Minyoung Jwa
Performance Comparison of Design Optimization and Deep Learning-based Inverse Design
Aug 23, 2023Abstract:Surrogate model-based optimization has been increasingly used in the field of engineering design. It involves creating a surrogate model with objective functions or constraints based on the data obtained from simulations or real-world experiments, and then finding the optimal solution from the model using numerical optimization methods. Recent advancements in deep learning-based inverse design methods have made it possible to generate real-time optimal solutions for engineering design problems, eliminating the requirement for iterative optimization processes. Nevertheless, no comprehensive study has yet closely examined the specific advantages and disadvantages of this novel approach compared to the traditional design optimization method. The objective of this paper is to compare the performance of traditional design optimization methods with deep learning-based inverse design methods by employing benchmark problems across various scenarios. Based on the findings of this study, we provide guidelines that can be taken into account for the future utilization of deep learning-based inverse design. It is anticipated that these guidelines will enhance the practical applicability of this approach to real engineering design problems.
Deep Learning-Based Inverse Design for Engineering Systems: Multidisciplinary Design Optimization of Automotive Brakes
Feb 27, 2022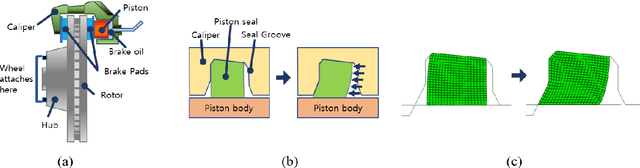
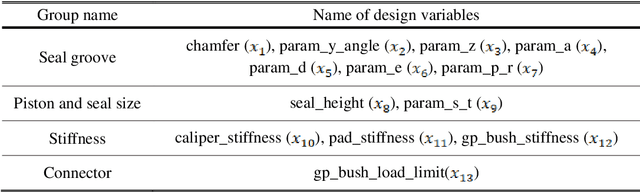
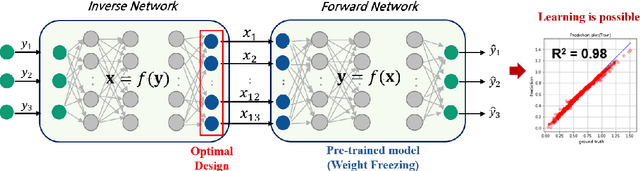

Abstract:The braking performance of the brake system is a target performance that must be considered for vehicle development. Apparent piston travel (APT) and drag torque are the most representative factors for evaluating braking performance. In particular, as the two performance factors have a conflicting relationship with each other, a multidisciplinary design optimization (MDO) approach is required for brake design. However, the computational cost of MDO increases as the number of disciplines increases. Recent studies on inverse design that use deep learning (DL) have established the possibility of instantly generating an optimal design that can satisfy the target performance without implementing an iterative optimization process. This study proposes a DL-based multidisciplinary inverse design (MID) that simultaneously satisfies multiple targets, such as the APT and drag torque of the brake system. Results show that the proposed inverse design can find the optimal design more efficiently compared with the conventional optimization methods, such as backpropagation and sequential quadratic programming. The MID achieved a similar performance to the single-disciplinary inverse design in terms of accuracy and computational cost. A novel design was derived on the basis of results, and the same performance was satisfied as that of the existing design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge