Mojtaba Kolahdouzi
Some Optimizers are More Equal: Understanding the Role of Optimizers in Group Fairness
Apr 21, 2025Abstract:We study whether and how the choice of optimization algorithm can impact group fairness in deep neural networks. Through stochastic differential equation analysis of optimization dynamics in an analytically tractable setup, we demonstrate that the choice of optimization algorithm indeed influences fairness outcomes, particularly under severe imbalance. Furthermore, we show that when comparing two categories of optimizers, adaptive methods and stochastic methods, RMSProp (from the adaptive category) has a higher likelihood of converging to fairer minima than SGD (from the stochastic category). Building on this insight, we derive two new theoretical guarantees showing that, under appropriate conditions, RMSProp exhibits fairer parameter updates and improved fairness in a single optimization step compared to SGD. We then validate these findings through extensive experiments on three publicly available datasets, namely CelebA, FairFace, and MS-COCO, across different tasks as facial expression recognition, gender classification, and multi-label classification, using various backbones. Considering multiple fairness definitions including equalized odds, equal opportunity, and demographic parity, adaptive optimizers like RMSProp and Adam consistently outperform SGD in terms of group fairness, while maintaining comparable predictive accuracy. Our results highlight the role of adaptive updates as a crucial yet overlooked mechanism for promoting fair outcomes.
Unmasking Deepfakes: Masked Autoencoding Spatiotemporal Transformers for Enhanced Video Forgery Detection
Jun 12, 2023



Abstract:We present a novel approach for the detection of deepfake videos using a pair of vision transformers pre-trained by a self-supervised masked autoencoding setup. Our method consists of two distinct components, one of which focuses on learning spatial information from individual RGB frames of the video, while the other learns temporal consistency information from optical flow fields generated from consecutive frames. Unlike most approaches where pre-training is performed on a generic large corpus of images, we show that by pre-training on smaller face-related datasets, namely Celeb-A (for the spatial learning component) and YouTube Faces (for the temporal learning component), strong results can be obtained. We perform various experiments to evaluate the performance of our method on commonly used datasets namely FaceForensics++ (Low Quality and High Quality, along with a new highly compressed version named Very Low Quality) and Celeb-DFv2 datasets. Our experiments show that our method sets a new state-of-the-art on FaceForensics++ (LQ, HQ, and VLQ), and obtains competitive results on Celeb-DFv2. Moreover, our method outperforms other methods in the area in a cross-dataset setup where we fine-tune our model on FaceForensics++ and test on CelebDFv2, pointing to its strong cross-dataset generalization ability.
Toward Fair Facial Expression Recognition with Improved Distribution Alignment
Jun 11, 2023Abstract:We present a novel approach to mitigate bias in facial expression recognition (FER) models. Our method aims to reduce sensitive attribute information such as gender, age, or race, in the embeddings produced by FER models. We employ a kernel mean shrinkage estimator to estimate the kernel mean of the distributions of the embeddings associated with different sensitive attribute groups, such as young and old, in the Hilbert space. Using this estimation, we calculate the maximum mean discrepancy (MMD) distance between the distributions and incorporate it in the classifier loss along with an adversarial loss, which is then minimized through the learning process to improve the distribution alignment. Our method makes sensitive attributes less recognizable for the model, which in turn promotes fairness. Additionally, for the first time, we analyze the notion of attractiveness as an important sensitive attribute in FER models and demonstrate that FER models can indeed exhibit biases towards more attractive faces. To prove the efficacy of our model in reducing bias regarding different sensitive attributes (including the newly proposed attractiveness attribute), we perform several experiments on two widely used datasets, CelebA and RAF-DB. The results in terms of both accuracy and fairness measures outperform the state-of-the-art in most cases, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed method.
FaceTopoNet: Facial Expression Recognition using Face Topology Learning
Sep 13, 2022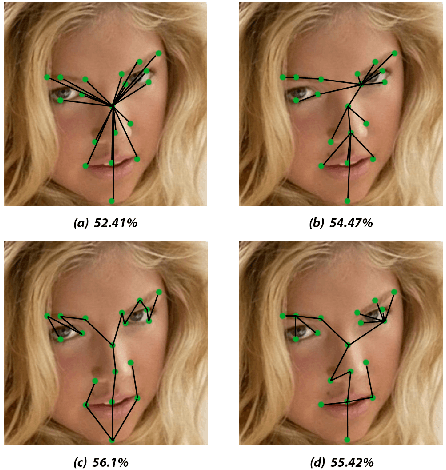
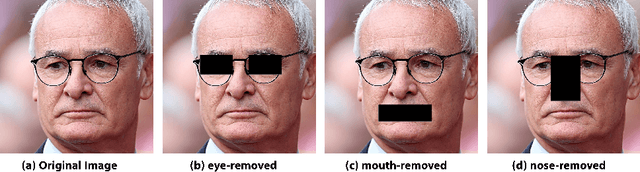
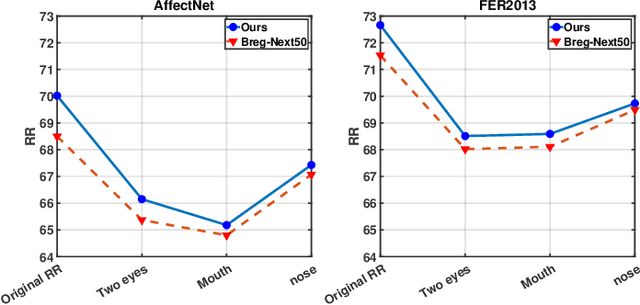
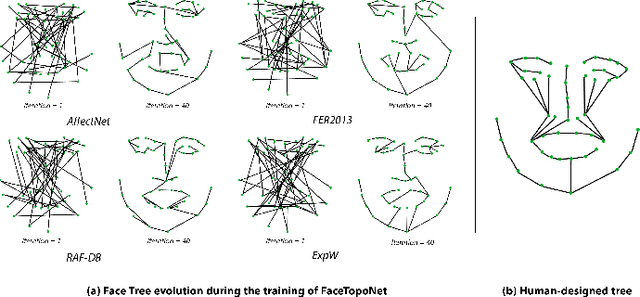
Abstract:Prior work has shown that the order in which different components of the face are learned using a sequential learner can play an important role in the performance of facial expression recognition systems. We propose FaceTopoNet, an end-to-end deep model for facial expression recognition, which is capable of learning an effective tree topology of the face. Our model then traverses the learned tree to generate a sequence, which is then used to form an embedding to feed a sequential learner. The devised model adopts one stream for learning structure and one stream for learning texture. The structure stream focuses on the positions of the facial landmarks, while the main focus of the texture stream is on the patches around the landmarks to learn textural information. We then fuse the outputs of the two streams by utilizing an effective attention-based fusion strategy. We perform extensive experiments on four large-scale in-the-wild facial expression datasets - namely AffectNet, FER2013, ExpW, and RAF-DB - and one lab-controlled dataset (CK+) to evaluate our approach. FaceTopoNet achieves state-of-the-art performance on three of the five datasets and obtains competitive results on the other two datasets. We also perform rigorous ablation and sensitivity experiments to evaluate the impact of different components and parameters in our model. Lastly, we perform robustness experiments and demonstrate that FaceTopoNet is more robust against occlusions in comparison to other leading methods in the area.
Face Trees for Expression Recognition
Dec 05, 2021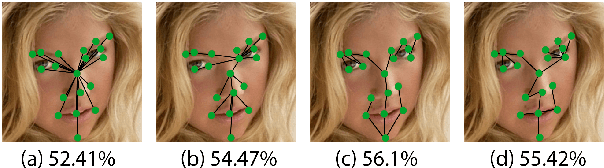
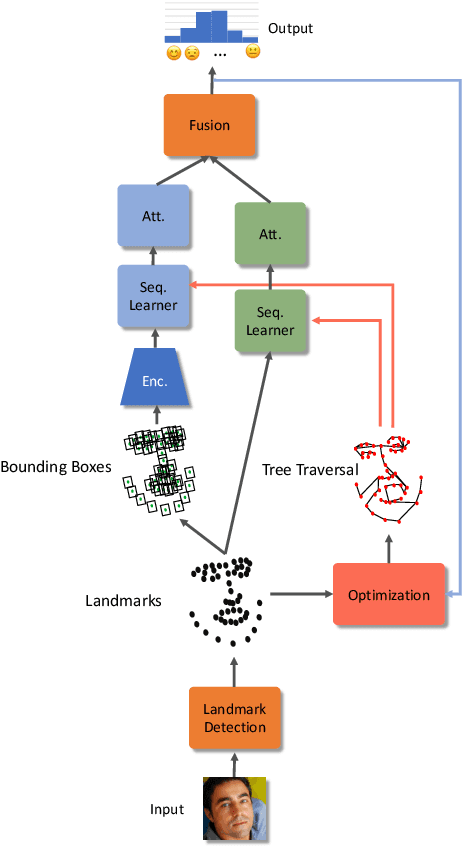
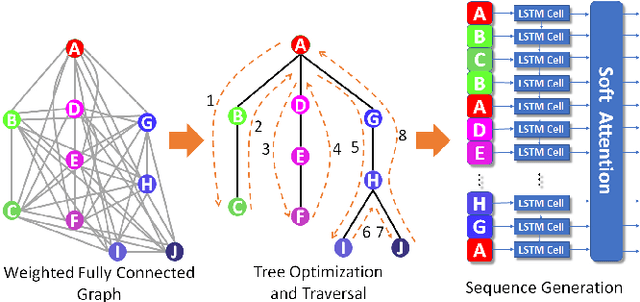
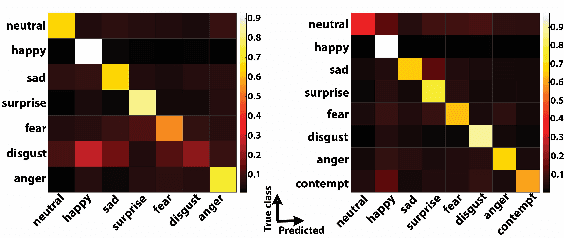
Abstract:We propose an end-to-end architecture for facial expression recognition. Our model learns an optimal tree topology for facial landmarks, whose traversal generates a sequence from which we obtain an embedding to feed a sequential learner. The proposed architecture incorporates two main streams, one focusing on landmark positions to learn the structure of the face, while the other focuses on patches around the landmarks to learn texture information. Each stream is followed by an attention mechanism and the outputs are fed to a two-stream fusion component to perform the final classification. We conduct extensive experiments on two large-scale publicly available facial expression datasets, AffectNet and FER2013, to evaluate the efficacy of our approach. Our method outperforms other solutions in the area and sets new state-of-the-art expression recognition rates on these datasets.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge