of two deep learning models, specifically a Transformer model and a Parameter-Optimized Graph Convolutional Network (PO-GCN), were evaluated using these datasets. The feature fusion technique integrated the final layer features from both models and inputted them into a classifier. Empirical evidence demonstrates that PO-GCN outperforms standard models in activity recognition. HuGaDB demonstrated a 2.3% improvement in accuracy and a 2.2% increase in F1-score. TUG showed a 5% increase in accuracy and a 0.5% rise in F1-score. On the other hand, LARa and PKU-MMD achieved lower accuracies of 64% and 69% respectively. This indicates that the integration of features enhanced the performance of both the Transformer model and PO-GCN.
Feature Fusion for Human Activity Recognition using Parameter-Optimized Multi-Stage Graph Convolutional Network and Transformer Models
Jun 24, 2024Abstract:Human activity recognition (HAR) is a crucial area of research that involves understanding human movements using computer and machine vision technology. Deep learning has emerged as a powerful tool for this task, with models such as Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and Transformers being employed to capture various aspects of human motion. One of the key contributions of this work is the demonstration of the effectiveness of feature fusion in improving HAR accuracy by capturing spatial and temporal features, which has important implications for the development of more accurate and robust activity recognition systems. The study uses sensory data from HuGaDB, PKU-MMD, LARa, and TUG datasets. Two model, the PO-MS-GCN and a Transformer were trained and evaluated, with PO-MS-GCN outperforming state-of-the-art models. HuGaDB and TUG achieved high accuracies and f1-scores, while LARa and PKU-MMD had lower scores. Feature fusion improved results across datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge