Moreno Coco
Action Anticipation: Reading the Intentions of Humans and Robots
Aug 10, 2018



Abstract:Humans have the fascinating capacity of processing non-verbal visual cues to understand and anticipate the actions of other humans. This "intention reading" ability is underpinned by shared motor-repertoires and action-models, which we use to interpret the intentions of others as if they were our own. We investigate how the different cues contribute to the legibility of human actions during interpersonal interactions. Our first contribution is a publicly available dataset with recordings of human body-motion and eye-gaze, acquired in an experimental scenario with an actor interacting with three subjects. From these data, we conducted a human study to analyse the importance of the different non-verbal cues for action perception. As our second contribution, we used the motion/gaze recordings to build a computational model describing the interaction between two persons. As a third contribution, we embedded this model in the controller of an iCub humanoid robot and conducted a second human study, in the same scenario with the robot as an actor, to validate the model's "intention reading" capability. Our results show that it is possible to model (non-verbal) signals exchanged by humans during interaction, and how to incorporate such a mechanism in robotic systems with the twin goal of : (i) being able to "read" human action intentions, and (ii) acting in a way that is legible by humans.
Dynamic Natural Language Processing with Recurrence Quantification Analysis
Mar 19, 2018


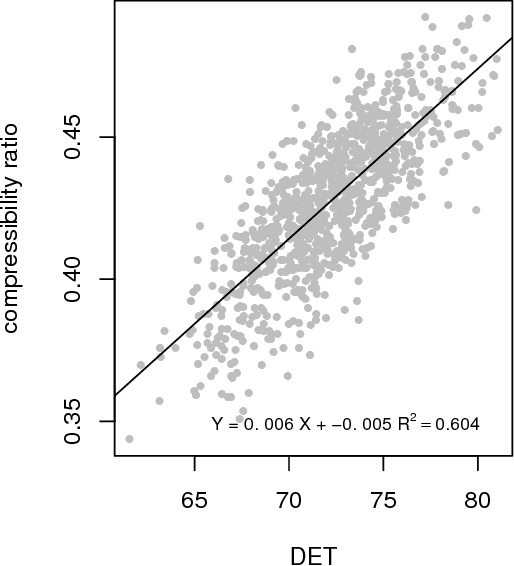
Abstract:Writing and reading are dynamic processes. As an author composes a text, a sequence of words is produced. This sequence is one that, the author hopes, causes a revisitation of certain thoughts and ideas in others. These processes of composition and revisitation by readers are ordered in time. This means that text itself can be investigated under the lens of dynamical systems. A common technique for analyzing the behavior of dynamical systems, known as recurrence quantification analysis (RQA), can be used as a method for analyzing sequential structure of text. RQA treats text as a sequential measurement, much like a time series, and can thus be seen as a kind of dynamic natural language processing (NLP). The extension has several benefits. Because it is part of a suite of time series analysis tools, many measures can be extracted in one common framework. Secondly, the measures have a close relationship with some commonly used measures from natural language processing. Finally, using recurrence analysis offers an opportunity expand analysis of text by developing theoretical descriptions derived from complex dynamic systems. We showcase an example analysis on 8,000 texts from the Gutenberg Project, compare it to well-known NLP approaches, and describe an R package (crqanlp) that can be used in conjunction with R library crqa.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge