Mohd Zeeshan Ansari
Language Identification of Hindi-English tweets using code-mixed BERT
Jul 02, 2021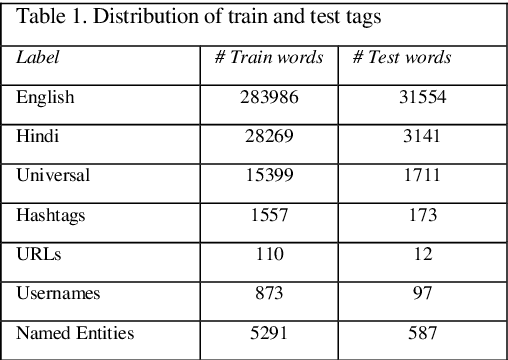
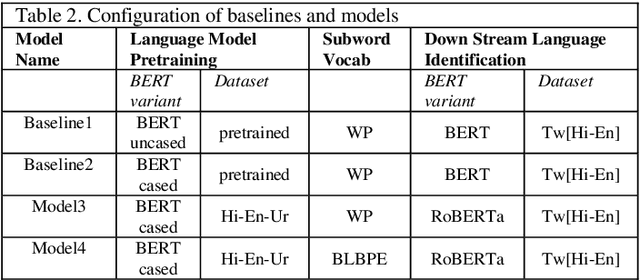
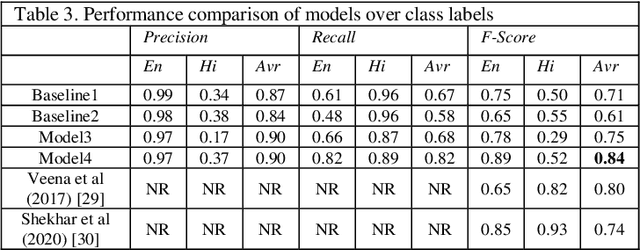
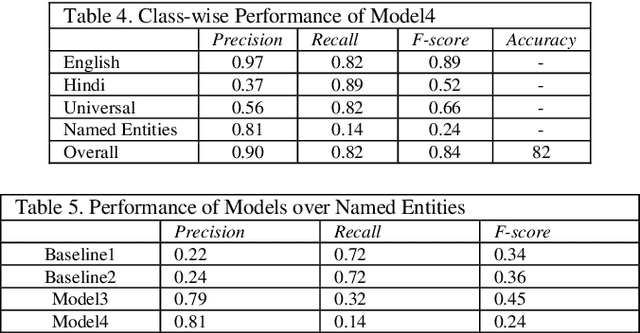
Abstract:Language identification of social media text has been an interesting problem of study in recent years. Social media messages are predominantly in code mixed in non-English speaking states. Prior knowledge by pre-training contextual embeddings have shown state of the art results for a range of downstream tasks. Recently, models such as BERT have shown that using a large amount of unlabeled data, the pretrained language models are even more beneficial for learning common language representations. Extensive experiments exploiting transfer learning and fine-tuning BERT models to identify language on Twitter are presented in this paper. The work utilizes a data collection of Hindi-English-Urdu codemixed text for language pre-training and Hindi-English codemixed for subsequent word-level language classification. The results show that the representations pre-trained over codemixed data produce better results by their monolingual counterpart.
Language Lexicons for Hindi-English Multilingual Text Processing
Jun 29, 2021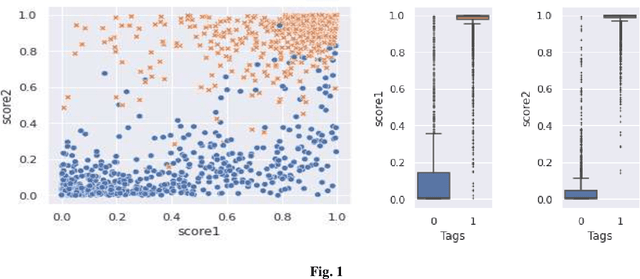
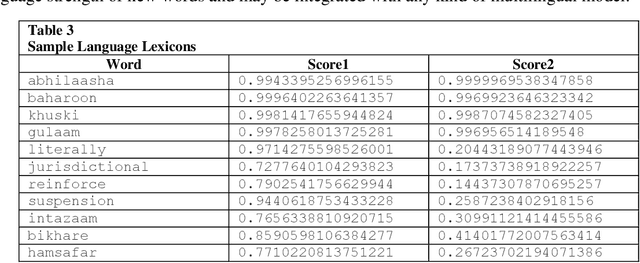
Abstract:Language Identification in textual documents is the process of automatically detecting the language contained in a document based on its content. The present Language Identification techniques presume that a document contains text in one of the fixed set of languages, however, this presumption is incorrect when dealing with multilingual document which includes content in more than one possible language. Due to the unavailability of large standard corpora for Hindi-English mixed lingual language processing tasks we propose the language lexicons, a novel kind of lexical database that supports several multilingual language processing tasks. These lexicons are built by learning classifiers over transliterated Hindi and English vocabulary. The designed lexicons possess richer quantitative characteristic than its primary source of collection which is revealed using the visualization techniques.
Inferring Political Preferences from Twitter
Jul 21, 2020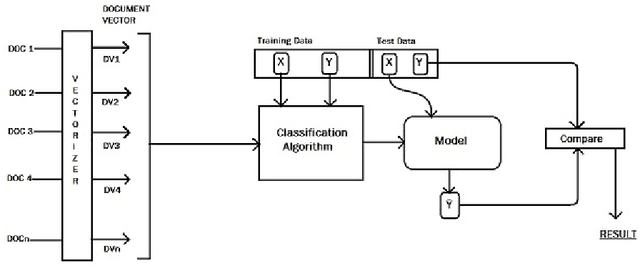
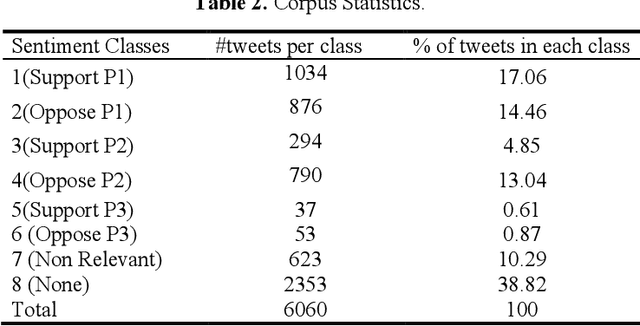
Abstract:Sentiment analysis is the task of automatic analysis of opinions and emotions of users towards an entity or some aspect of that entity. Political Sentiment Analysis of social media helps the political strategists to scrutinize the performance of a party or candidate and improvise their weaknesses far before the actual elections. During the time of elections, the social networks get flooded with blogs, chats, debates and discussions about the prospects of political parties and politicians. The amount of data generated is much large to study, analyze and draw inferences using the latest techniques. Twitter is one of the most popular social media platforms enables us to perform domain-specific data preparation. In this work, we chose to identify the inclination of political opinions present in Tweets by modelling it as a text classification problem using classical machine learning. The tweets related to the Delhi Elections in 2020 are extracted and employed for the task. Among the several algorithms, we observe that Support Vector Machines portrays the best performance.
Feature Selection on Noisy Twitter Short Text Messages for Language Identification
Jul 11, 2020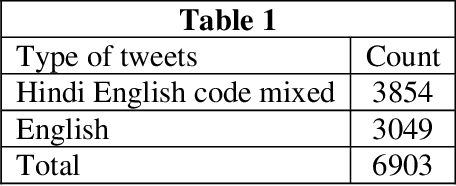
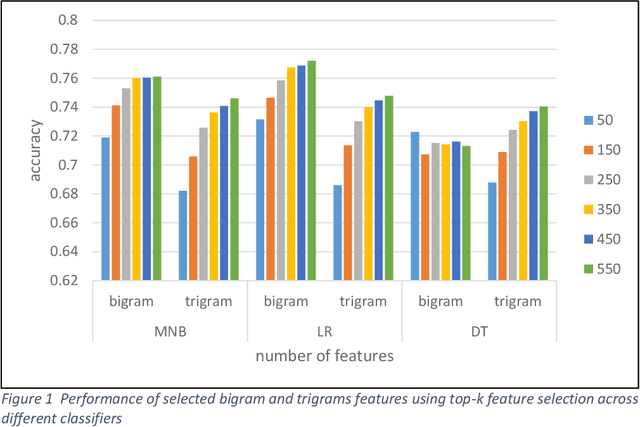
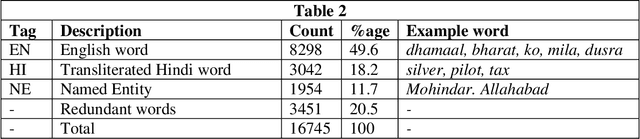
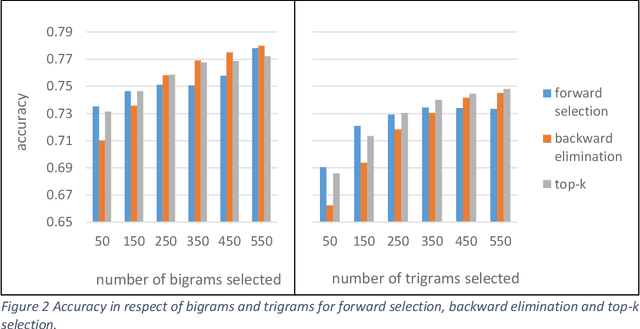
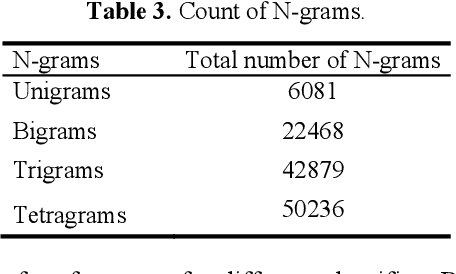
Abstract:The task of written language identification involves typically the detection of the languages present in a sample of text. Moreover, a sequence of text may not belong to a single inherent language but also may be mixture of text written in multiple languages. This kind of text is generated in large volumes from social media platforms due to its flexible and user friendly environment. Such text contains very large number of features which are essential for development of statistical, probabilistic as well as other kinds of language models. The large number of features have rich as well as irrelevant and redundant features which have diverse effect over the performance of the learning model. Therefore, feature selection methods are significant in choosing feature that are most relevant for an efficient model. In this article, we basically consider the Hindi-English language identification task as Hindi and English are often two most widely spoken languages of India. We apply different feature selection algorithms across various learning algorithms in order to analyze the effect of the algorithm as well as the number of features on the performance of the task. The methodology focuses on the word level language identification using a novel dataset of 6903 tweets extracted from Twitter. Various n-gram profiles are examined with different feature selection algorithms over many classifiers. Finally, an exhaustive comparative analysis is put forward with respect to the overall experiments conducted for the task.
Context based Analysis of Lexical Semantics for Hindi Language
Jan 23, 2019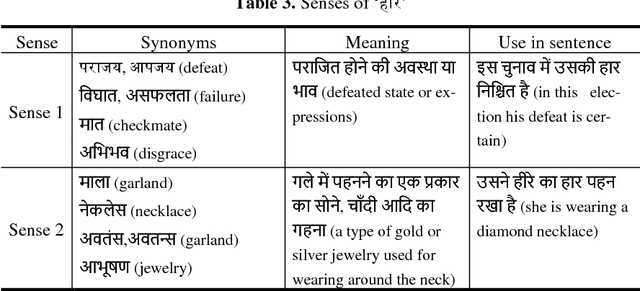
Abstract:A word having multiple senses in a text introduces the lexical semantic task to find out which particular sense is appropriate for the given context. One such task is Word sense disambiguation which refers to the identification of the most appropriate meaning of the polysemous word in a given context using computational algorithms. The language processing research in Hindi, the official language of India, and other Indian languages is restricted by unavailability of the standard corpus. For Hindi word sense disambiguation also, the large corpus is not available. In this work, we prepared the text containing new senses of certain words leading to the enrichment of the sense-tagged Hindi corpus of sixty polysemous words. Furthermore, we analyzed two novel lexical associations for Hindi word sense disambiguation based on the contextual features of the polysemous word. The evaluation of these methods is carried out over learning algorithms and favorable results are achieved.
Cross Script Hindi English NER Corpus from Wikipedia
Oct 08, 2018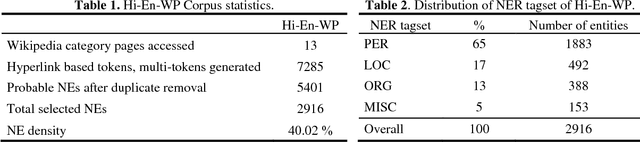
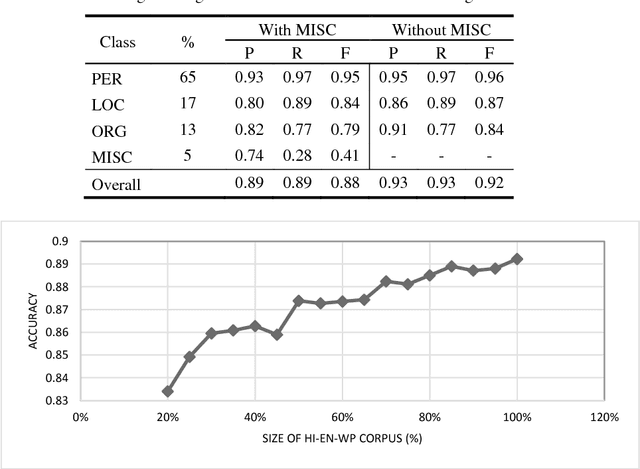
Abstract:The text generated on social media platforms is essentially a mixed lingual text. The mixing of language in any form produces considerable amount of difficulty in language processing systems. Moreover, the advancements in language processing research depends upon the availability of standard corpora. The development of mixed lingual Indian Named Entity Recognition (NER) systems are facing obstacles due to unavailability of the standard evaluation corpora. Such corpora may be of mixed lingual nature in which text is written using multiple languages predominantly using a single script only. The motivation of our work is to emphasize the automatic generation such kind of corpora in order to encourage mixed lingual Indian NER. The paper presents the preparation of a Cross Script Hindi-English Corpora from Wikipedia category pages. The corpora is successfully annotated using standard CoNLL-2003 categories of PER, LOC, ORG, and MISC. Its evaluation is carried out on a variety of machine learning algorithms and favorable results are achieved.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge