Morris Repeta
Evolution of 3GPP Standards Towards True Extended Reality (XR) Support in 6G Networks
Jun 06, 2023Abstract:Extended reality (XR) is a key innovation of 5G-advanced and beyond networks. The diverse XR use-cases, including virtual reality, augmented reality, and mixed reality, transform the way humans interact with surrounding environments. Thus, XR technology enables true immersive experiences of novel services spanning, e.g., e-commerce, healthcare, and education, respectively. However, the efficient support of XR services over existing and future cellular systems is highly challenging and requires multiple radio design improvements, due to the unique XR traffic and performance characteristics. Thus, this article surveys the state-of-art 3GPP standardization activities (release-18) for integrating the XR service class into the 5G-advanced specifications, highlighting the major XR performance challenges. Furthermore, the paper introduces valuable insights and research directions for supporting true XR services over the next-generation 6G networks, where multiple novel radio design mindsets and protocol enhancements are proposed and evaluated using extensive system level simulations, including solutions for application-native dynamic performance reporting, traffic-dependent control channel design, collaborative device aggregation for XR capacity boosting and offload, respectively.
A Scalable 256-Elements E-Band Phased-Array Transceiver for Broadband Communication
Jun 20, 2021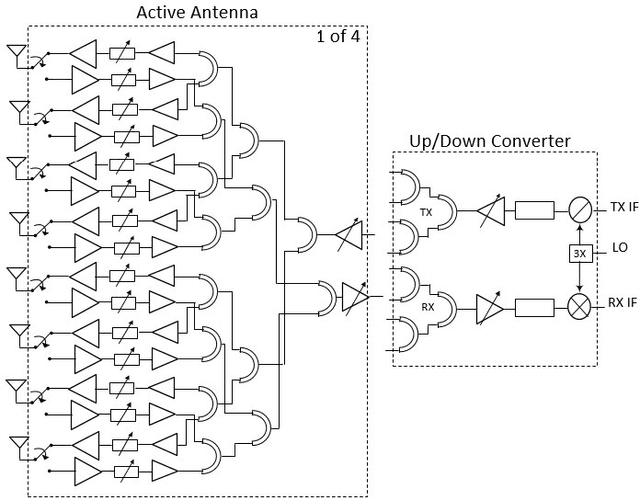
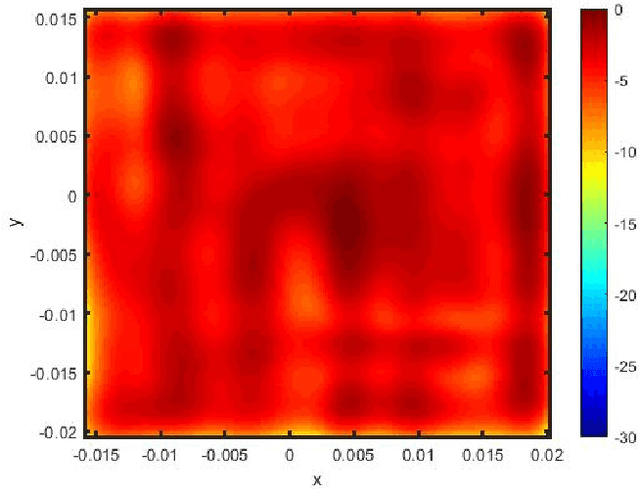
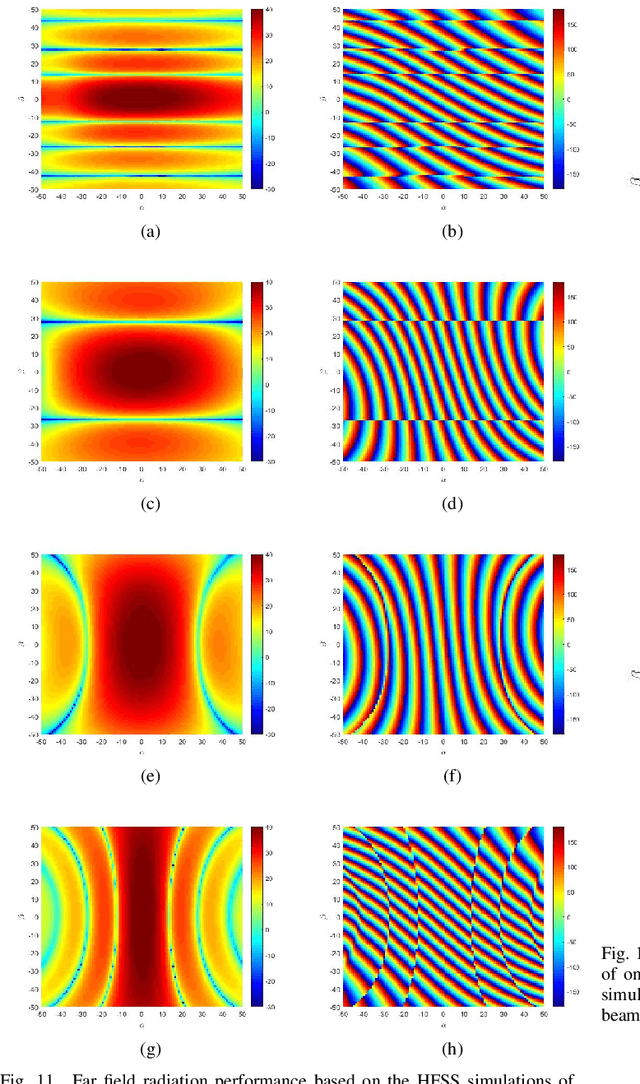
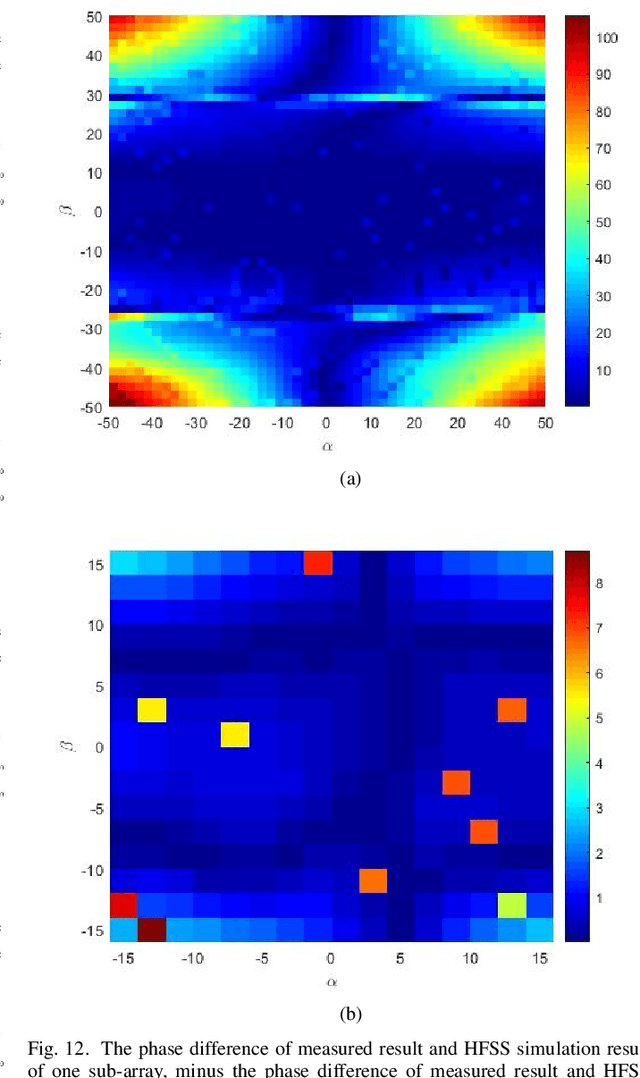
Abstract:For E-band wireless communications, a high gain steerable antenna with sub-arrays is desired to reduce the implementation complexity. This paper presents an E-band communication link with 256-elements antennas based on 8-elements sub-arrays and four beam-forming chips in silicon germanium (SiGe) bipolar complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor (BiCMOS), which is packaged on a 19-layer low temperature co-fired ceramic (LTCC) substrate. After the design and manufacture of the 256-elements antenna, a fast near-field calibration method is proposed for calibration, where a single near-field measurement is required. Then near-field to far-field (NFFF) transform and far-field to near-field (FFNF) transform are used for the bore-sight calibration. The comparison with high frequency structure simulator (HFSS) is utilized for the non-bore-sight calibration. Verified on the 256-elements antenna, the beam-forming performance measured in the chamber is in good agreement with the simulations. The communication in the office environment is also realized using a fifth generation (5G) new radio (NR) system, whose bandwidth is 400 megahertz (MHz) and waveform format is orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM) with 120 kilohertz (kHz) sub-carrier spacing.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge