M M Sufyan Beg
Language Identification of Hindi-English tweets using code-mixed BERT
Jul 02, 2021
Abstract:Language identification of social media text has been an interesting problem of study in recent years. Social media messages are predominantly in code mixed in non-English speaking states. Prior knowledge by pre-training contextual embeddings have shown state of the art results for a range of downstream tasks. Recently, models such as BERT have shown that using a large amount of unlabeled data, the pretrained language models are even more beneficial for learning common language representations. Extensive experiments exploiting transfer learning and fine-tuning BERT models to identify language on Twitter are presented in this paper. The work utilizes a data collection of Hindi-English-Urdu codemixed text for language pre-training and Hindi-English codemixed for subsequent word-level language classification. The results show that the representations pre-trained over codemixed data produce better results by their monolingual counterpart.
A Simple and Efficient Probabilistic Language model for Code-Mixed Text
Jun 29, 2021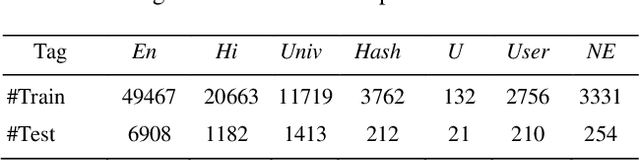
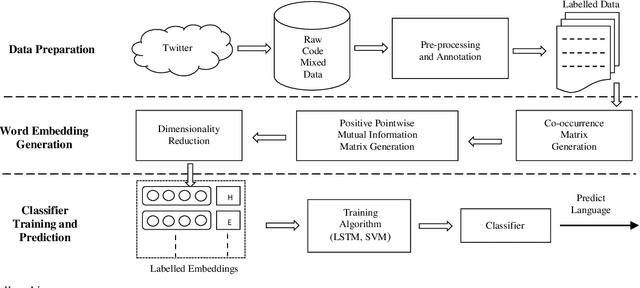
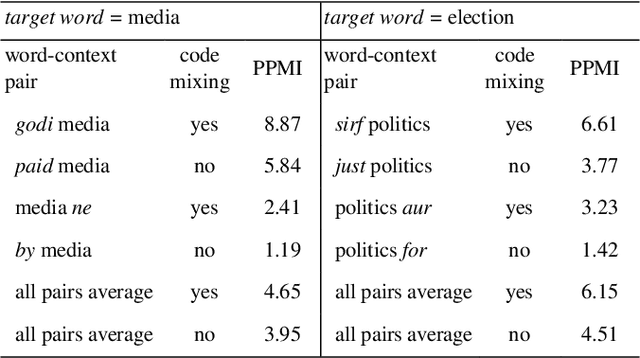
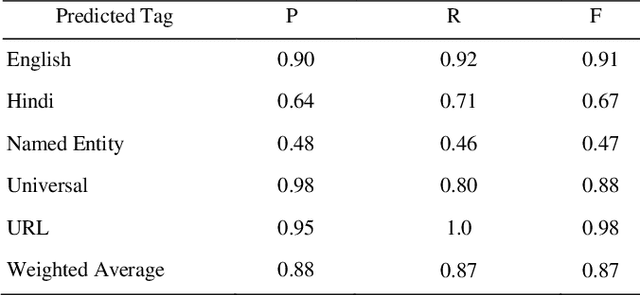
Abstract:The conventional natural language processing approaches are not accustomed to the social media text due to colloquial discourse and non-homogeneous characteristics. Significantly, the language identification in a multilingual document is ascertained to be a preceding subtask in several information extraction applications such as information retrieval, named entity recognition, relation extraction, etc. The problem is often more challenging in code-mixed documents wherein foreign languages words are drawn into base language while framing the text. The word embeddings are powerful language modeling tools for representation of text documents useful in obtaining similarity between words or documents. We present a simple probabilistic approach for building efficient word embedding for code-mixed text and exemplifying it over language identification of Hindi-English short test messages scrapped from Twitter. We examine its efficacy for the classification task using bidirectional LSTMs and SVMs and observe its improved scores over various existing code-mixed embeddings
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge